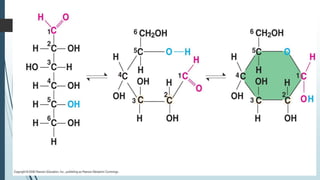
This document discusses the main biomolecules found in living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It provides details on their building blocks, functions, and examples. Carbohydrates like glucose are a main energy source and include monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Lipids store energy and form cell membranes, with examples being triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. Proteins have amino acids and roles like structure, defense, and catalysis. Nucleic acids DNA and RNA carry genetic information and provide energy, with DNA in the nucleus and RNA in the nucleus or cytoplasm.