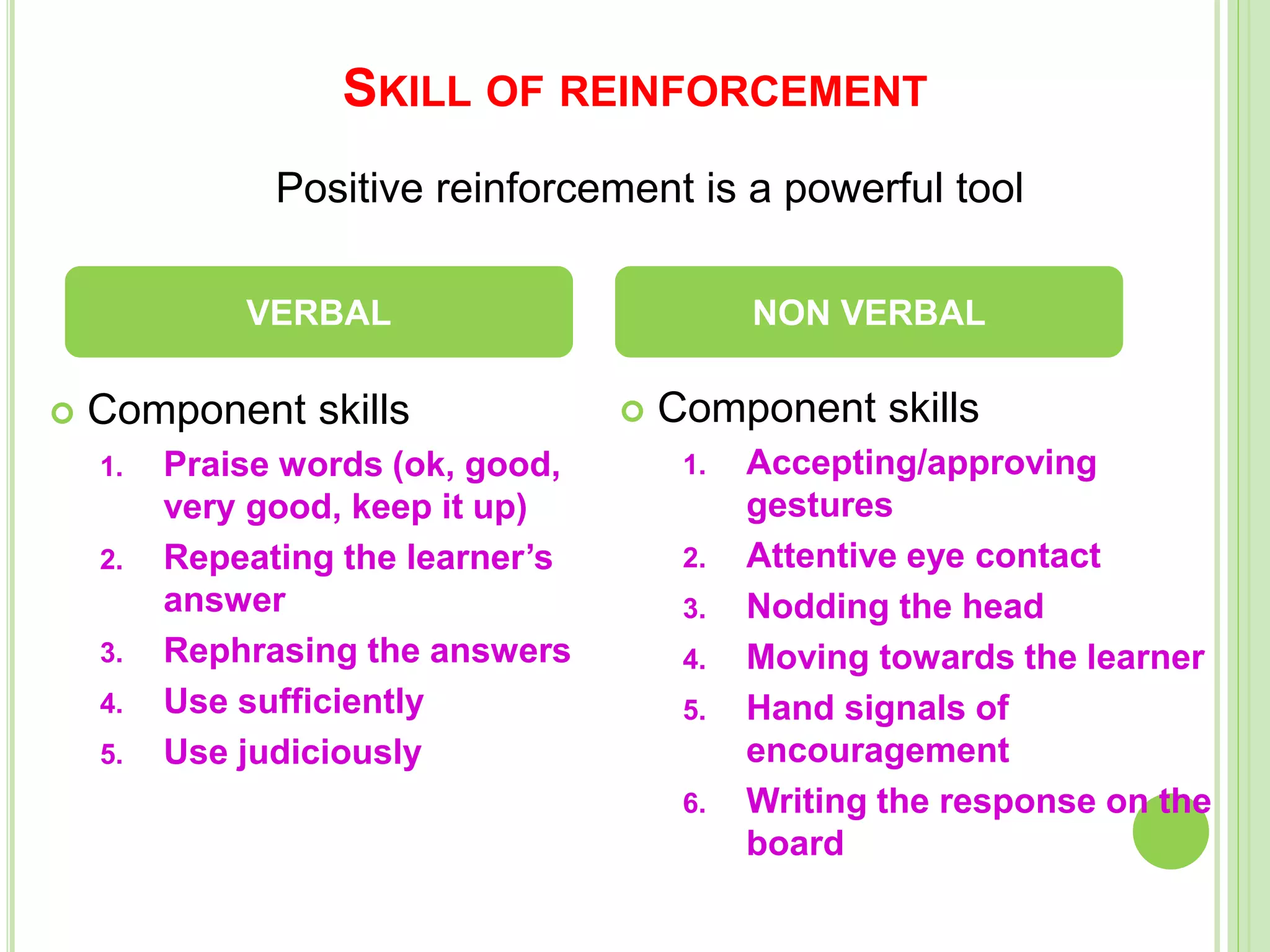
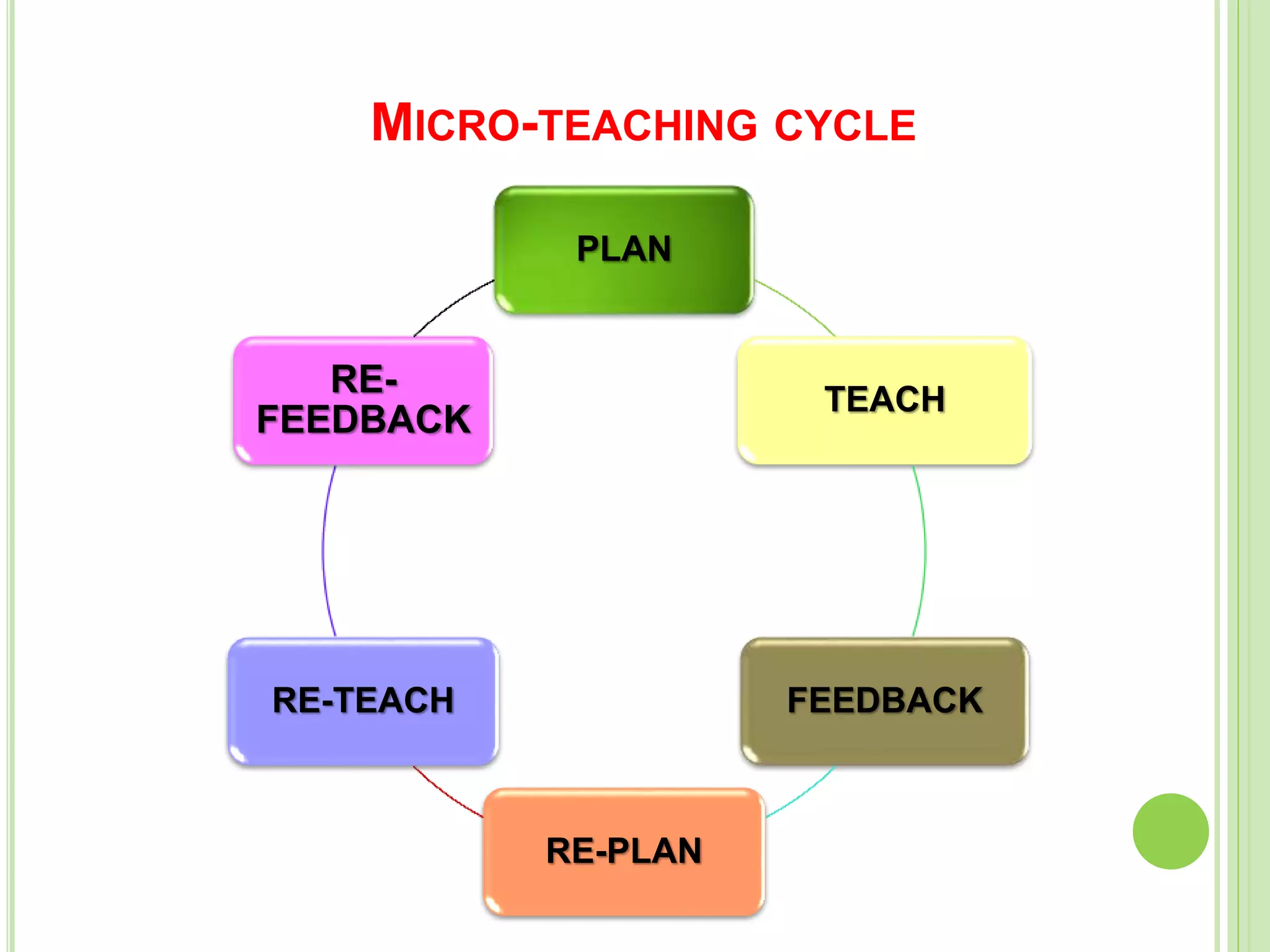
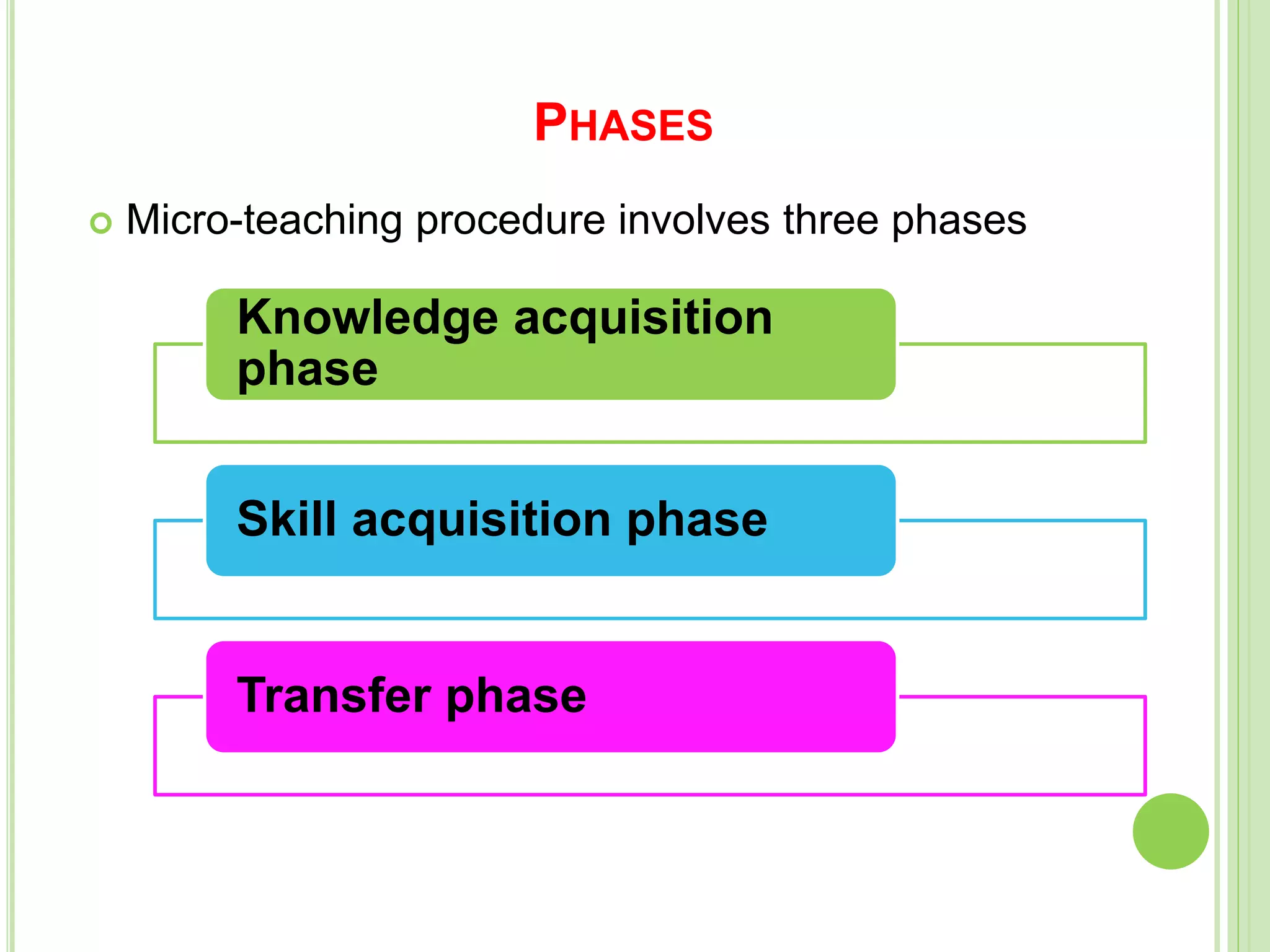
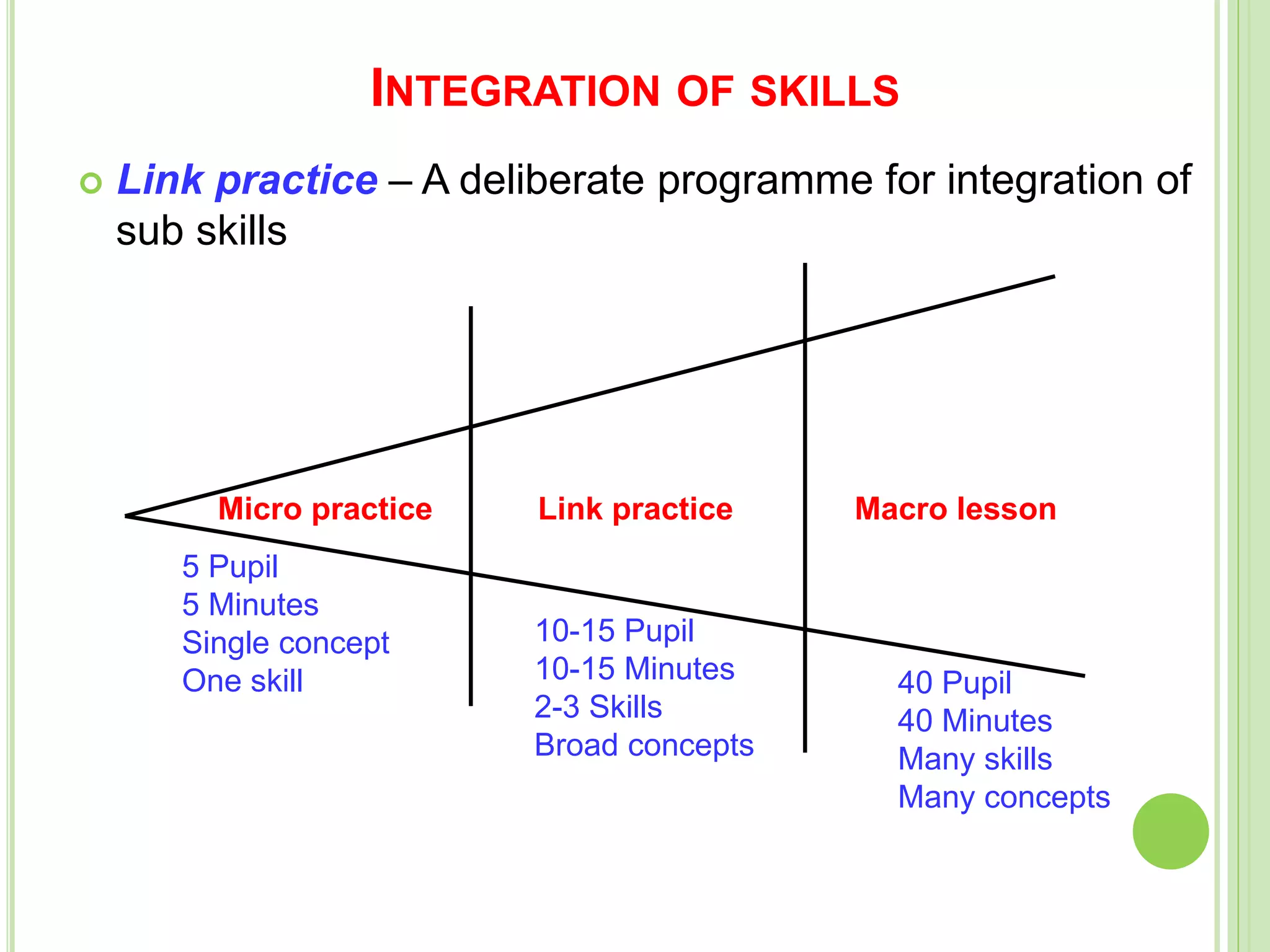
This document discusses teaching skills and microteaching. It identifies 8 core teaching skills: introducing a lesson, explaining, illustrating with examples, questioning, using the blackboard, reinforcement, stimulus variation, and probing questions. Each skill is broken down into components. It also describes microteaching as a training procedure involving teaching short lessons to small groups with feedback, aimed at simplifying the complexities of regular teaching. The microteaching cycle involves planning, teaching, feedback, re-planning, and re-teaching lessons with increasing integration of skills over time.