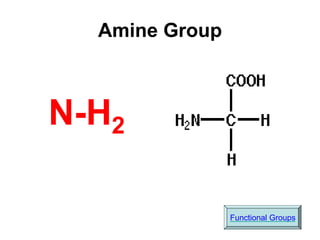
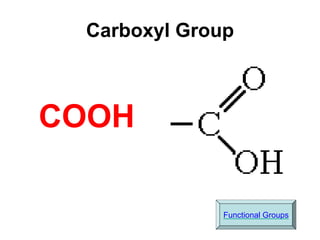
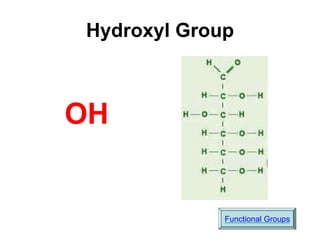
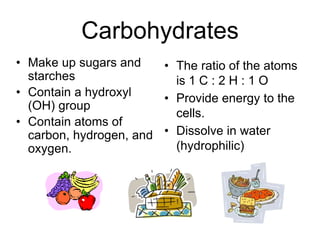
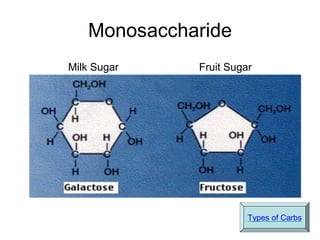
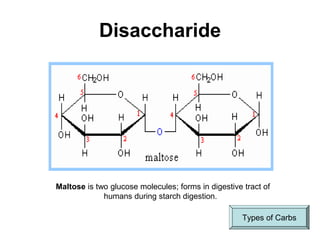
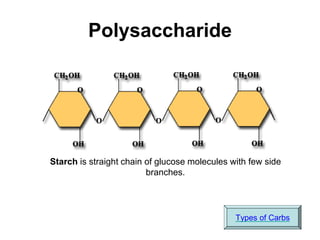
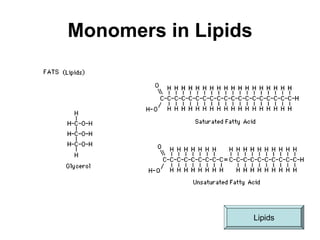
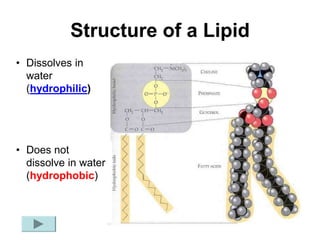
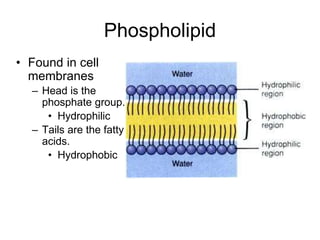
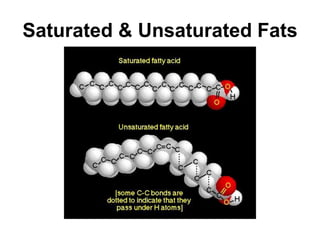
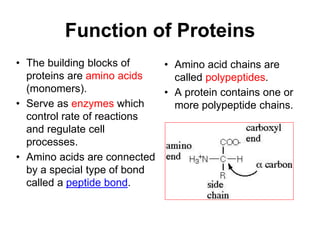
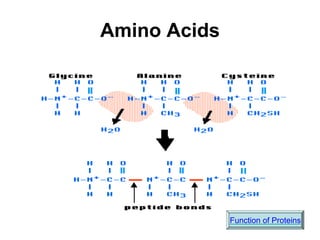
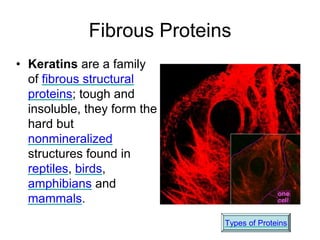
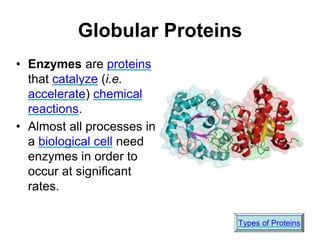
This document provides an overview of biochemistry and the four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It describes the basic composition and properties of each macromolecule type including their monomers, polymers, functional groups, and roles in maintaining life processes. Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and provide energy. Lipids contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and store energy. Proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen and serve as the building blocks for tissues and enzymes.