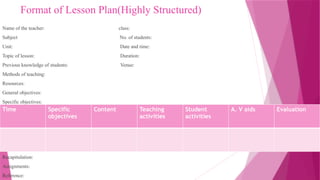
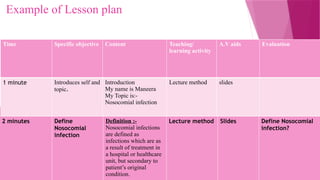
Meaning of lesson plan, purposes of lesson plan, planning and designing of lesson plan, characteristics of good lesson plan, steps in lesson planning, types of lesson plan, approaches to lesson plan, importance of lesson plan, format of lesson plan, examples of lesson plan, advantages and disadvantages of lesson plan.