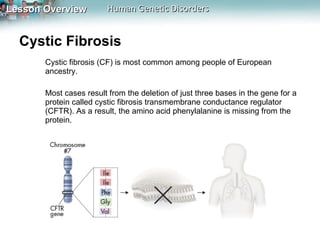
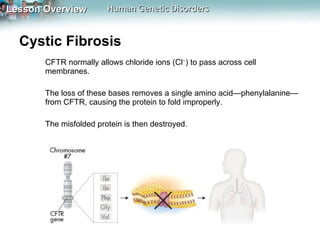
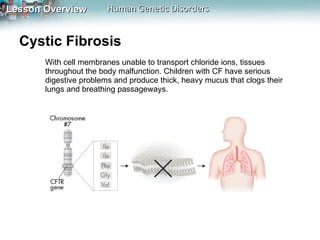
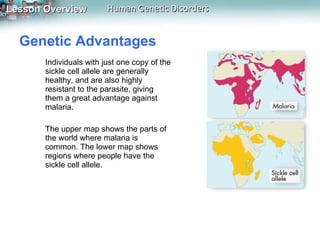
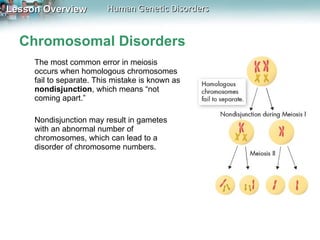
Genetic disorders can be caused by changes in individual genes or chromosomes. Changes in a gene's DNA sequence can alter proteins and affect phenotypes. Sickle cell disease is caused by a defective allele that makes hemoglobin less soluble, causing red blood cells to take on a sickle shape. Cystic fibrosis is usually caused by the deletion of three DNA bases, causing a protein to fold improperly and preventing chloride transport. Huntington's disease involves a dominant allele with an abnormal number of repeats of the codon CAG, coding for glutamine. Chromosomal disorders can result from errors in meiosis like nondisjunction, leading to an abnormal number of chromosomes and conditions like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, or Klinefelter syndrome.