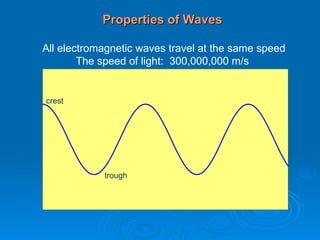
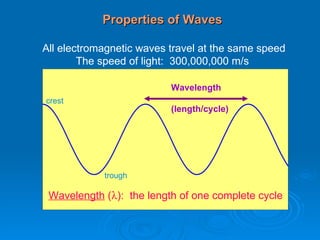
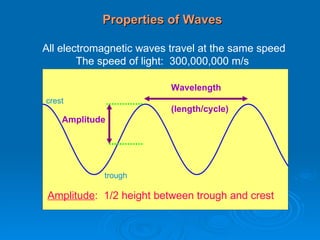
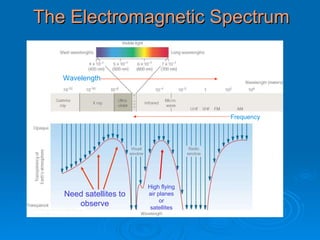
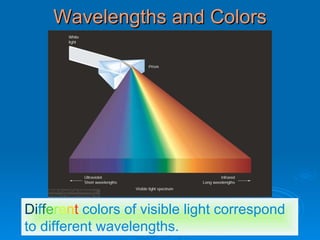
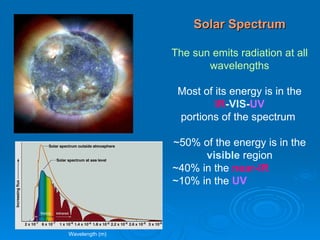
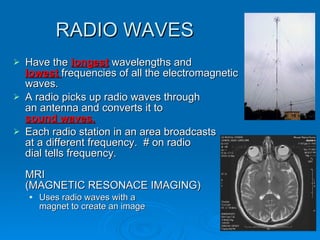
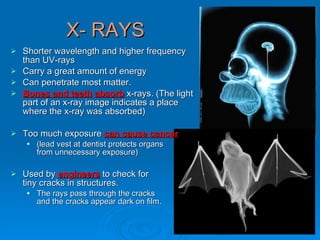
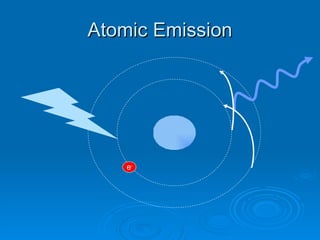
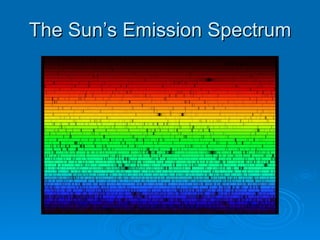
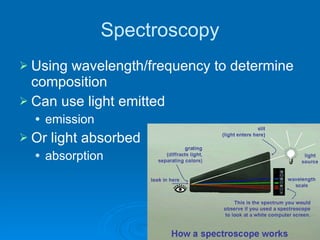
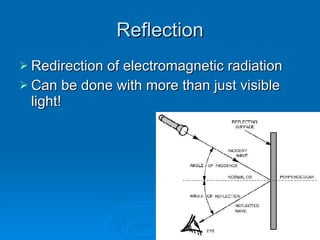
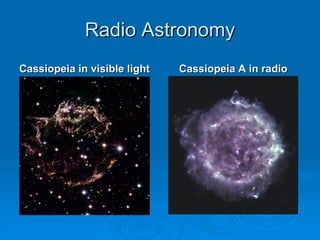
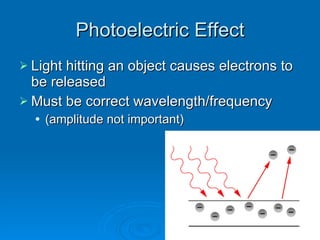
Light can be described as both a wave and a particle. As a wave, it travels at 300 million meters per second and is characterized by its wavelength and frequency. The different wavelengths of light make up the electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to gamma rays. As the frequency increases, so does the energy of the electromagnetic waves. Light also behaves as particles called photons, which are emitted or absorbed in specific wavelengths by electrons in atoms. This allows spectroscopy to be used to determine the composition of different objects by their emission or absorption spectra.