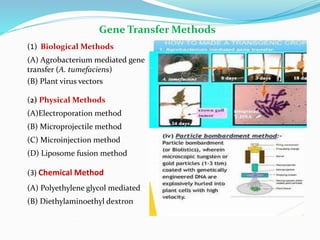
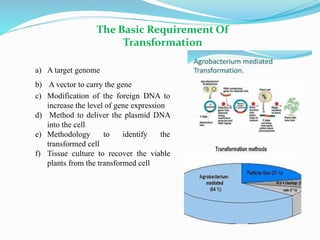
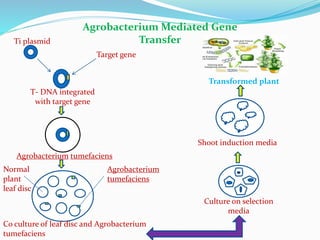
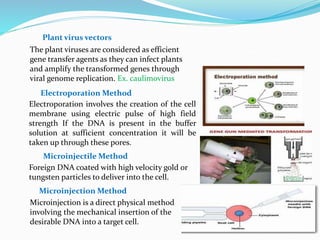
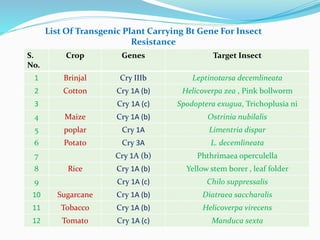
The document discusses transgenic crops, highlighting their benefits such as increased yield and pest resistance, along with their history and gene transfer methods. It also addresses the advantages and limitations of biotechnology, including environmental and socio-economic concerns. The conclusion emphasizes the potential of genetically modified crops to meet food demands while reducing pesticide reliance and the need for collaborative efforts in safe genetic modifications.