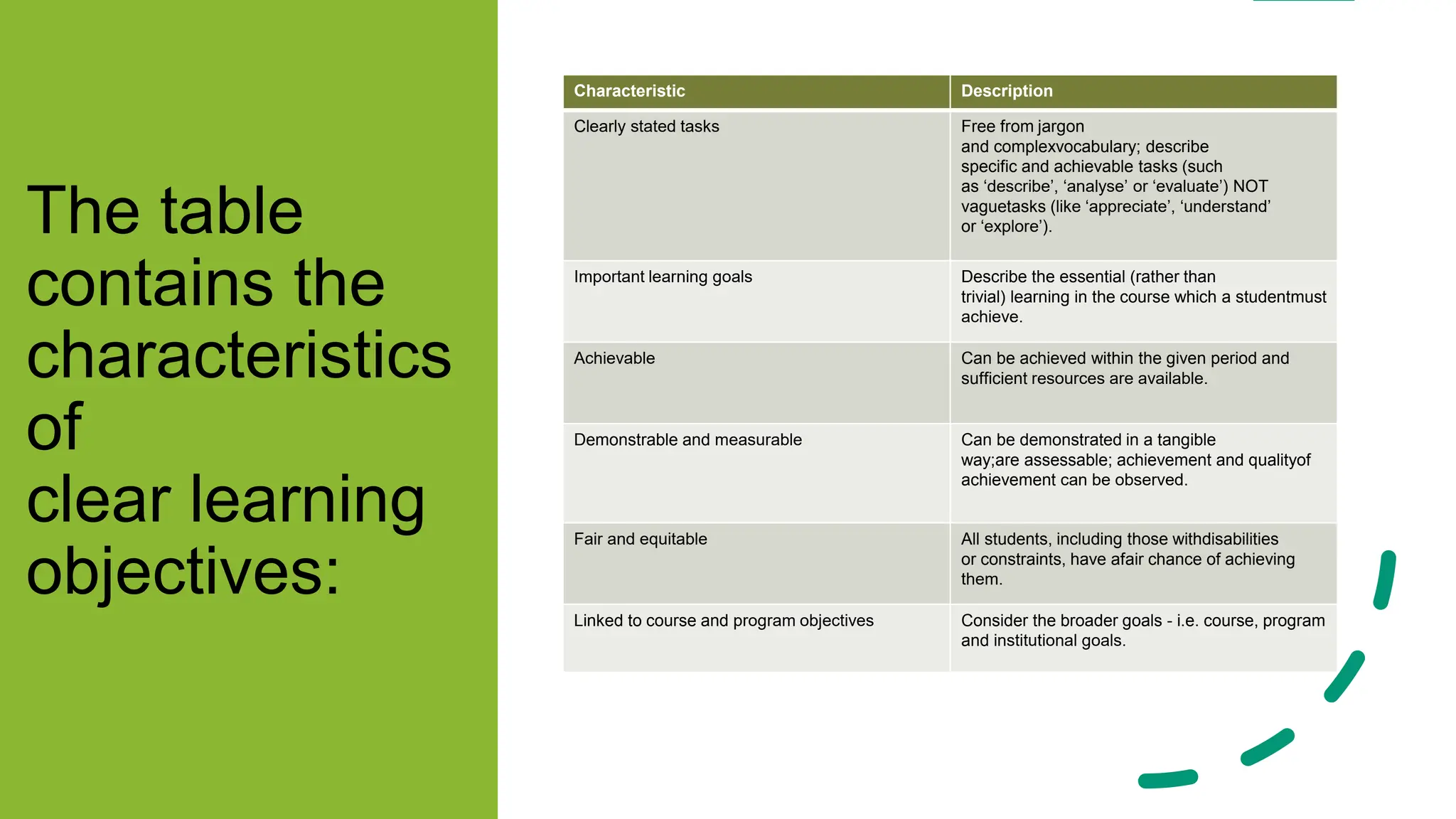
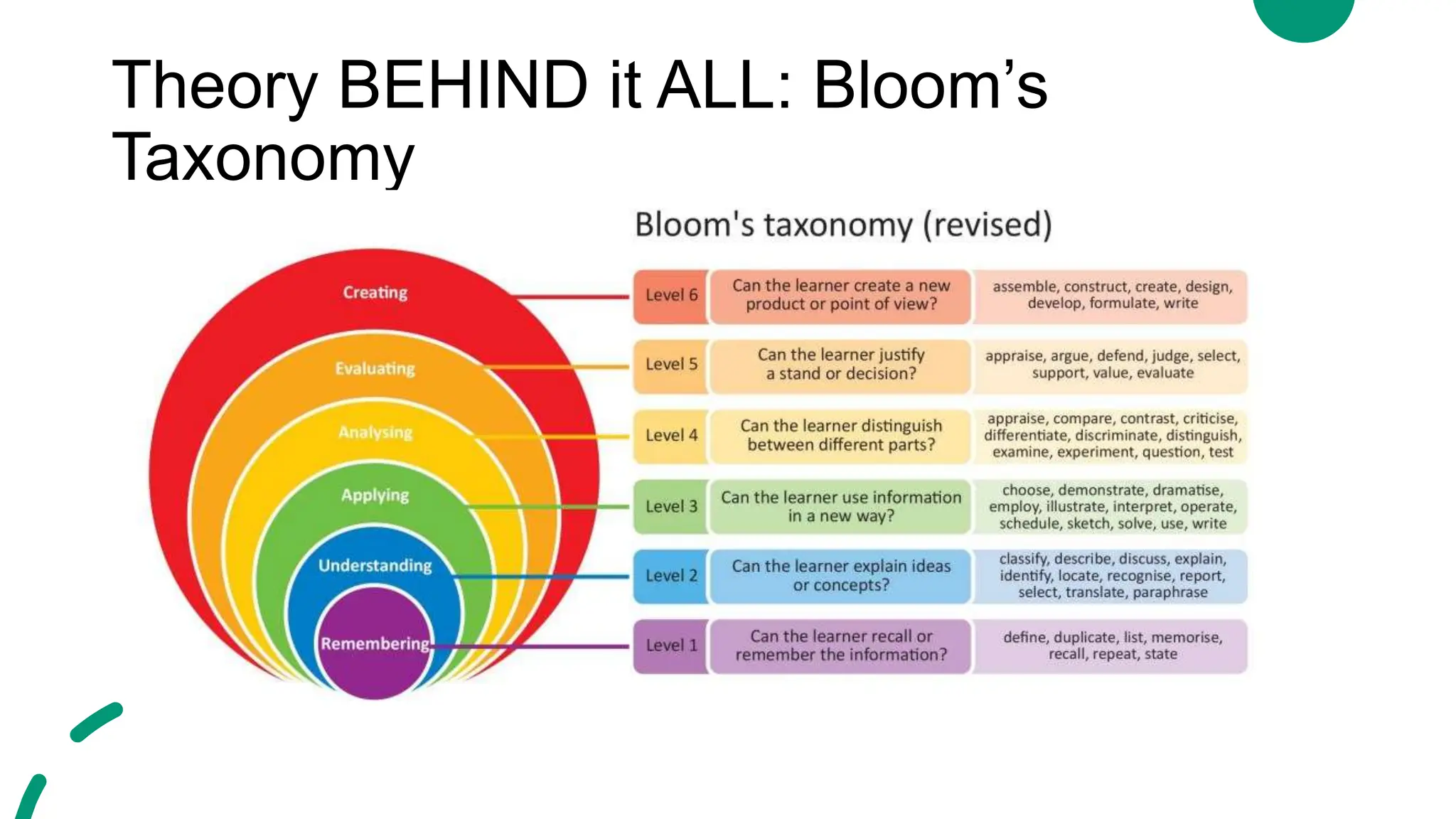
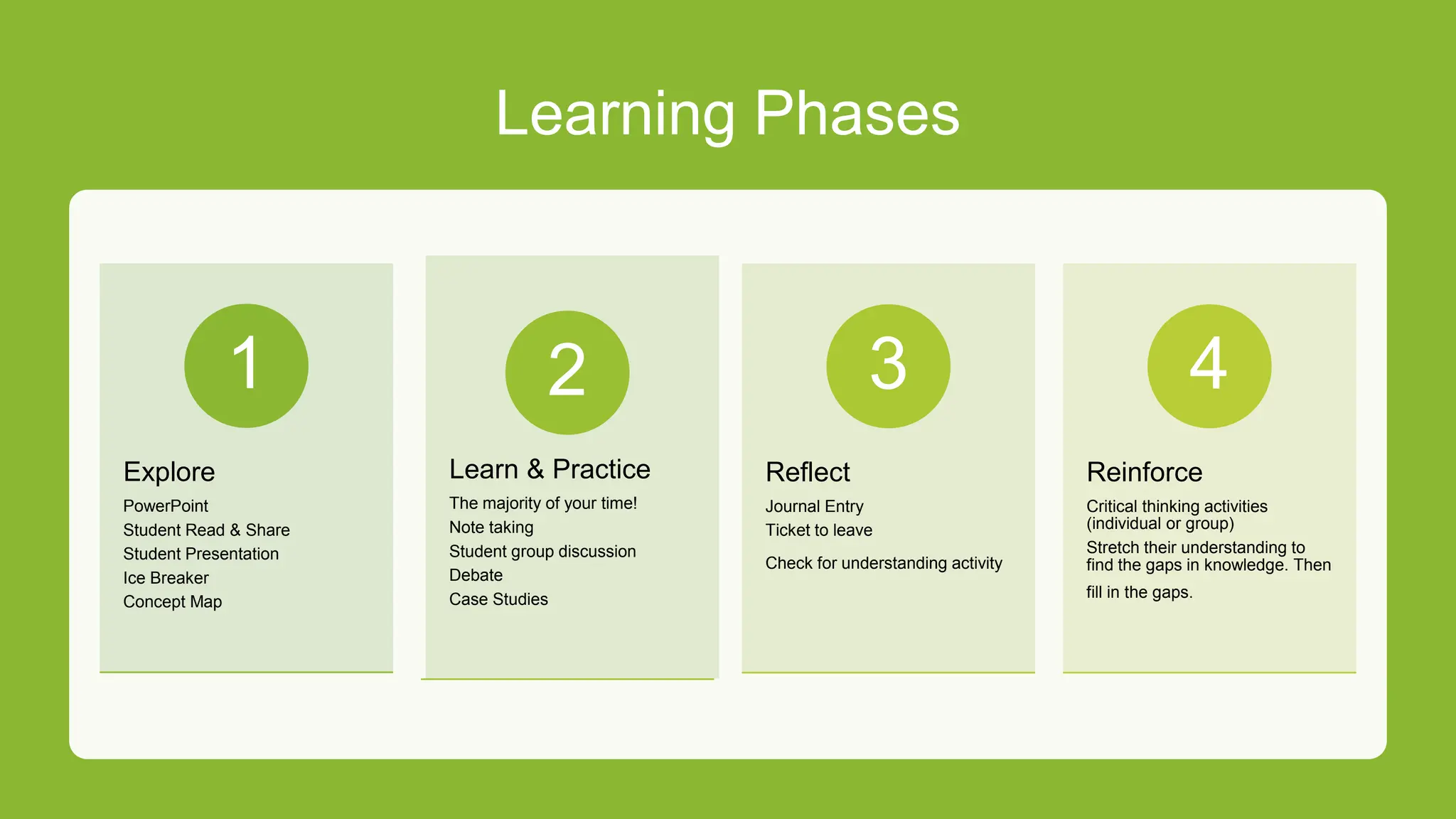
This document outlines the key elements of effective lesson plans, including the six main parts: objectives, requirements, materials, procedure, assessment, and reflection. It discusses each part in detail, such as explaining that objectives should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-based. The lesson procedure explains how to structure a lesson from introduction to assessment. Formative and summative assessments are defined. Reflection is emphasized as important for improving lessons. Sample lesson plans and activities are provided to illustrate the concepts.