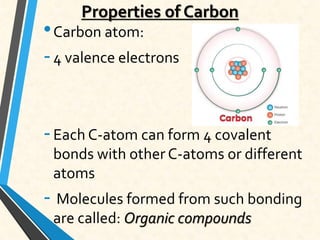
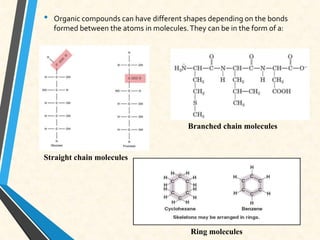
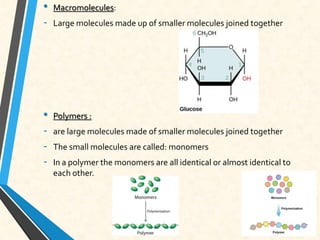
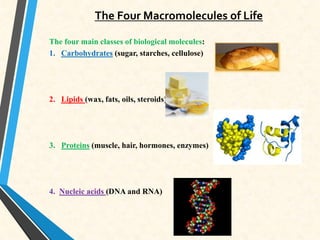
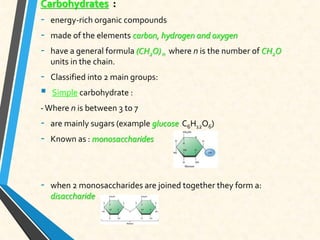
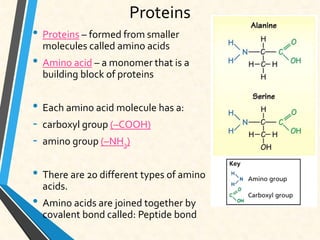
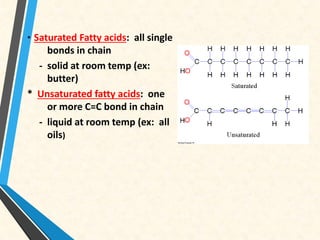
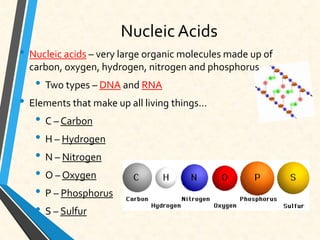
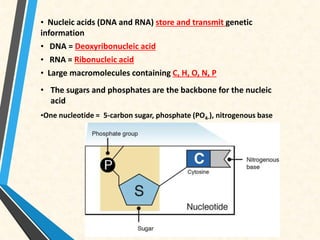
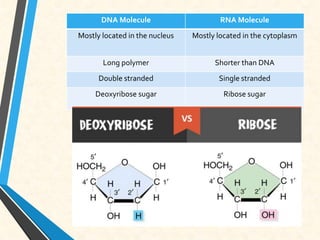
Carbon is essential for all biological molecules due to its ability to form four covalent bonds. There are four main classes of macromolecules that make up living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates like glycogen store glucose for energy. Lipids such as triglycerides are made of fatty acids and glycerol and provide over twice as much energy per gram as carbohydrates. Proteins are composed of amino acids and perform important functions like enzyme catalysis. Nucleic acids DNA and RNA contain genetic information and are made up of nucleotides with nitrogenous bases attached to sugars and phosphates.