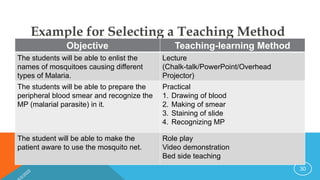
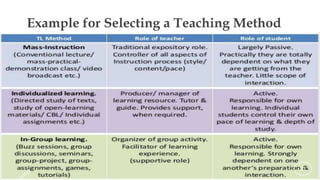
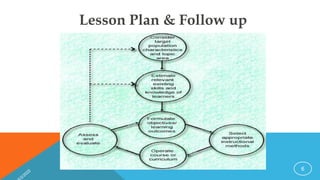
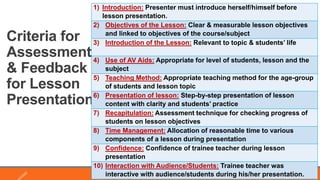
The document discusses the key components of an effective lesson plan, including objectives, introduction, teaching methods, and assessment. It emphasizes that a lesson plan provides a framework and roadmap to guide teaching and ensure students achieve the intended learning outcomes. Effective lesson plans clearly identify objectives, select appropriate teaching methods matched to the topic and students, and incorporate formative assessment techniques to evaluate student understanding. Developing high-quality lesson plans takes time and practice but is essential for organizing instruction.

![Main Components of a Lesson Plan
Lesson Objectives (what to achieve by the end of lesson)
Introduction (checking previous knowledge with reference to topic in hand)
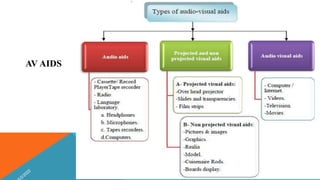
Learning Resources Required (blackboard, charts, photographs, models, video)
Presentation [ 1. presentation and illustration of concepts with the help of AV aids- here one
or a combination of teaching methods and/or a teaching method with one/more teaching techniques can
be used; 2. application of the concept(s); Guided & independent practice]
Recapitulation (to assess the understanding/learning and progress of students on the lesson.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) are helpful at this stage.
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplanshams-220502075558/85/Lesson-plan-Shams-pptx-2-320.jpg)




















![Steps for Selecting a Teaching Method
Clear Objectives
Choose teaching method(s) [choose one method or mix of methods]
Will the students be comfortable with this method?
Are you (teacher) comfortable with this method?
Will the selected teaching method be practicable?
Will you (the teacher) be allowed to use that teaching method?
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplanshams-220502075558/85/Lesson-plan-Shams-pptx-29-320.jpg)