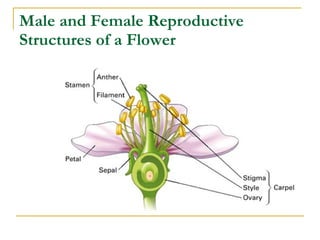
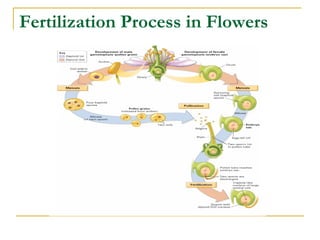
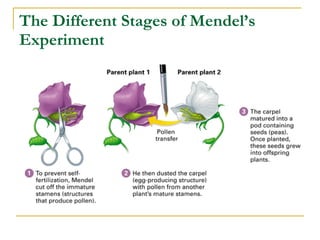
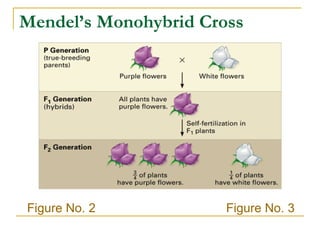
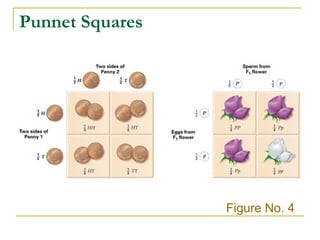
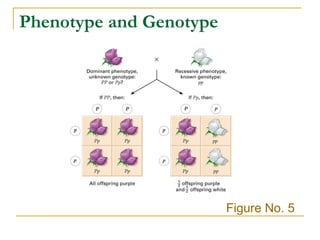
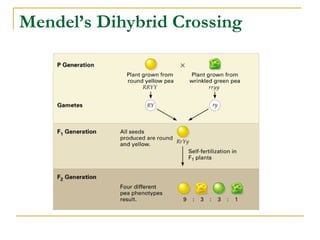
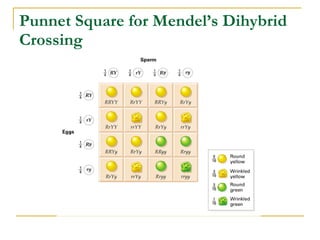
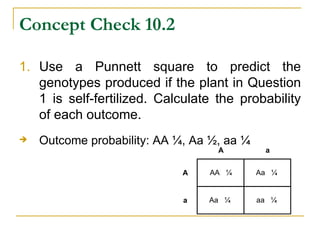
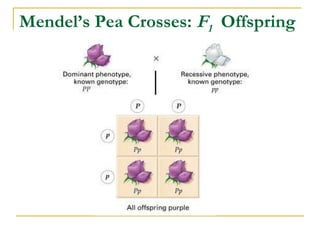
This document provides information about Gregor Mendel and his experiments with pea plants that formed the basis of genetics. It discusses key terms like genotype, phenotype, dominant and recessive traits. It explains how Mendel used controlled breeding experiments and statistical analysis to discover that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes) that segregate and assort independently. It also explains how his findings differed from and eventually replaced the earlier blending hypothesis of heredity.