Embed presentation


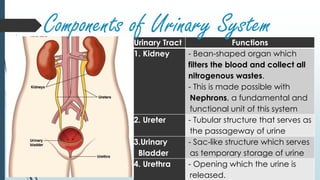
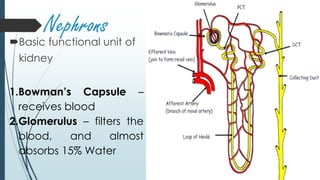
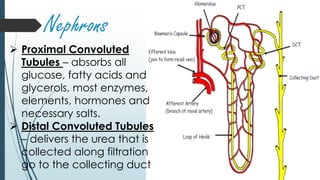
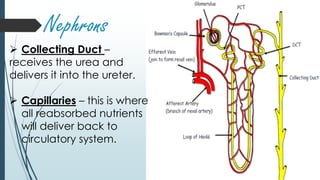

The urinary system filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body as urine. It includes the kidneys, which filter blood and remove waste as urine, ureters that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, the bladder that stores urine, and the urethra through which urine exits the body. The kidneys contain nephrons, the basic functional units that filter blood and regulate water and electrolyte balance by selectively reabsorbing useful substances and secreting waste products into urine.





