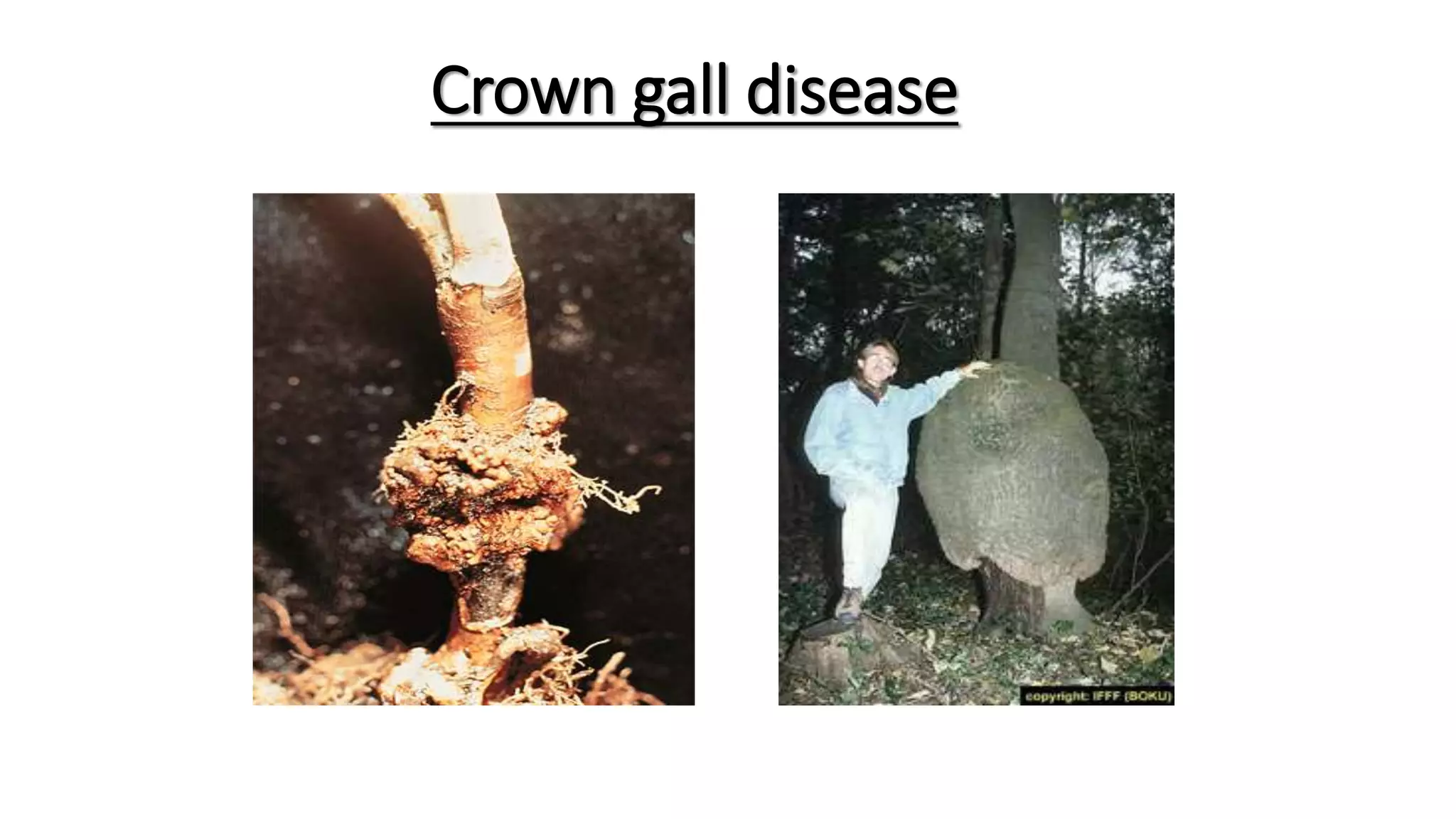
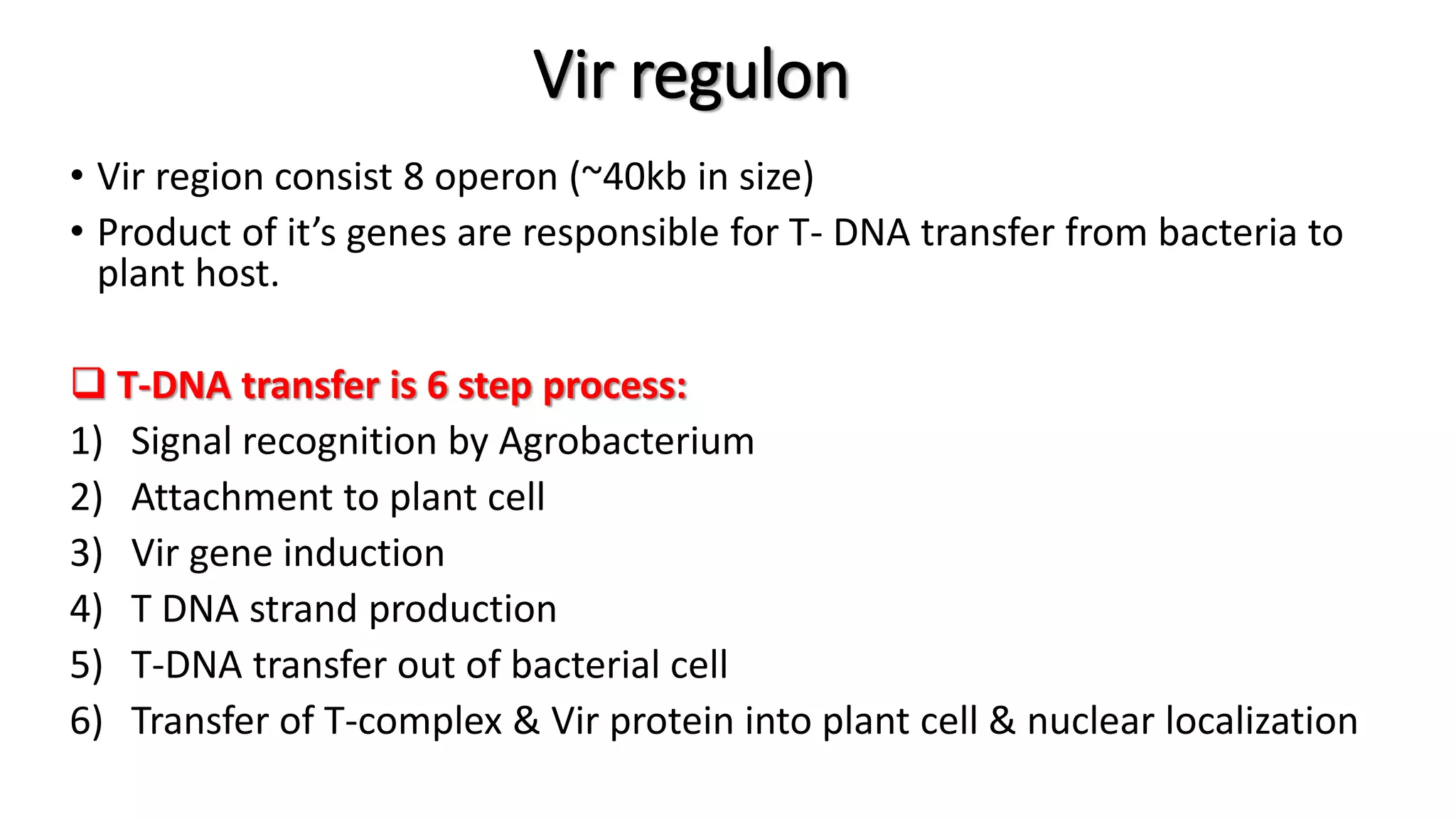
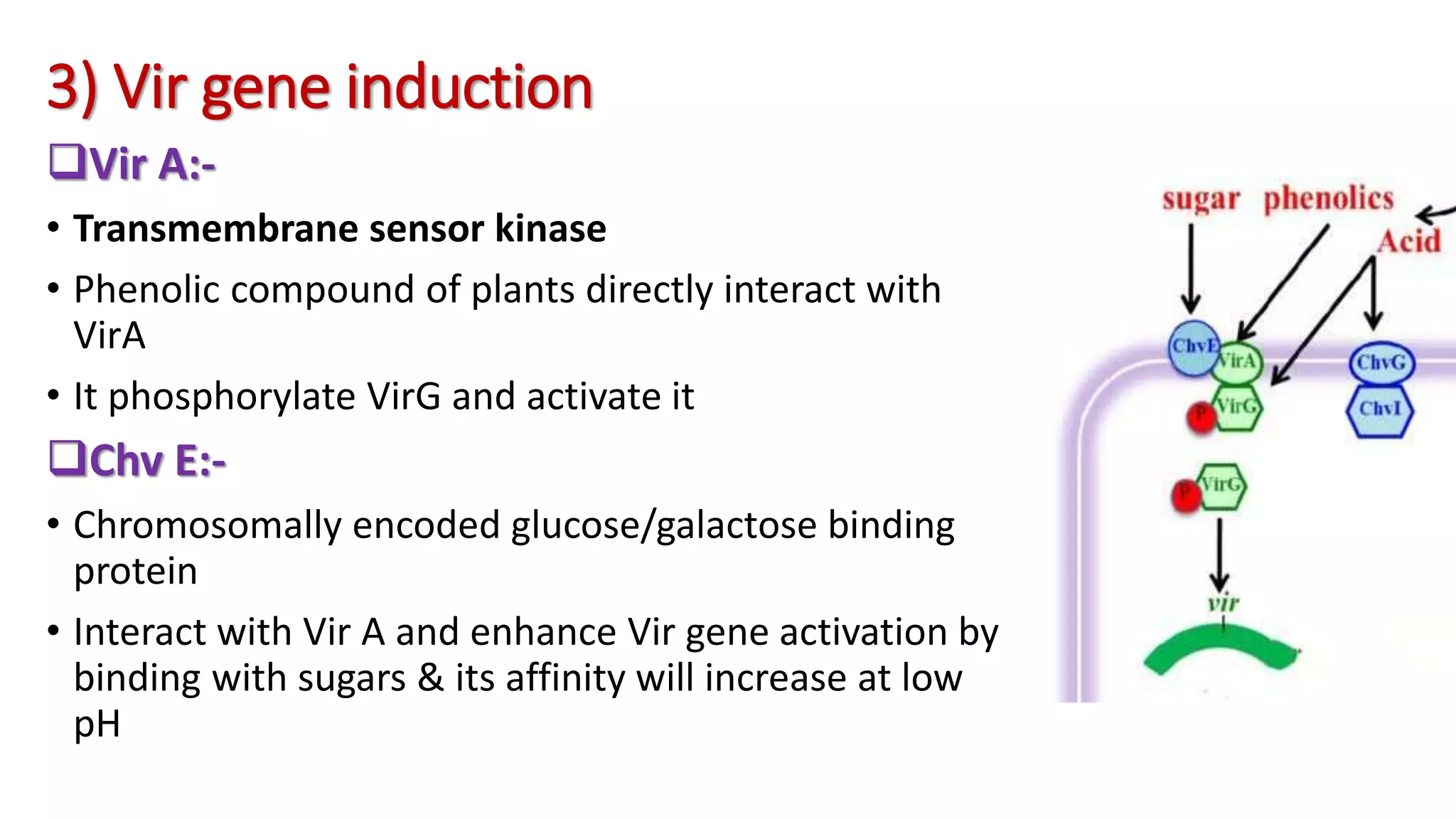
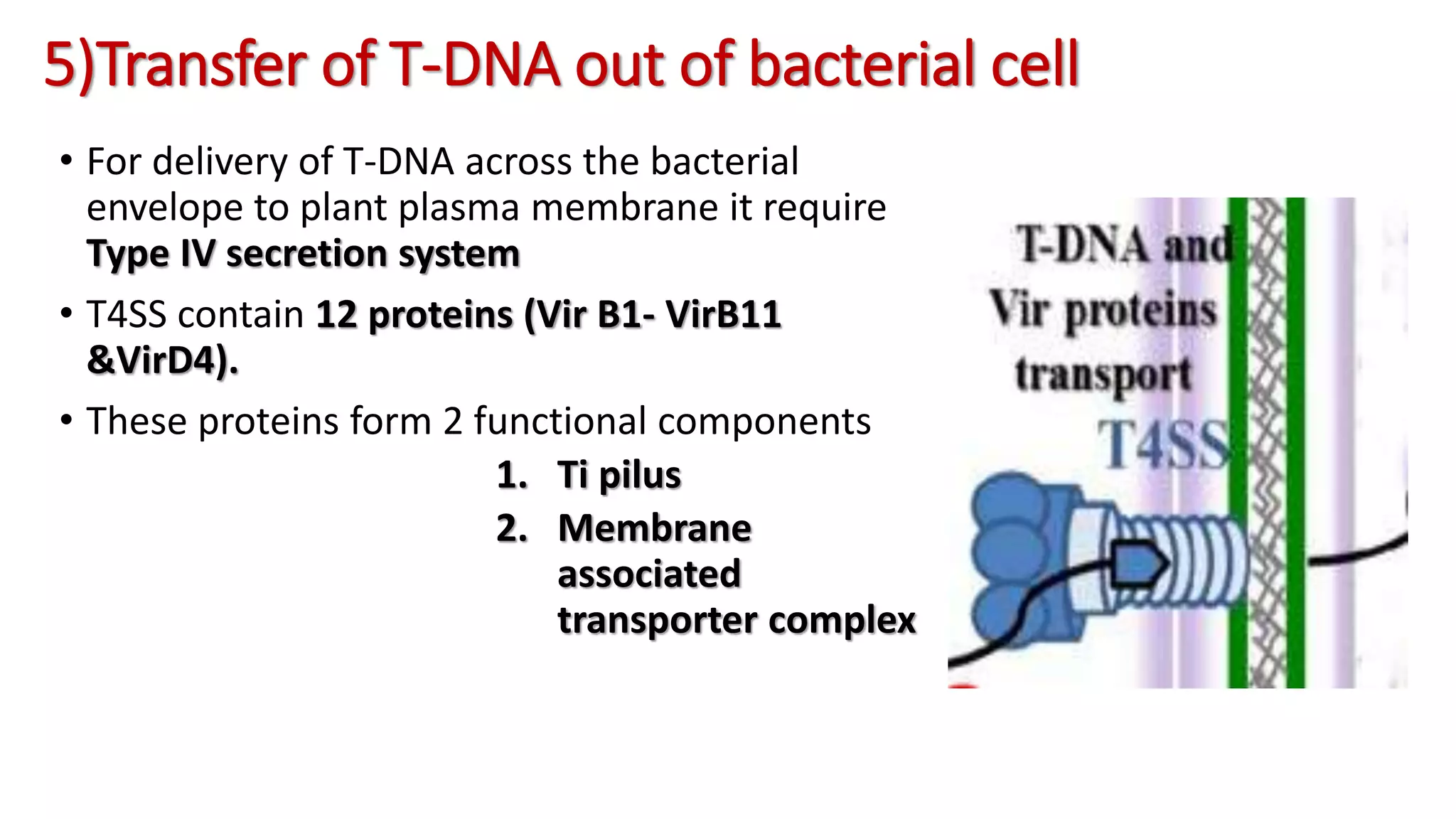
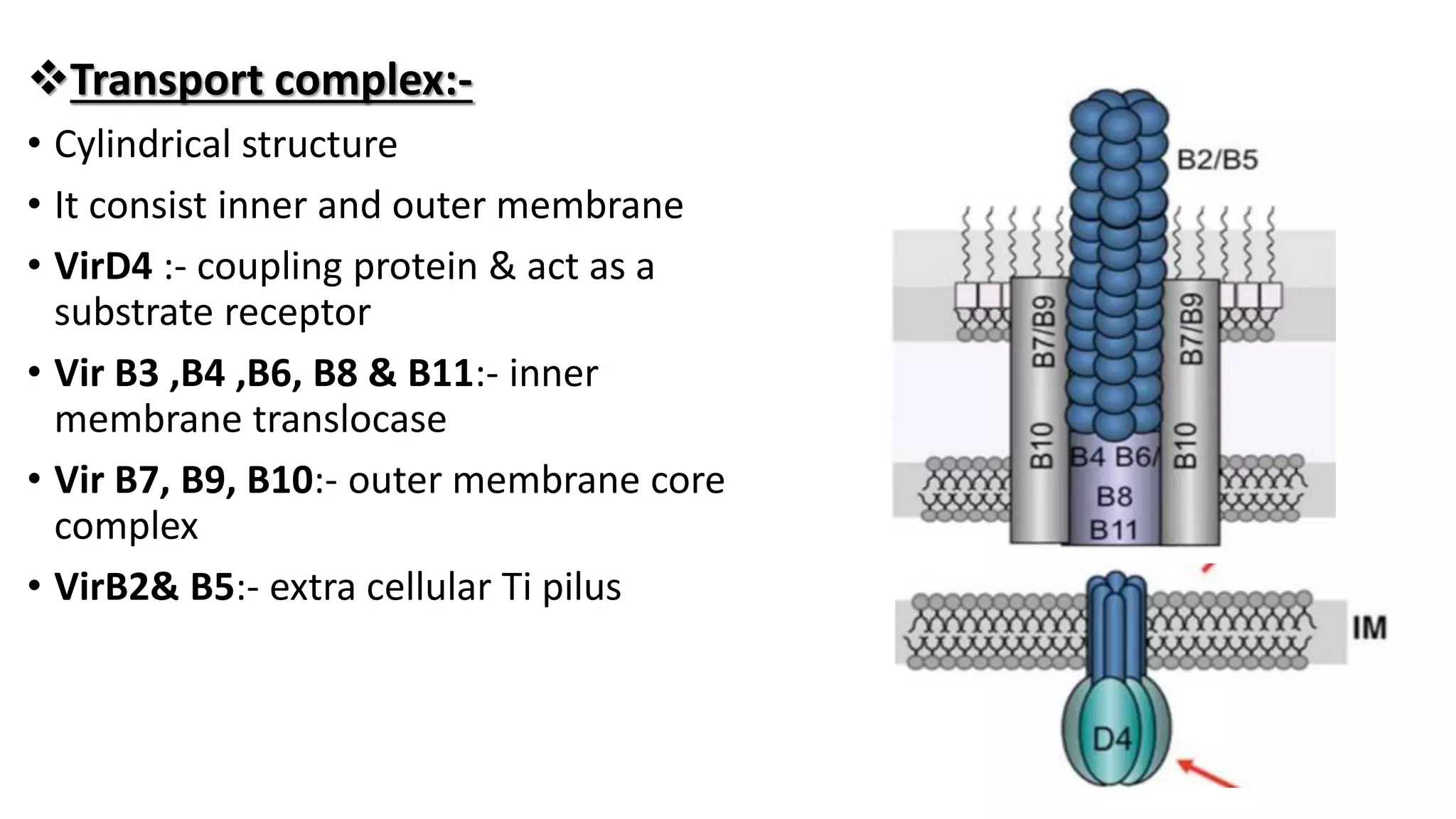
The document discusses the vir regulon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and its role in transferring T-DNA to plant hosts, detailing the six-step process that begins with signal recognition and ends with integration into the plant cell nucleus. Key components involved in this process include various virulence genes and proteins that facilitate attachment, T-DNA processing, and transport across bacterial and plant cell membranes. It also highlights the regulatory effects of plant hormones such as auxin, cytokinin, salicylic acid, and ethylene on the Agrobacterium infection and T-DNA transfer process.