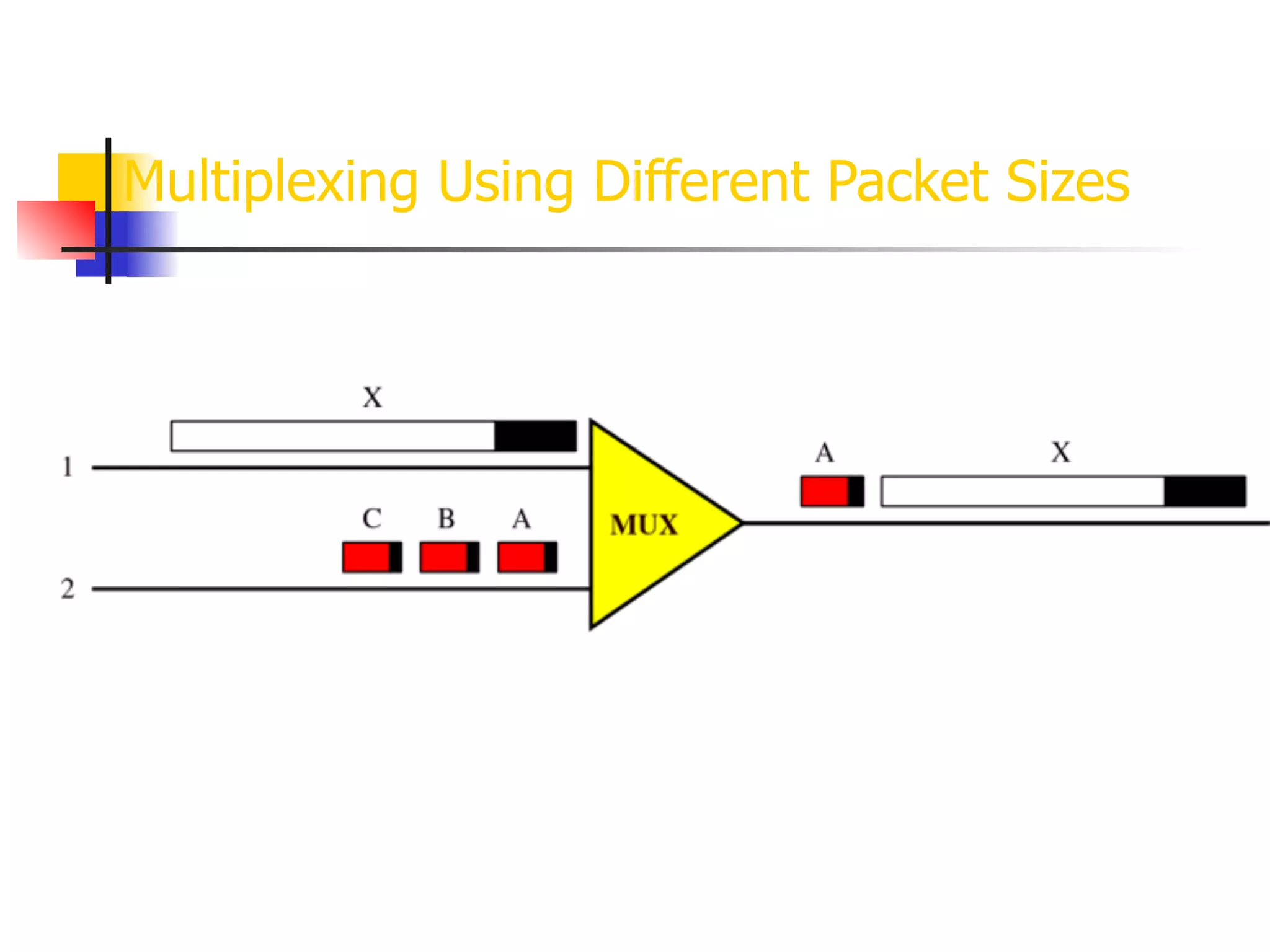
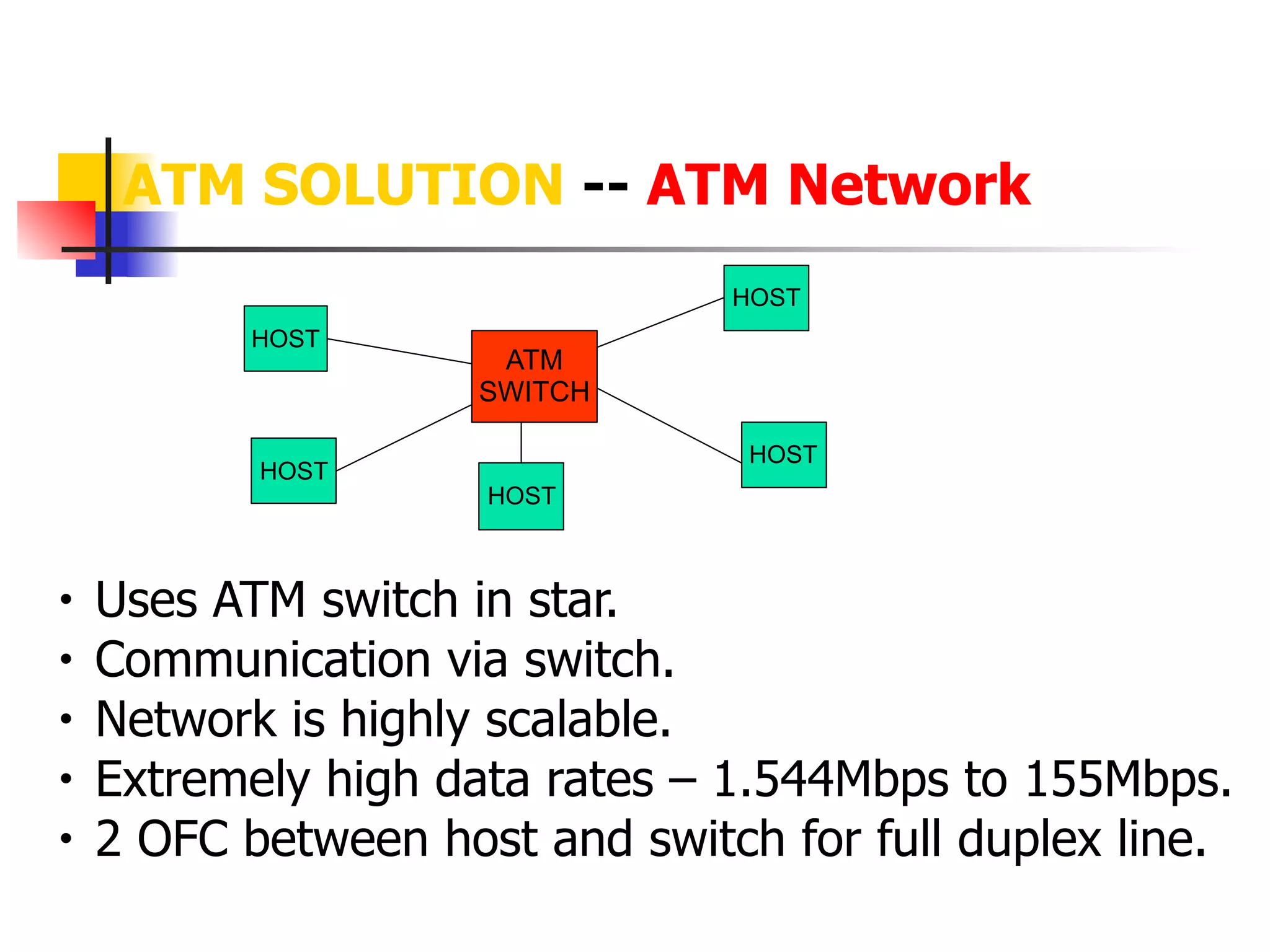
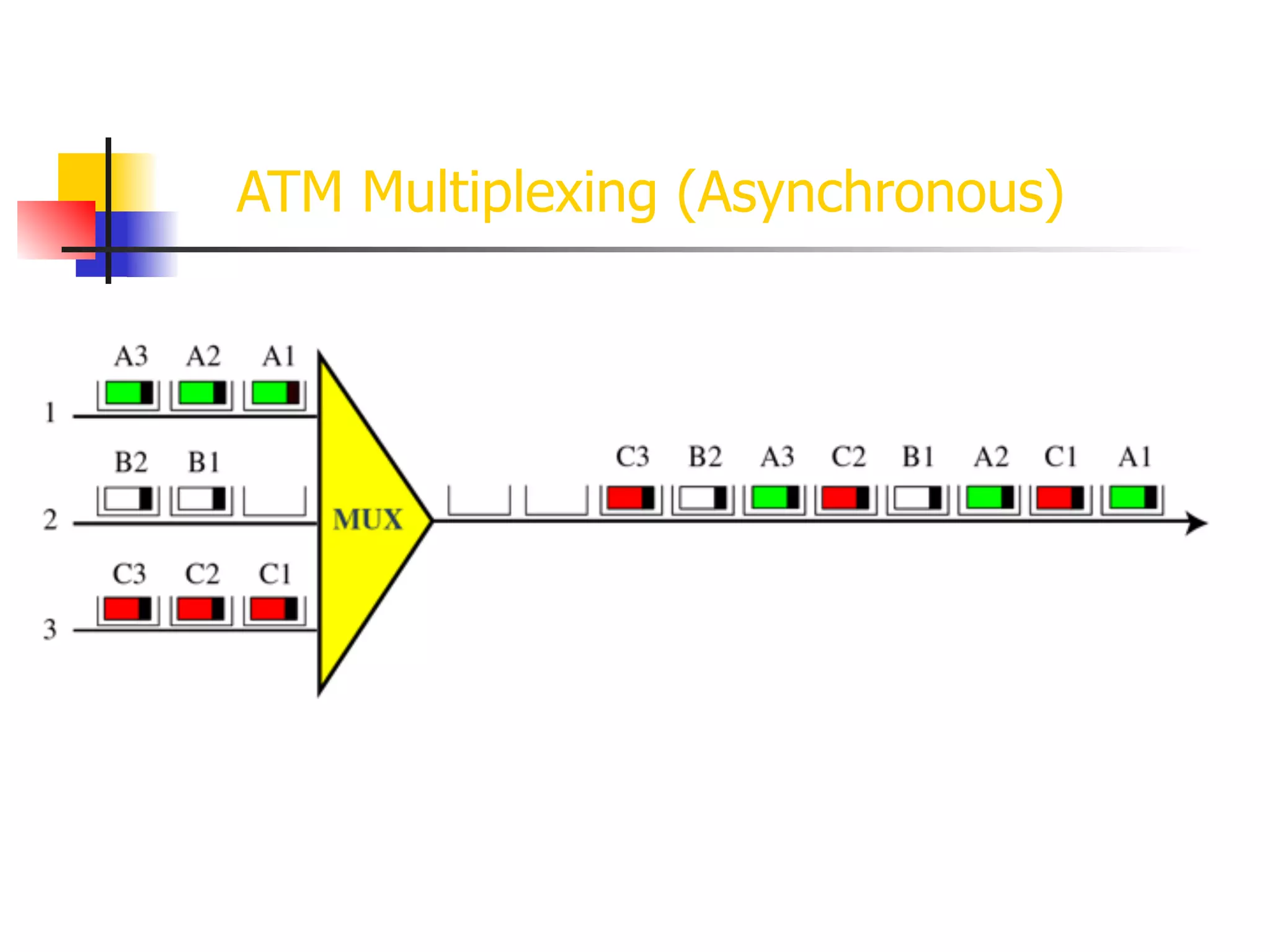
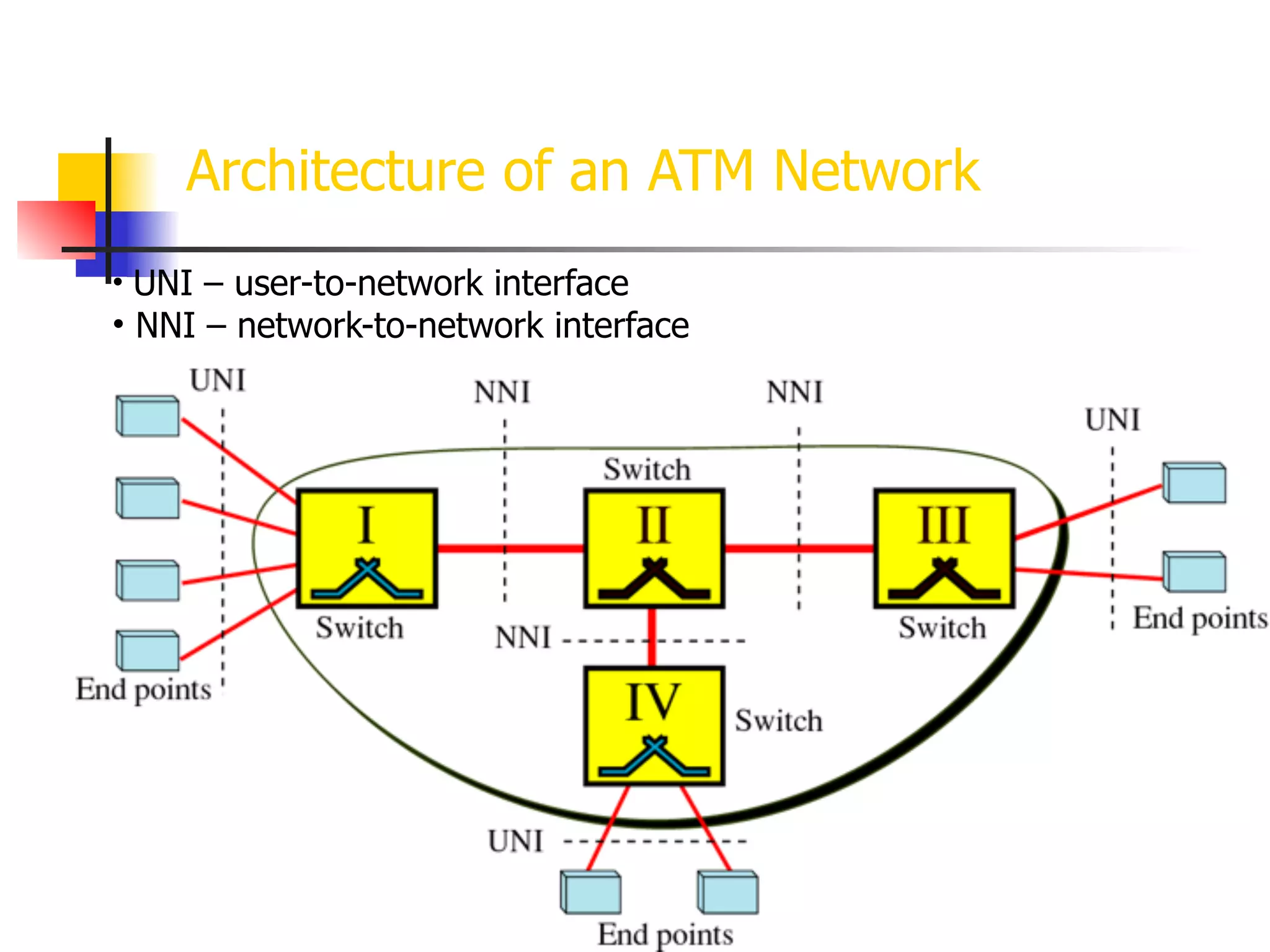
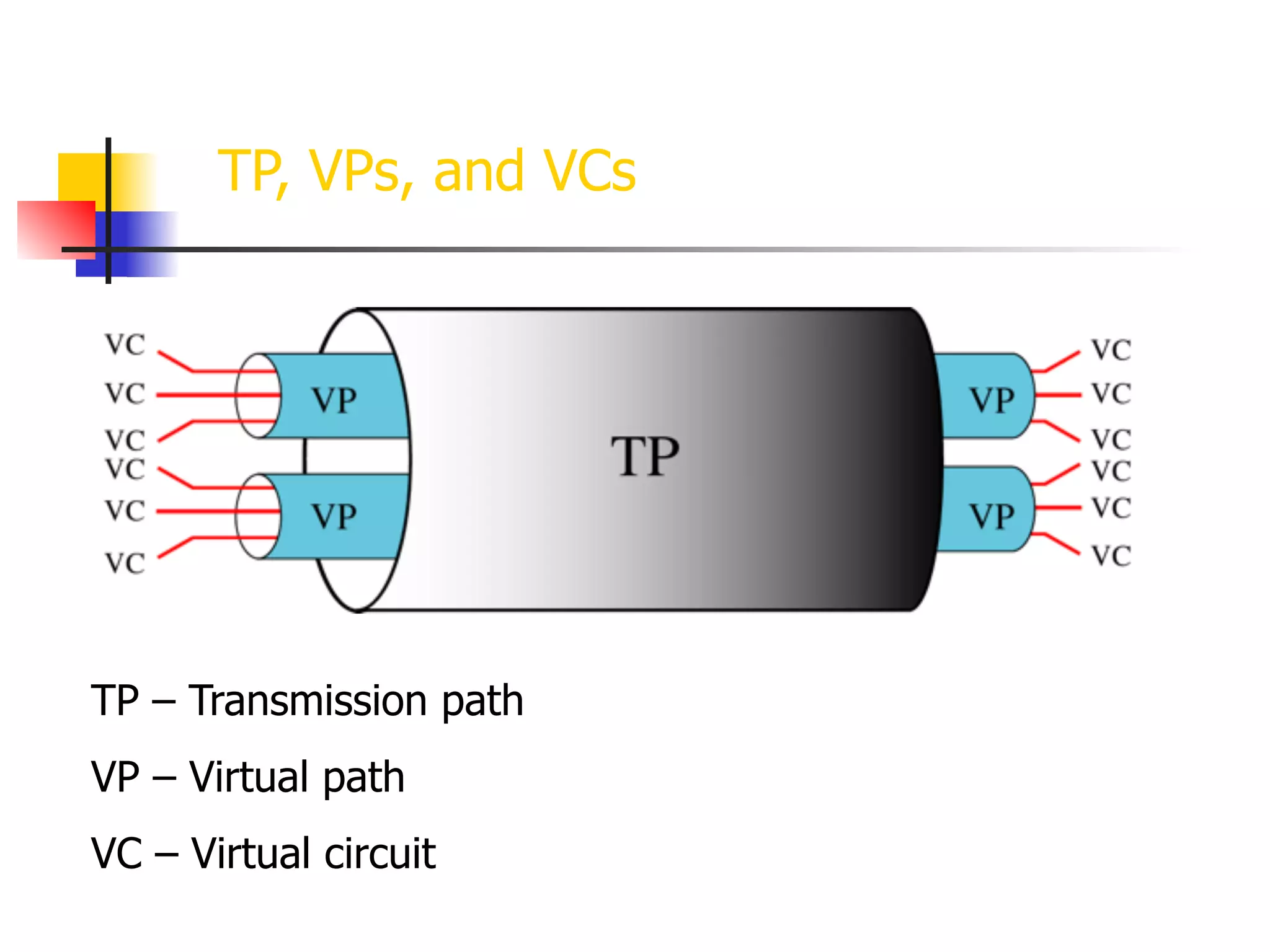
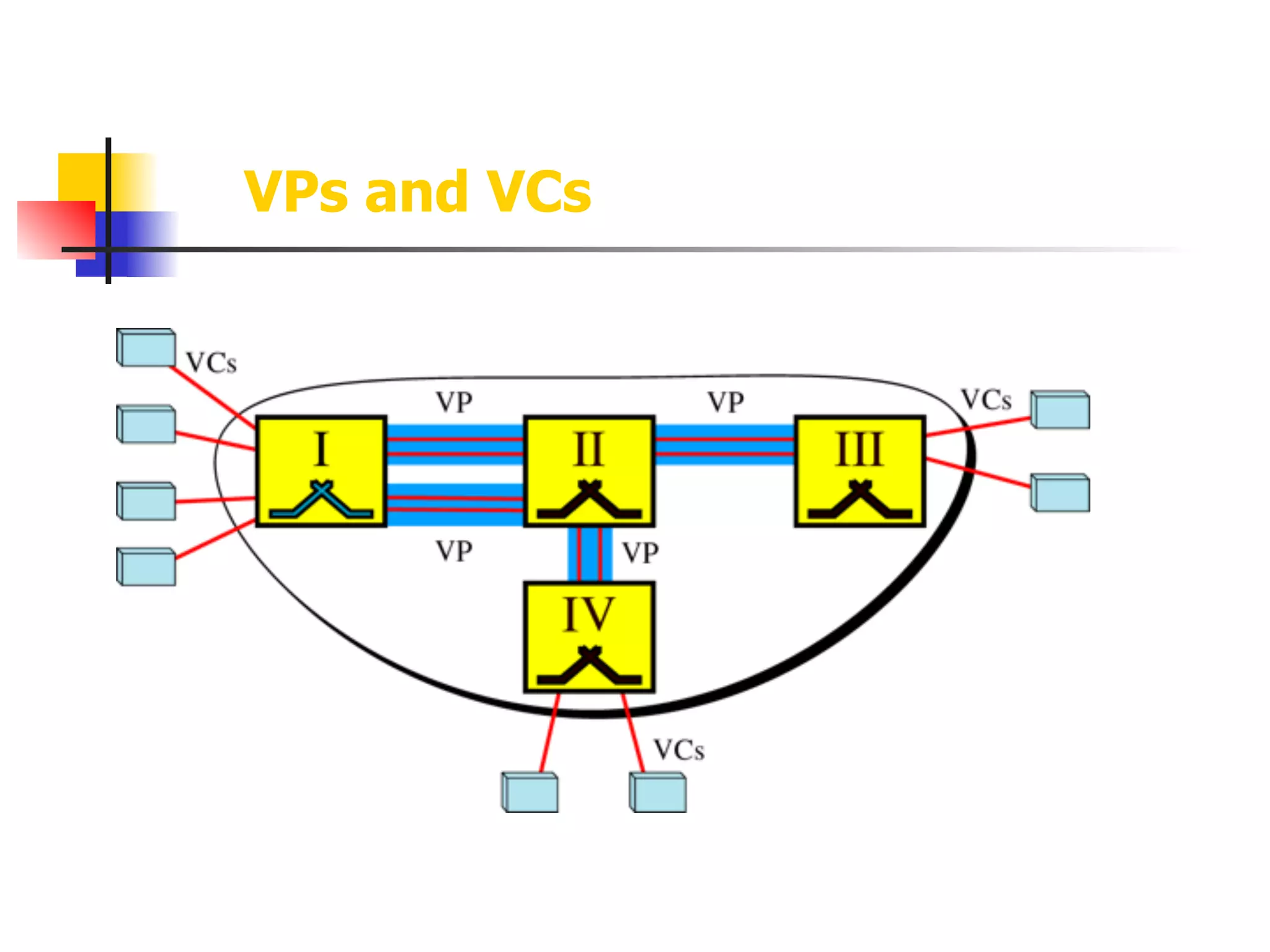
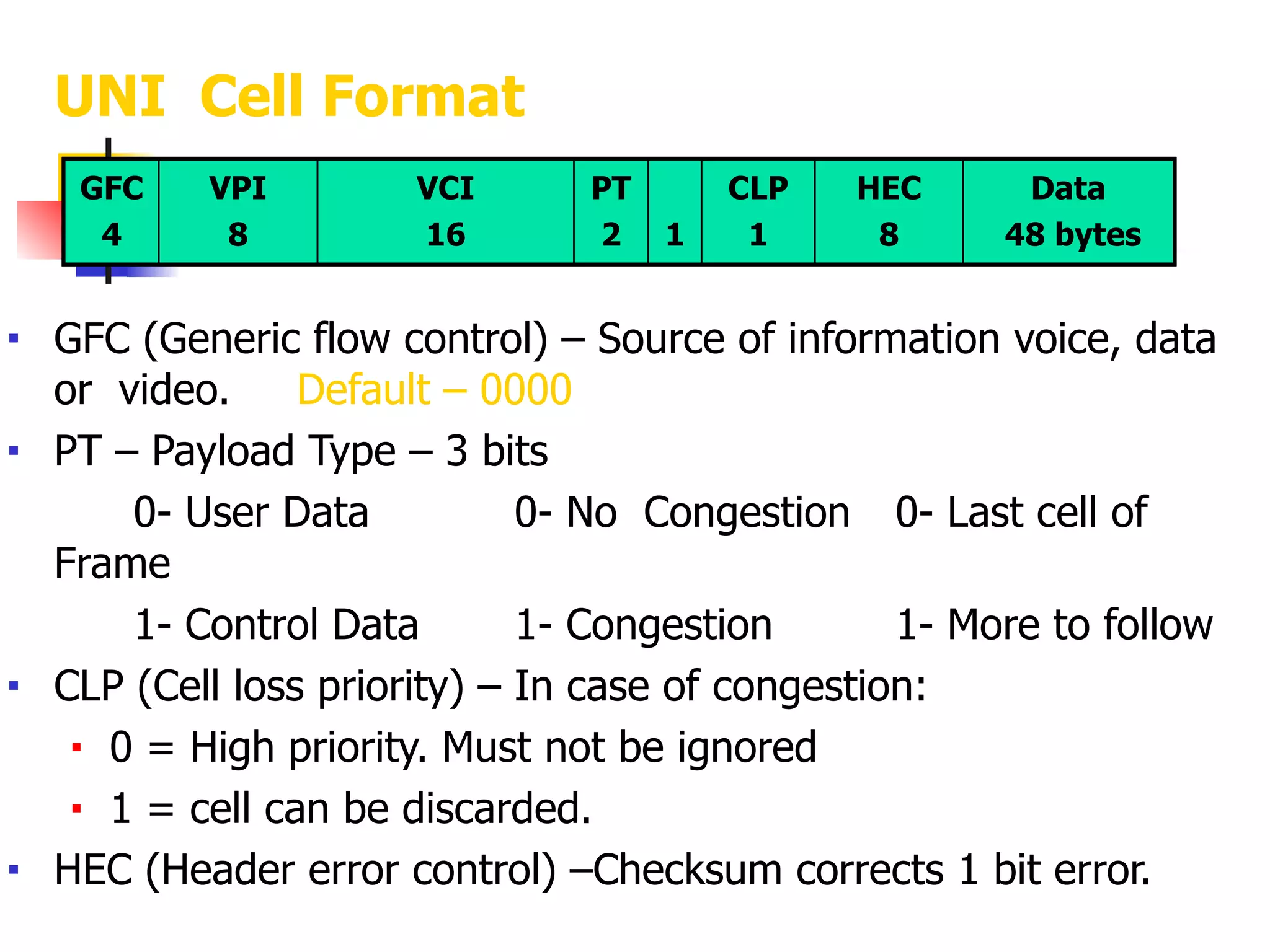
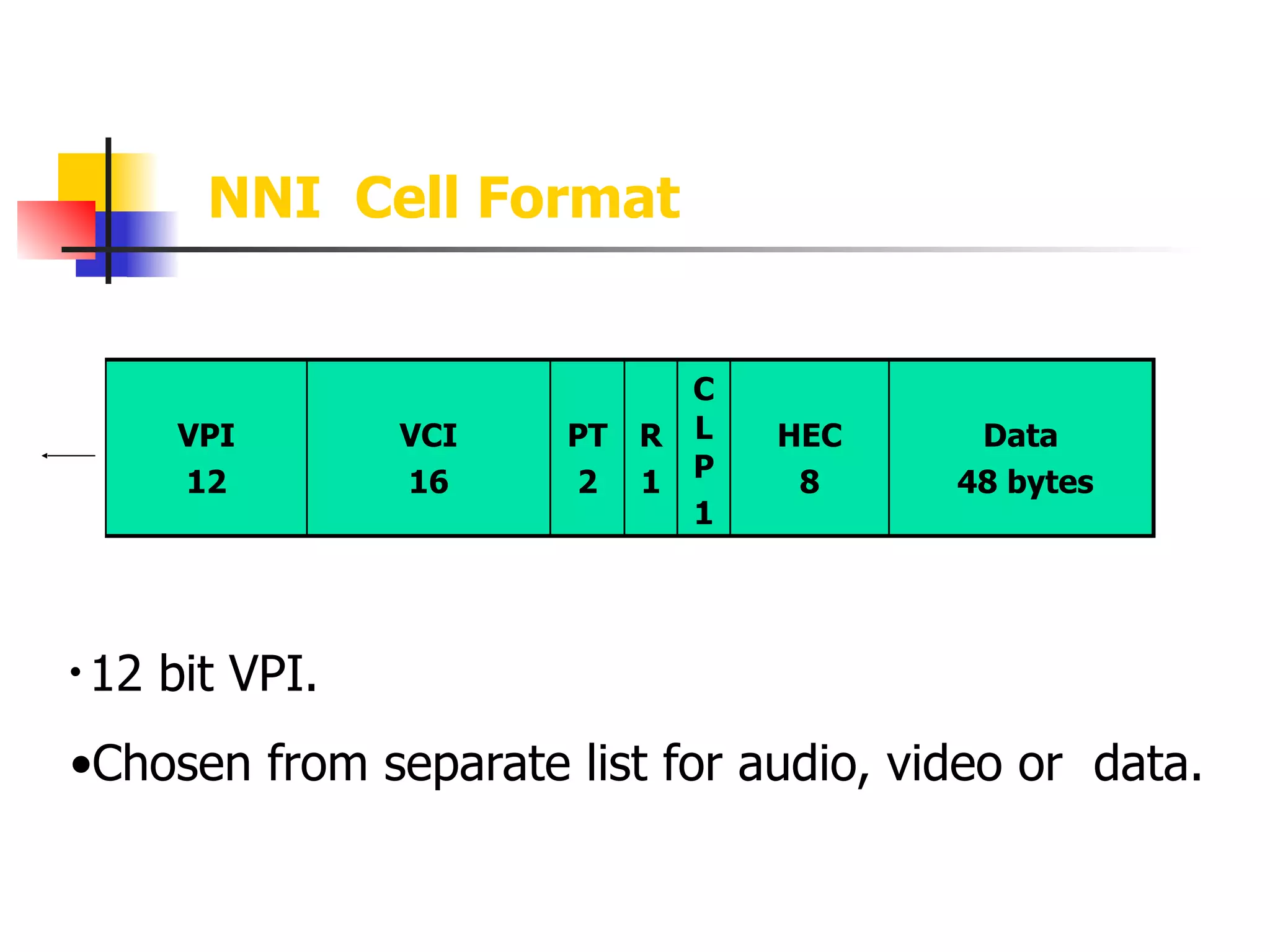
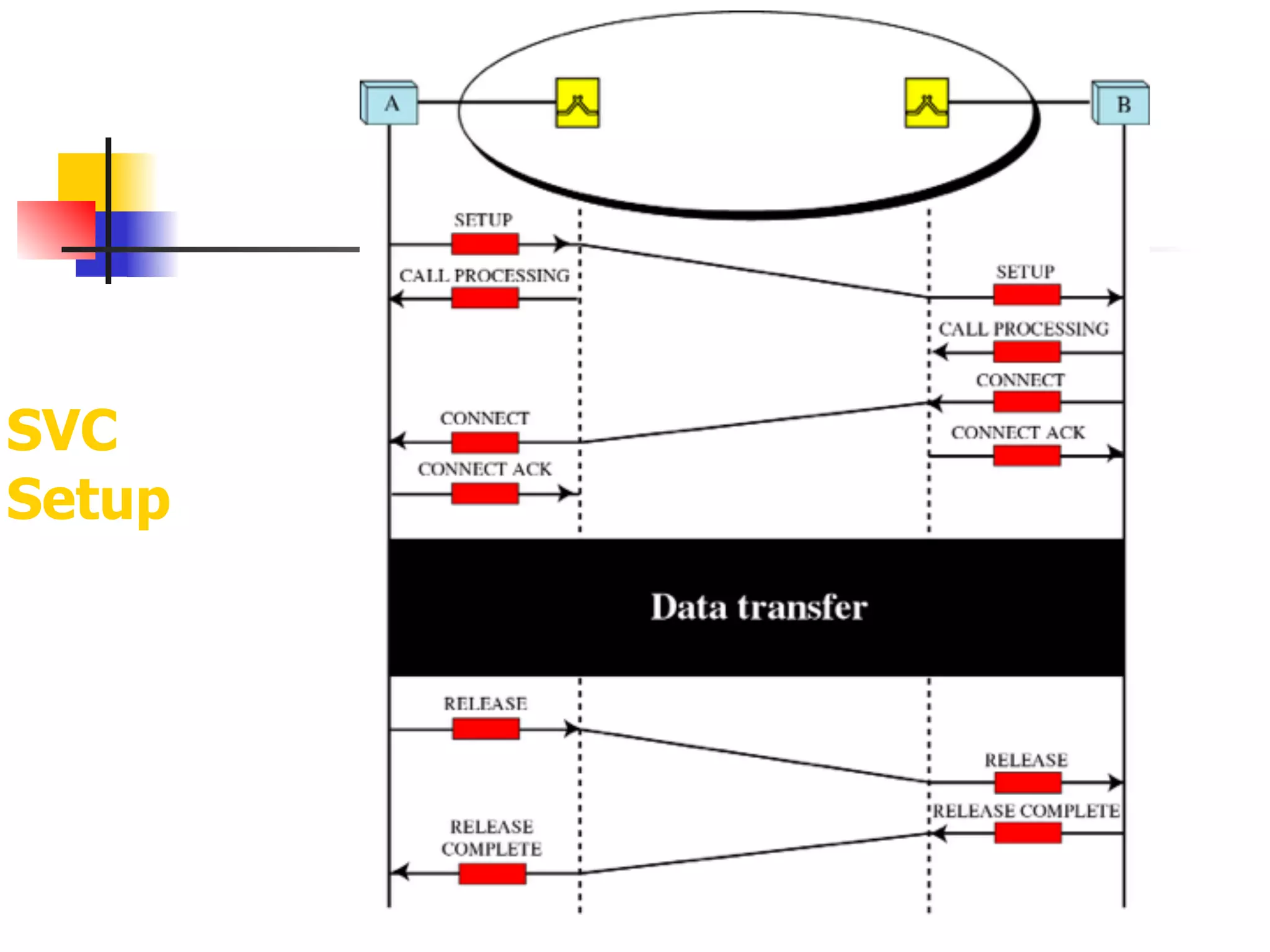
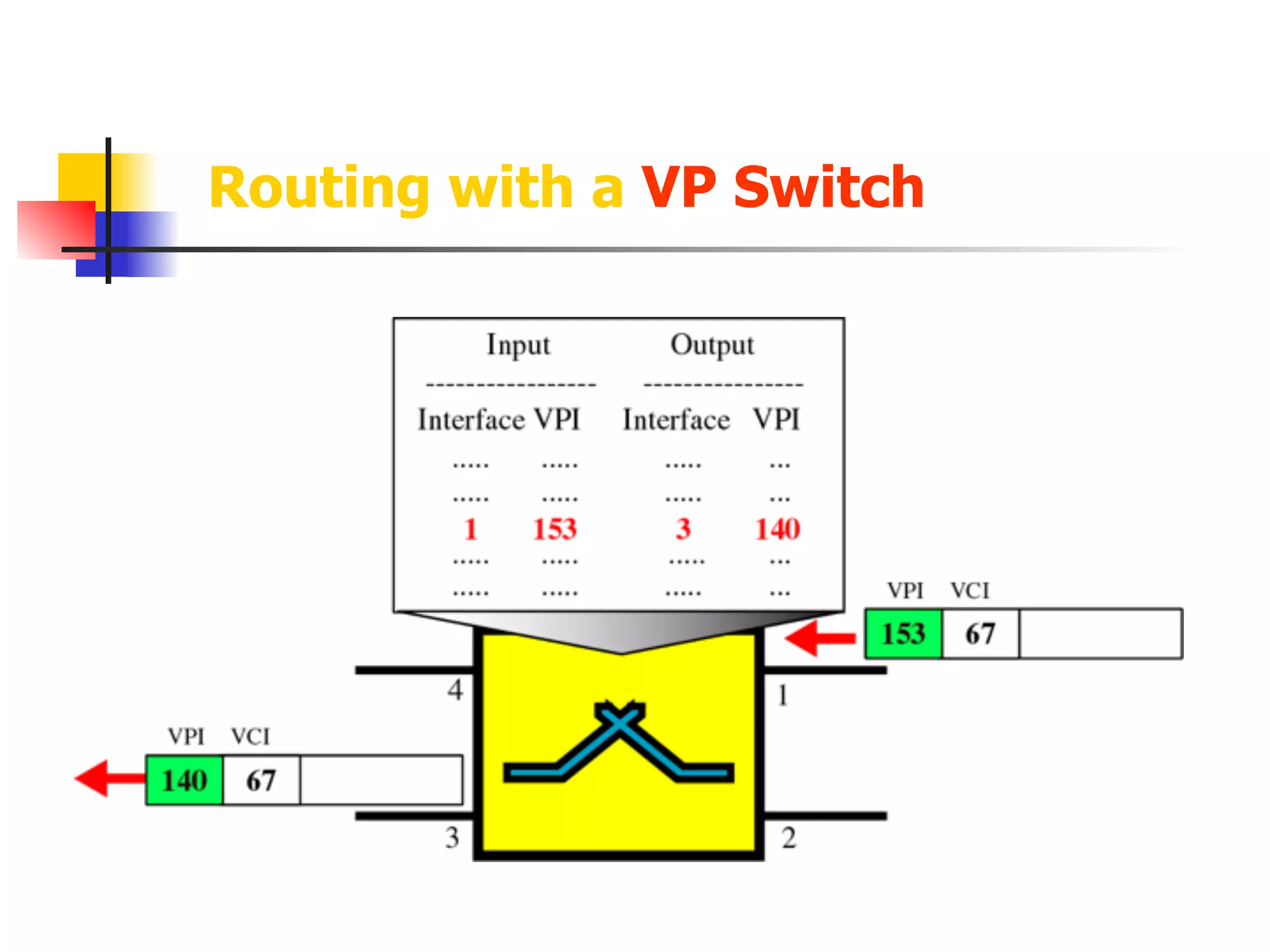
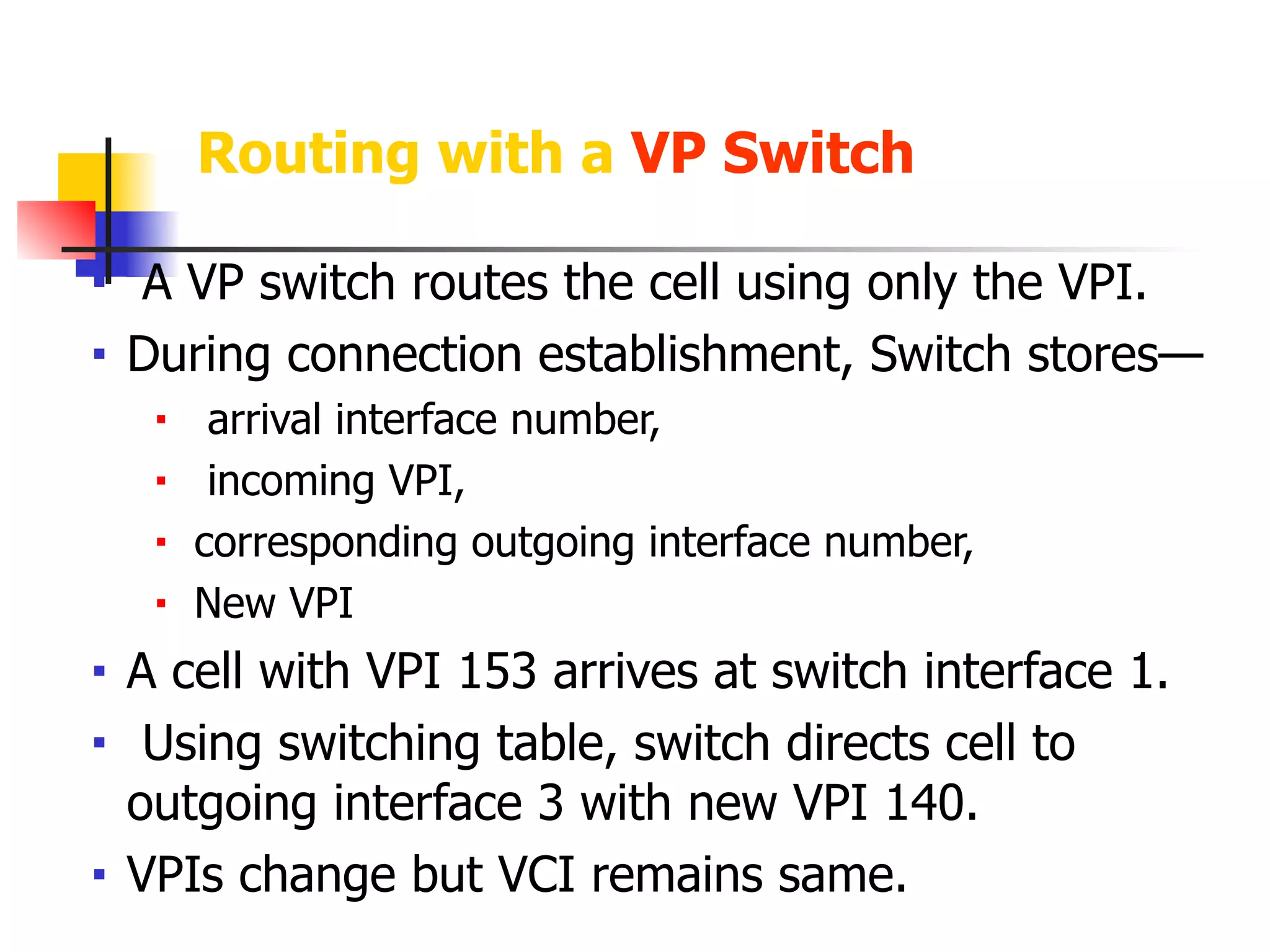
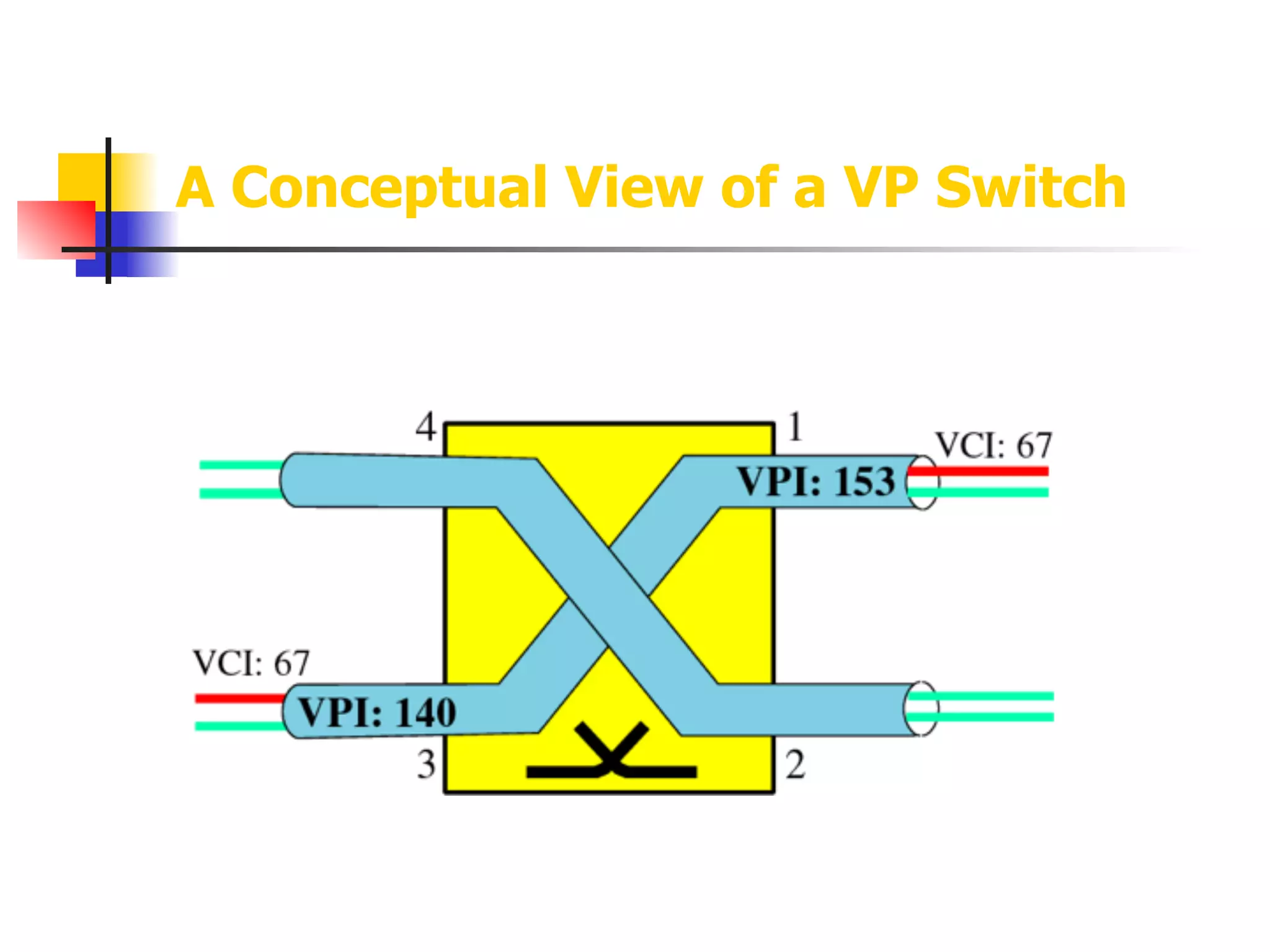
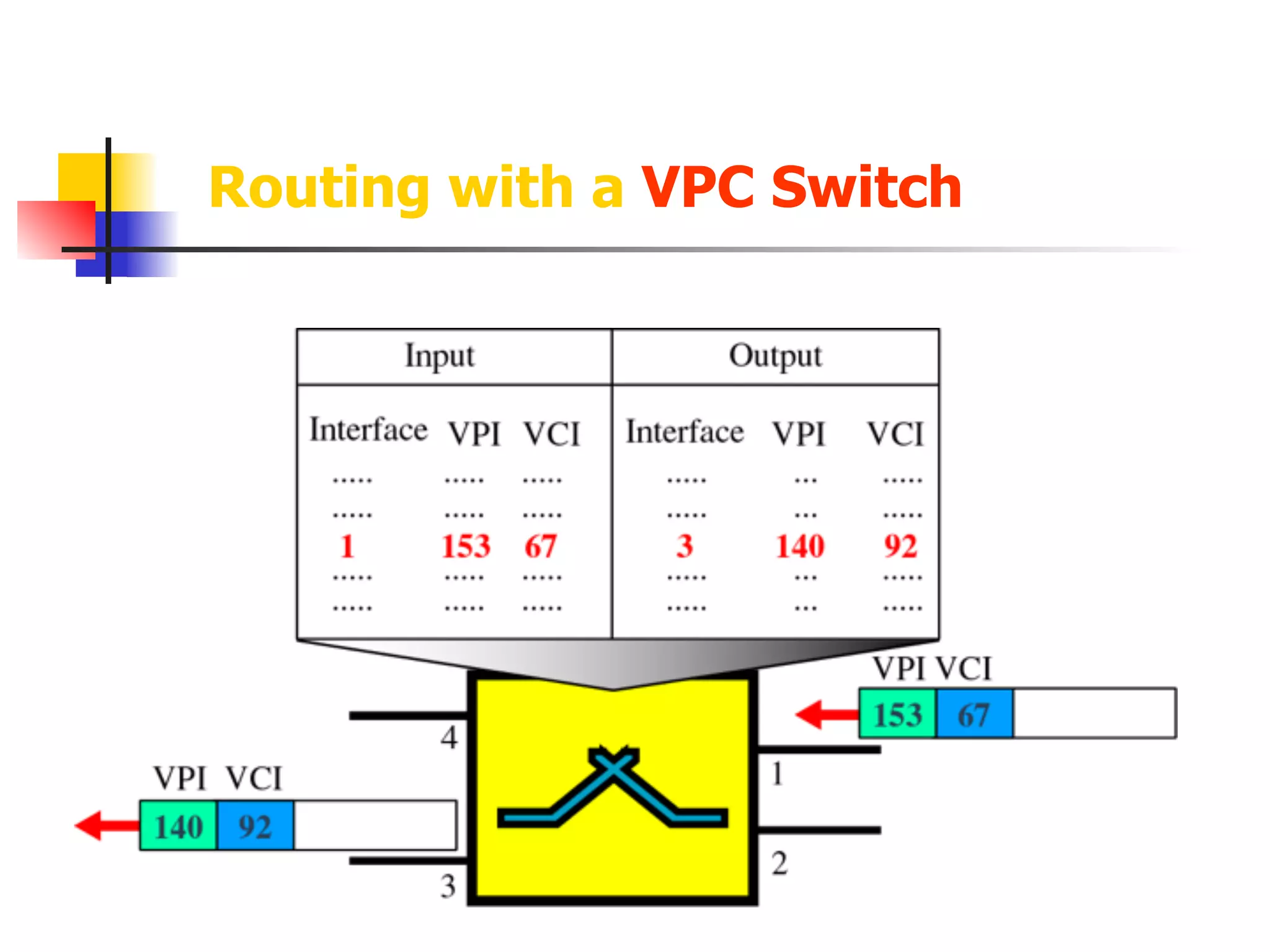
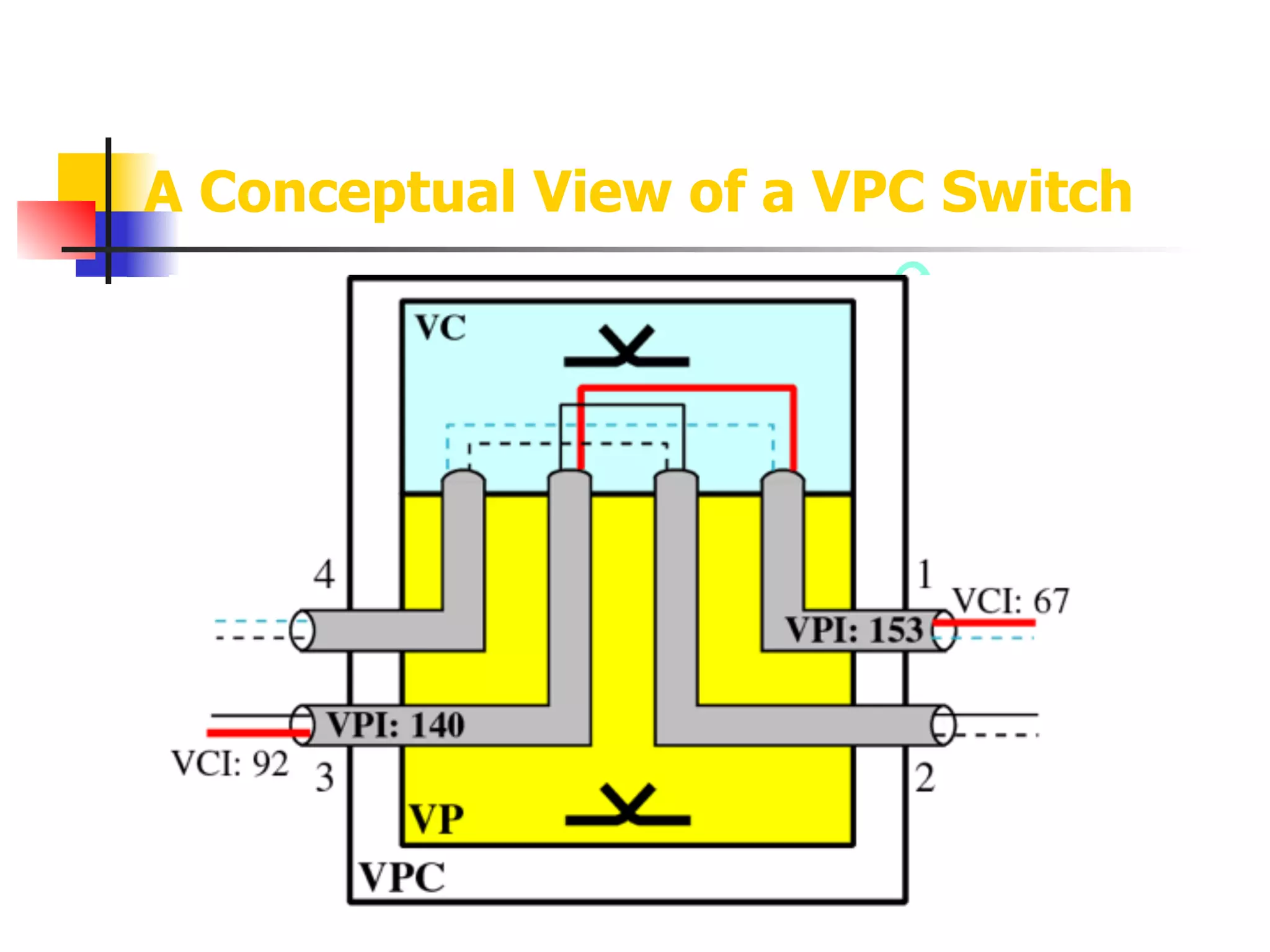
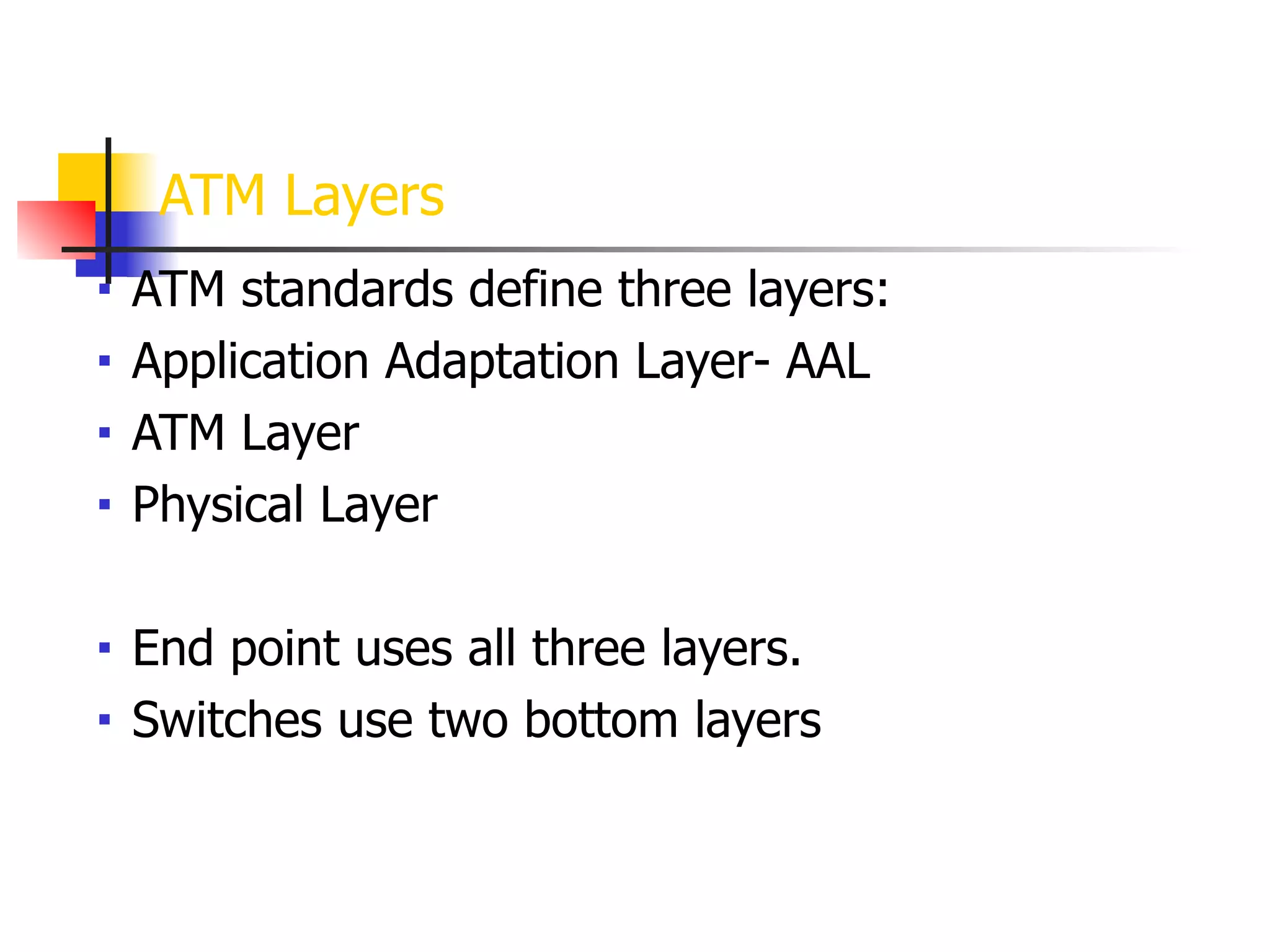
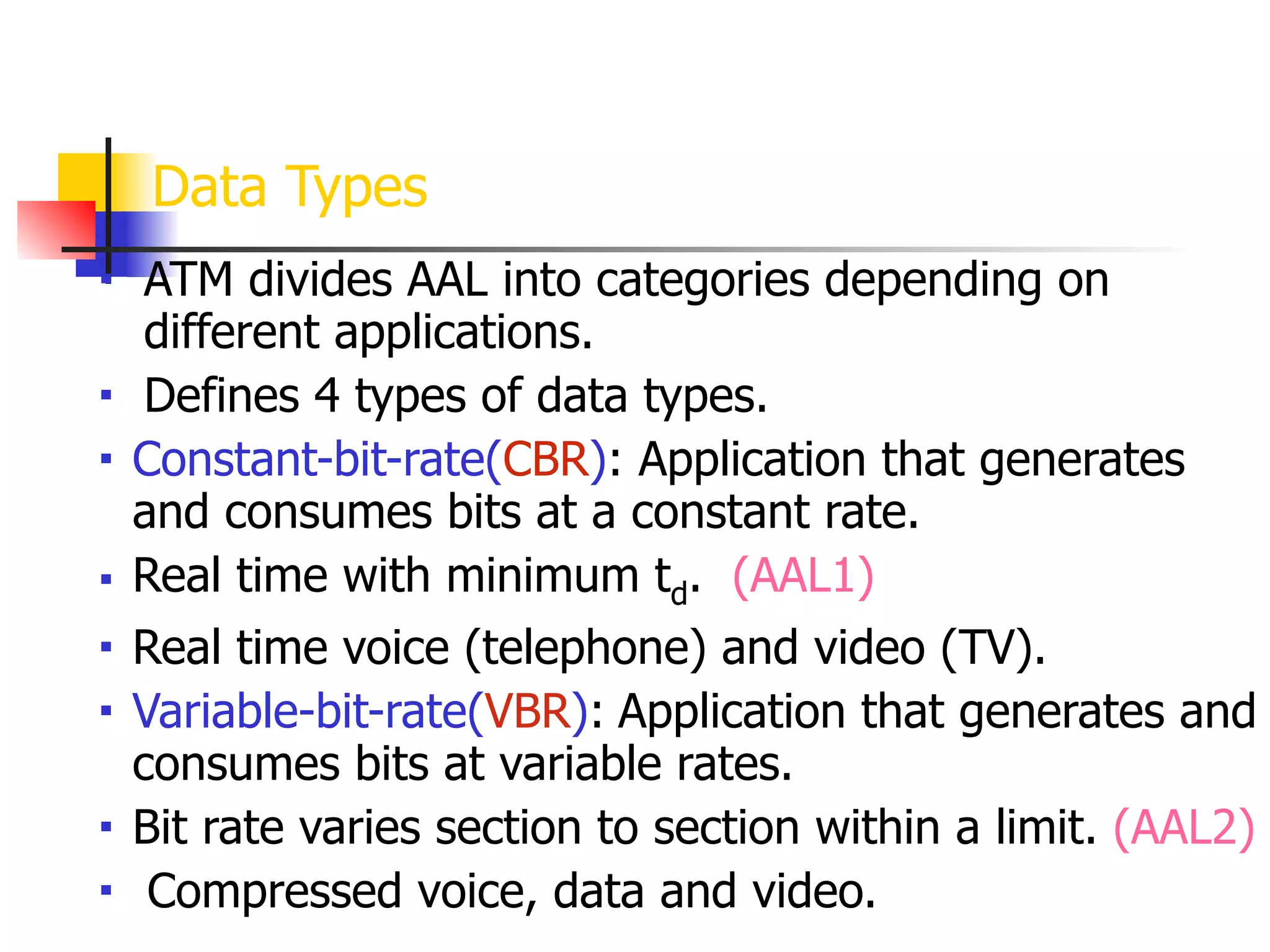
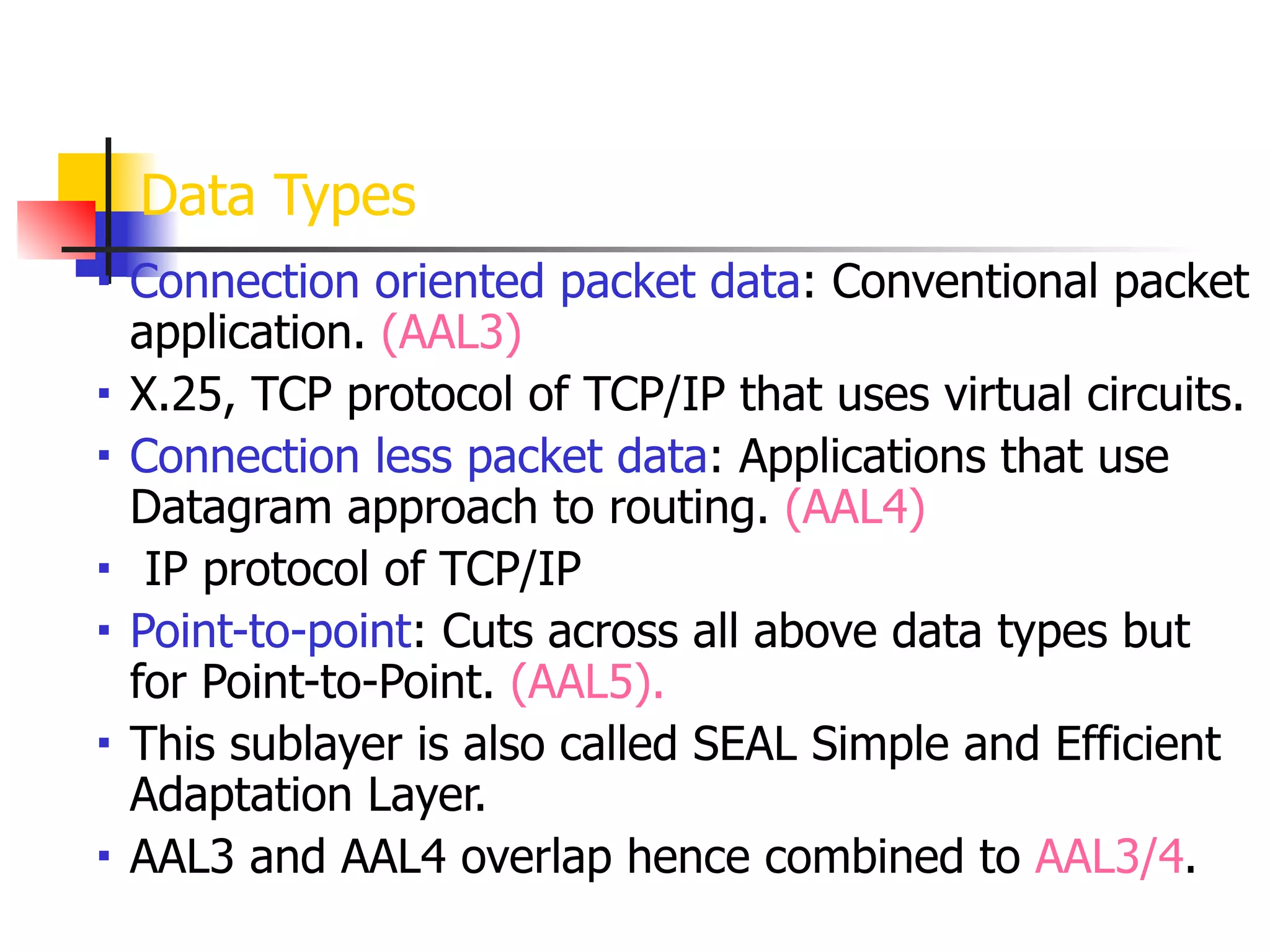
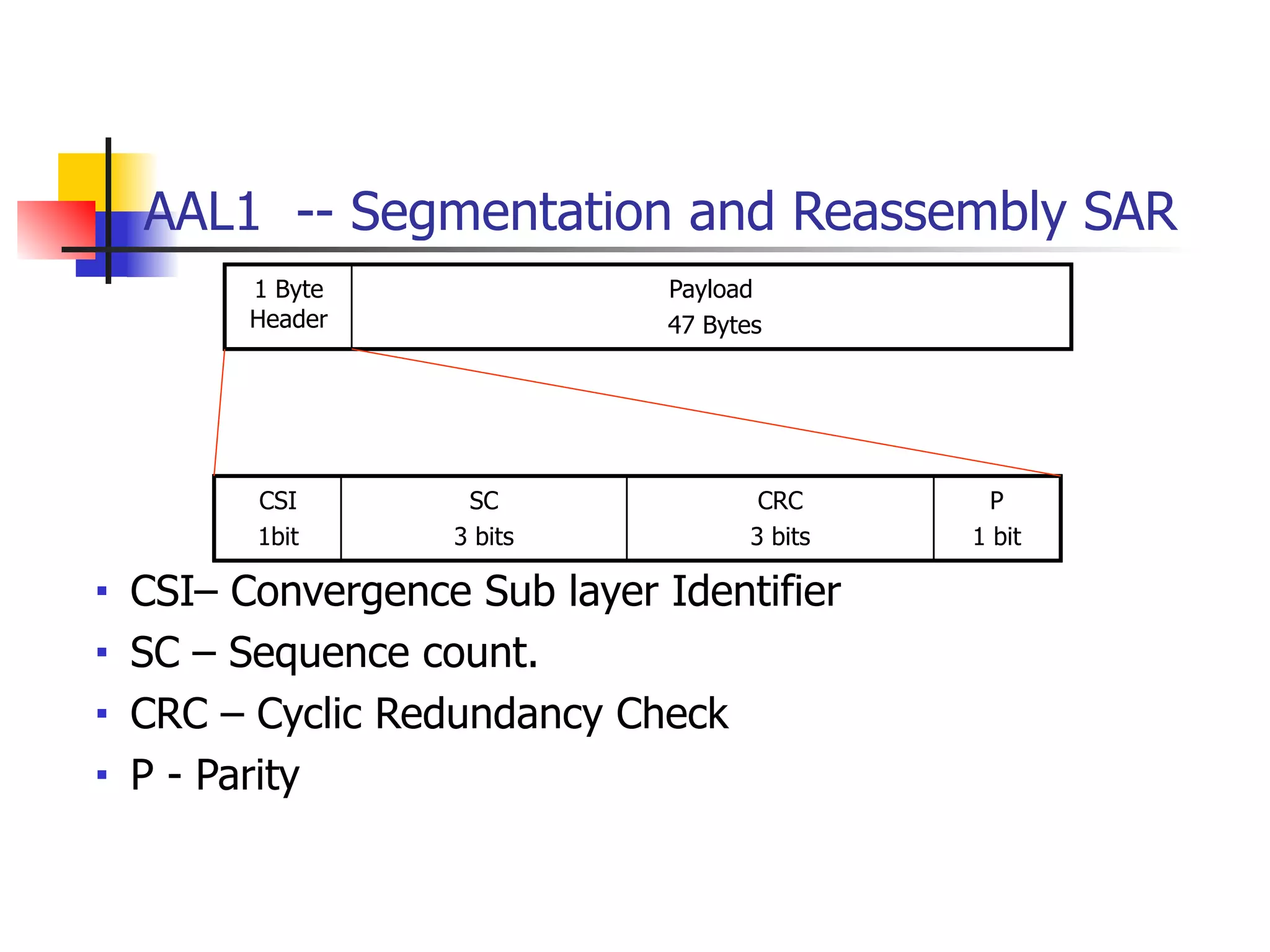
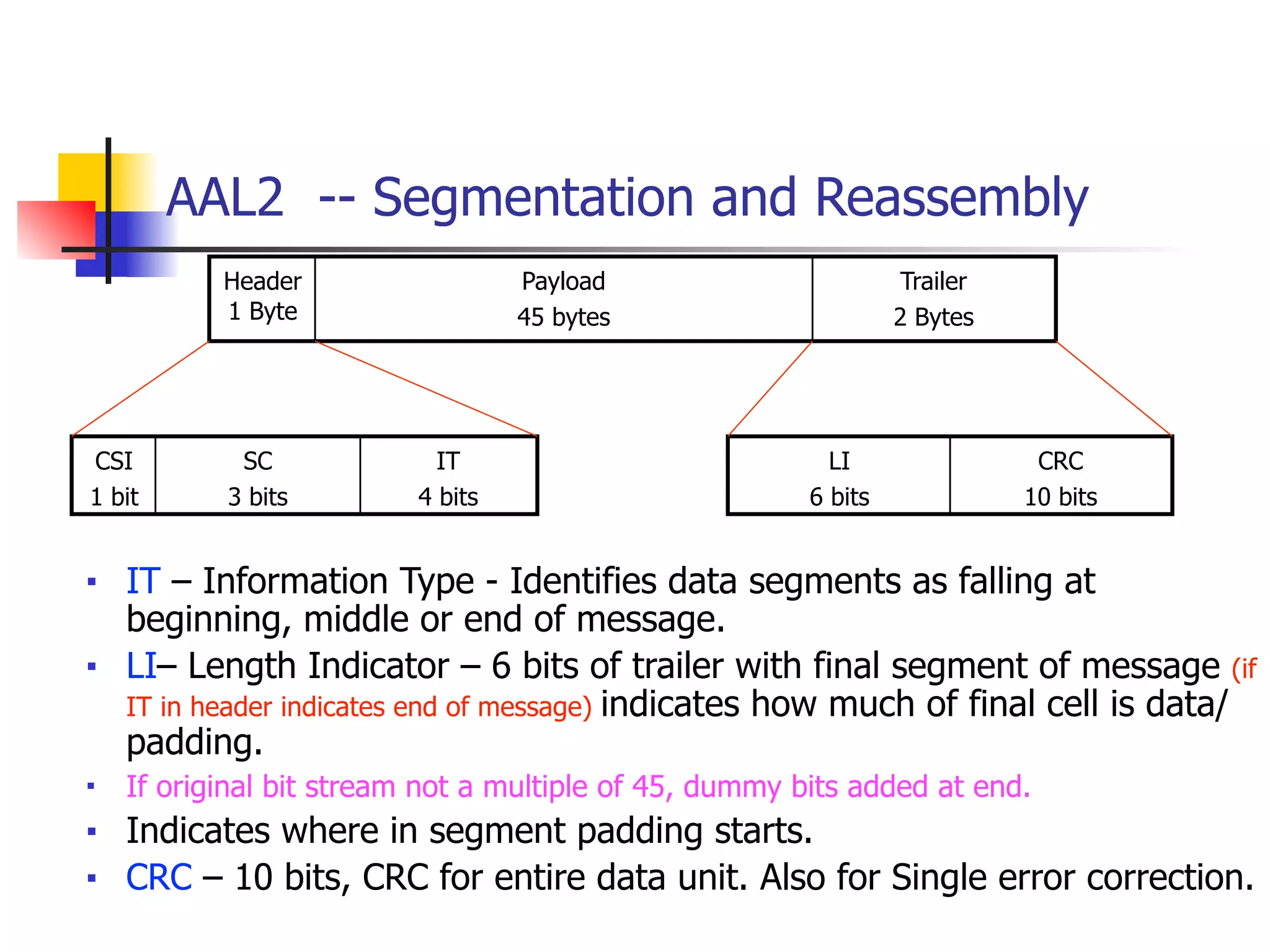
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a cell-switching and multiplexing technology designed to provide scalable bandwidth for data, audio, and video transmission, combining the benefits of circuit and packet switching. It features fixed-size cells for efficient traffic management, and establishes connections using hierarchical identifiers for virtual paths and circuits, allowing high scalability and minimal delays. ATM networks can serve as a backbone for existing systems and support various data types through the Application Adaptation Layer.