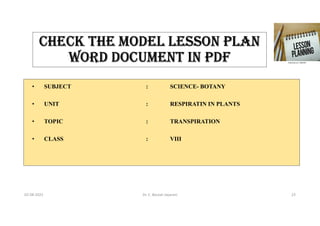
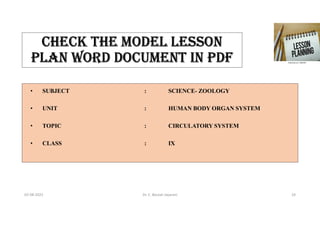
The document outlines the importance and structure of lesson planning in teaching, emphasizing its role in organizing objectives, engaging students, and guiding teachers through the instructional process. It details the components of effective lesson plans, including preparation, presentation, comparison, generalization, application, and recapitulation. Lastly, it highlights the advantages of lesson planning, such as systematic organization, time efficiency, and fostering student participation.