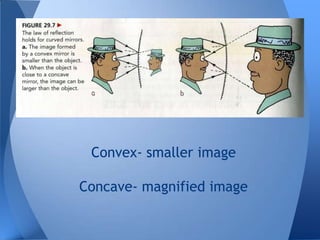
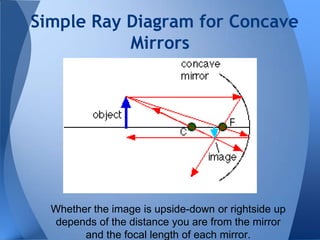
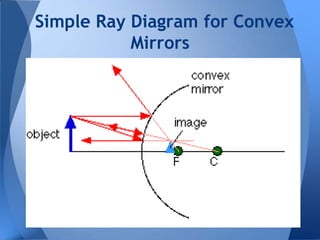
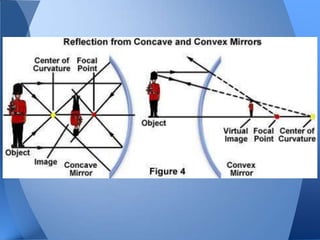
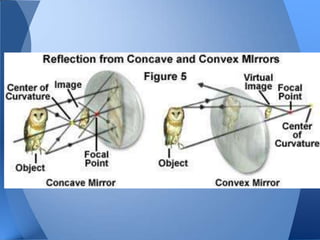
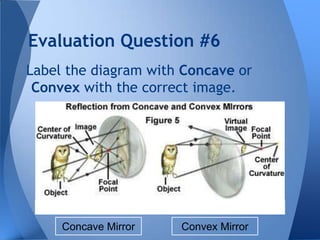
This document discusses different types of mirrors and how they work. It explains that convex mirrors produce smaller, virtual images behind the mirror, while concave mirrors can produce either magnified real images or virtual images, depending on the object's distance from the mirror. The document also introduces ray diagrams as a tool to determine image characteristics like location, size, and whether the image is real or virtual.