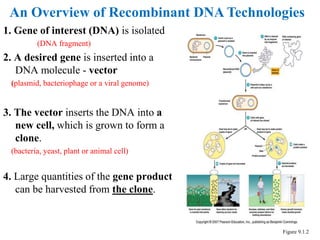
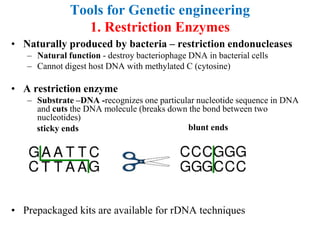
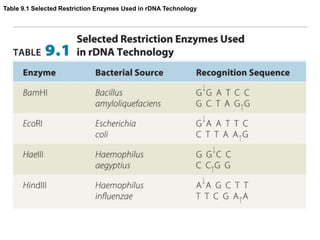
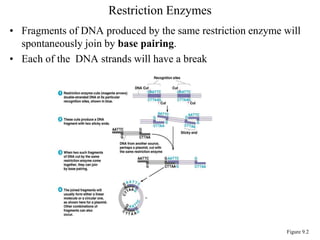
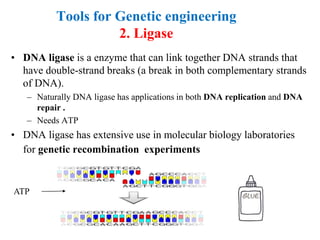
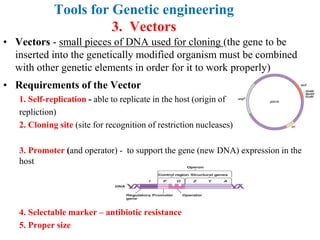
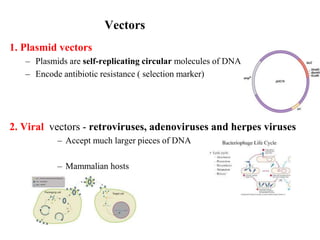
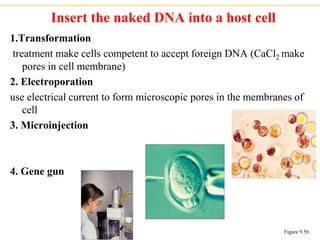
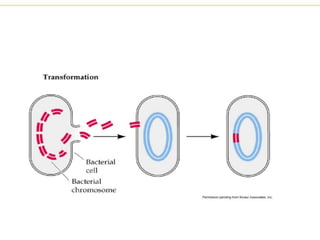
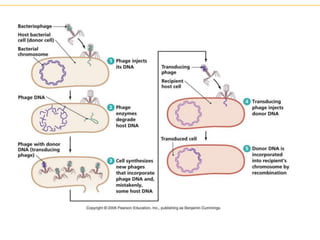
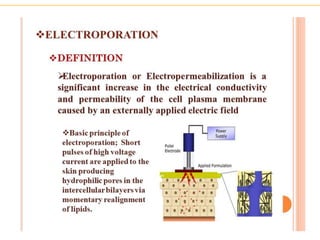
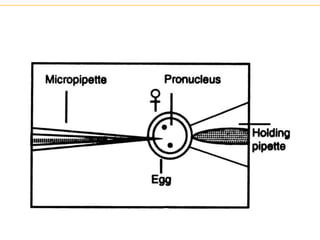
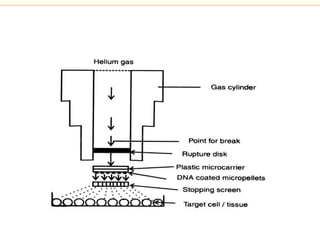
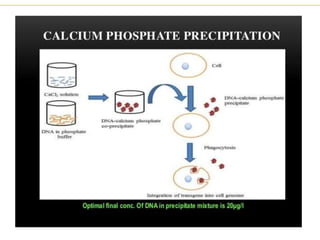
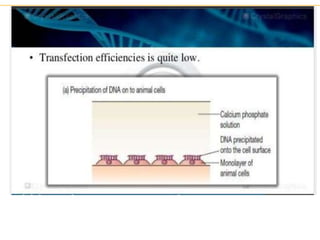
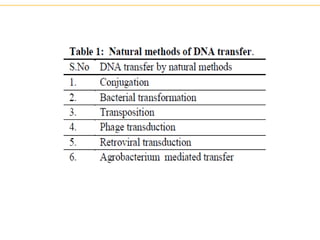
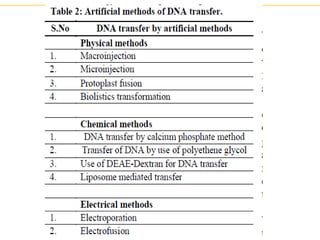
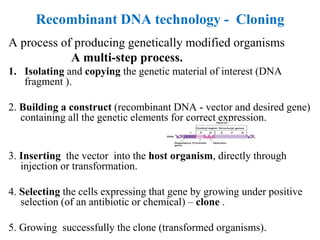
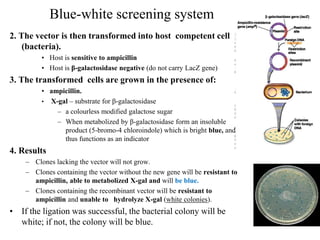
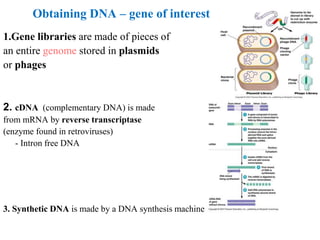
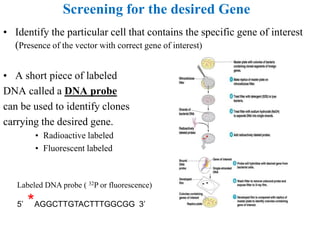
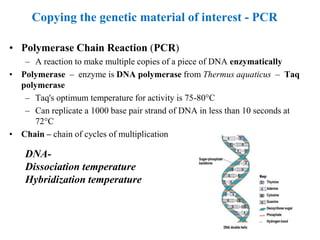
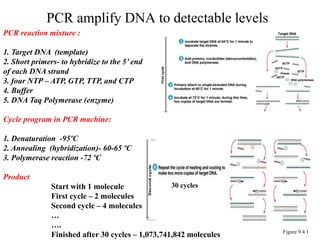
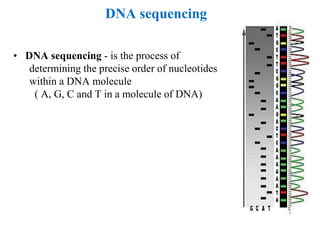
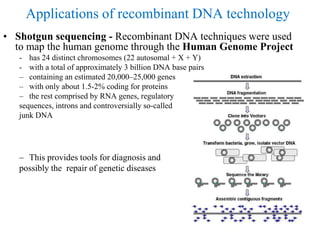
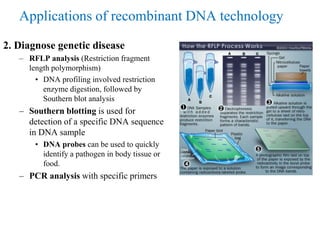
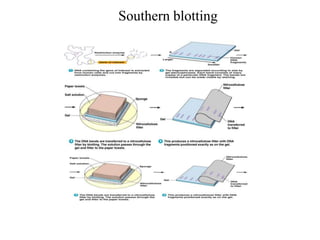
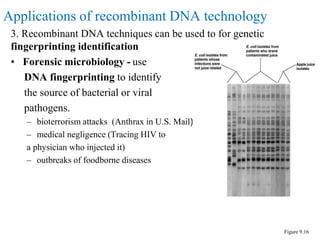
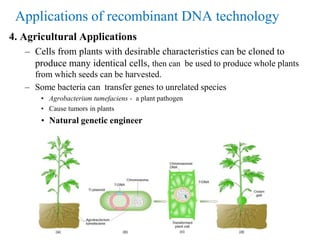
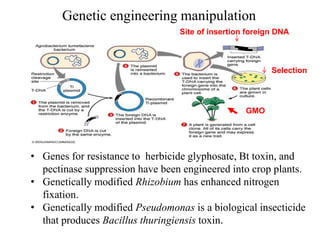
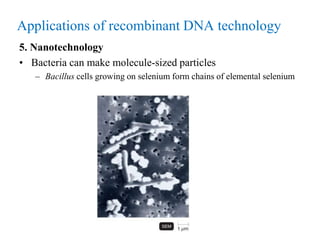
Recombinant DNA technology allows for the manipulation of genes from different species in the laboratory. The process involves isolating the gene of interest, inserting it into a vector, and introducing the vector into a host cell. This allows the gene to be expressed, producing its protein product in large quantities. Key tools that enable recombinant DNA techniques are restriction enzymes, DNA ligase, bacterial plasmids as vectors, and methods for introducing DNA into host cells like transformation, transduction, and microinjection. Recombinant DNA technology has applications in producing foods, antibiotics, enzymes and more through genetic engineering of microbes, plants and animals.