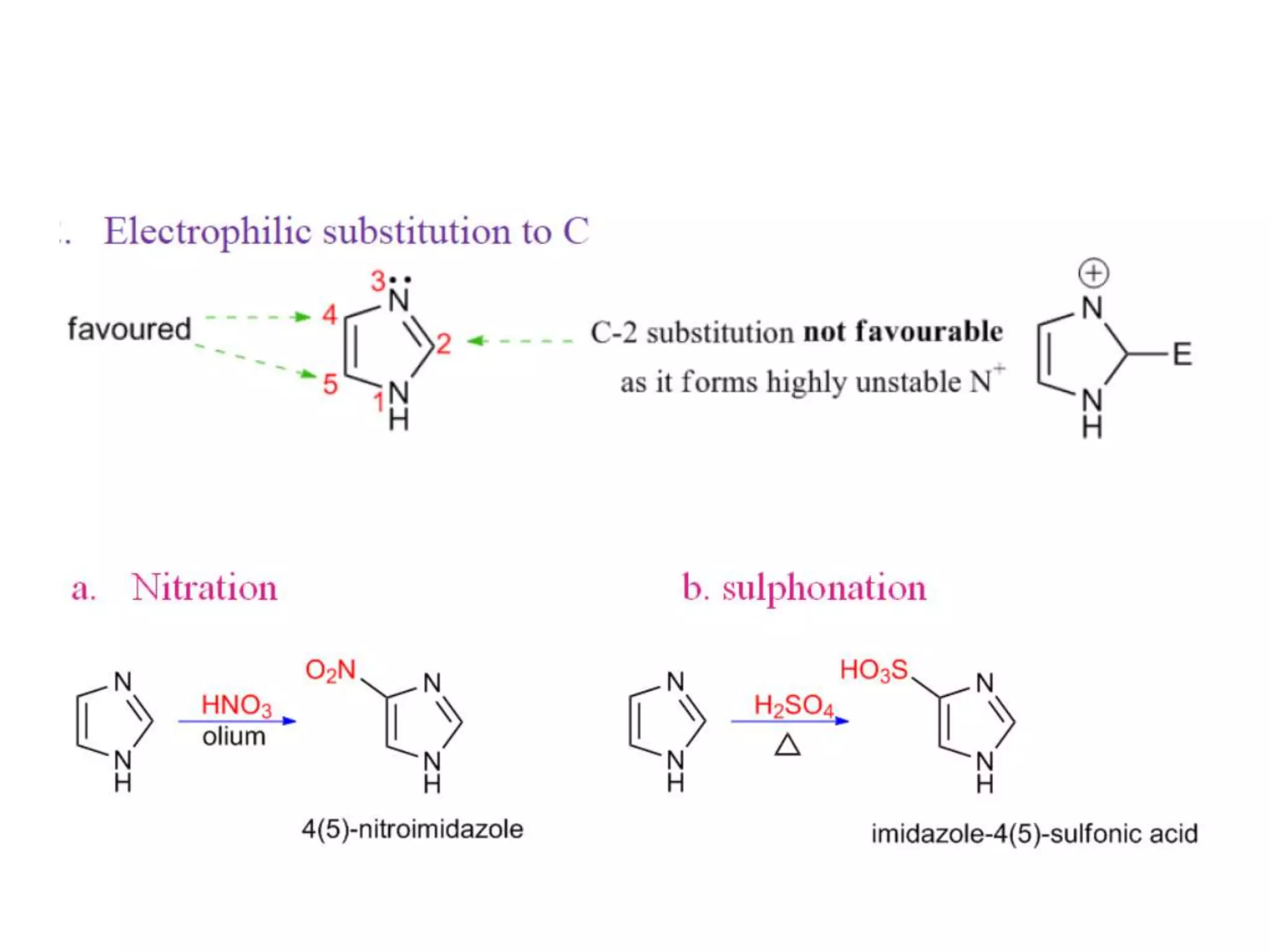
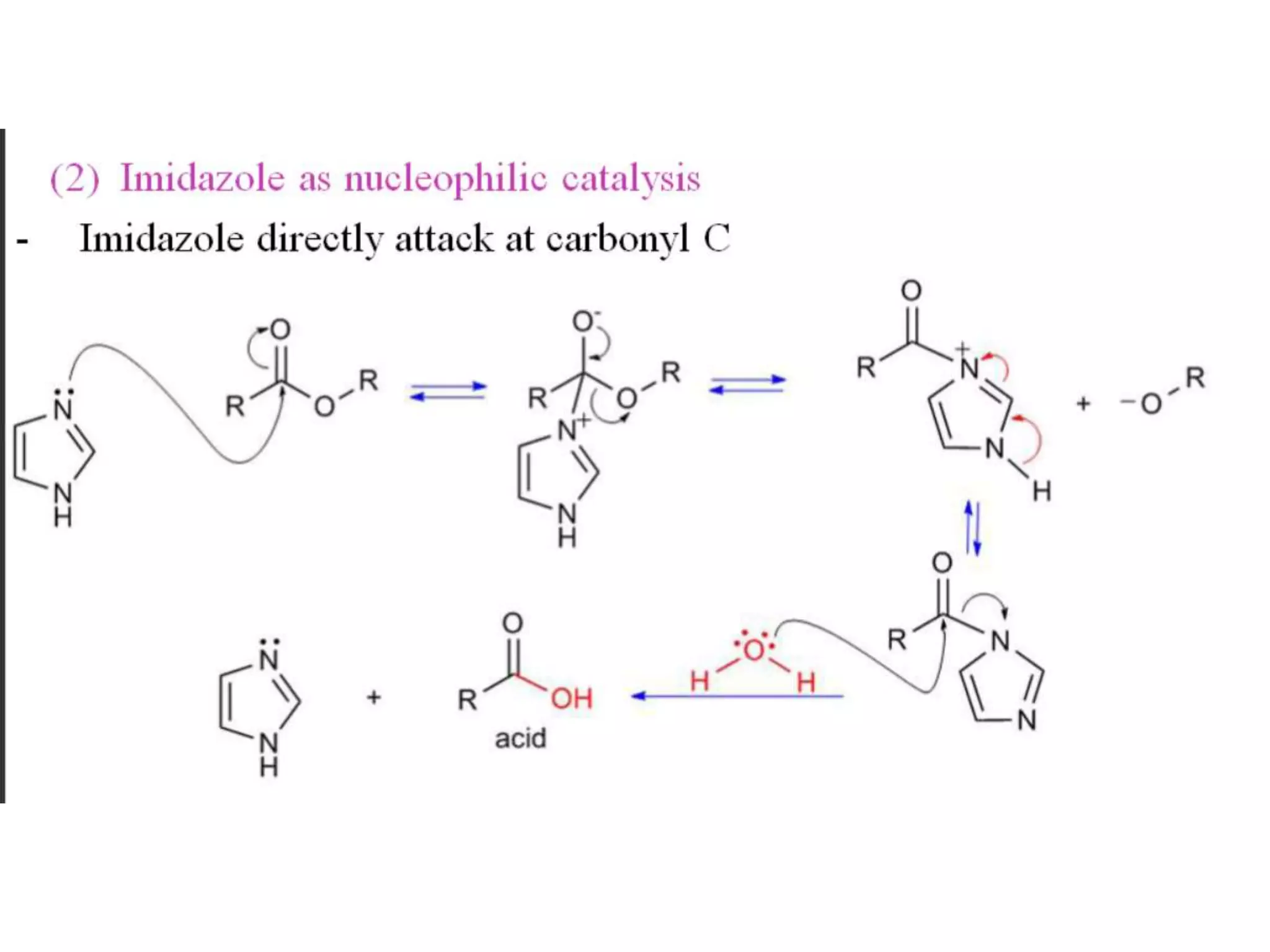
Imidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H4N2. It was first reported in 1858 and is an aromatic heterocycle that is classified as an alkaloid. The imidazole ring is present in important biological molecules like histidine and histamine. Many drugs contain imidazoles, such as antifungal, antiulcer, and antimicrobial agents. Imidazole has applications as an acid, a base, and in organic synthesis. It exhibits various pharmacological activities including antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antitubercular, and anticancer effects.