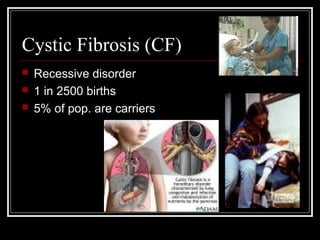
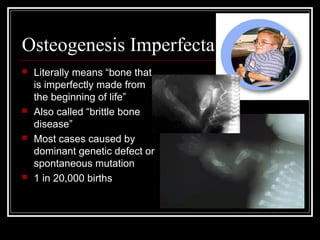
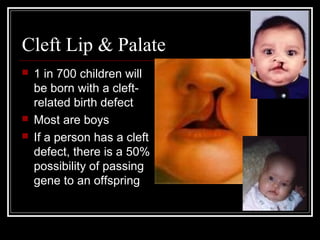
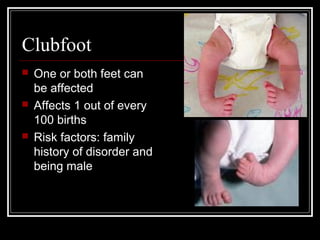
Genetic disorders result from changes or mutations in an individual's DNA. They can be caused by changes in the number or structure of chromosomes. Some examples of genetic disorders described in the document are cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria, Down syndrome, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, albinism, dwarfism, progeria, osteogenesis imperfecta, cleft lip and palate, and clubfoot. Each has distinct characteristics in terms of inheritance, prevalence, symptoms, and effects. Genetic disorders demonstrate how disruptions to the DNA code can profoundly impact health.