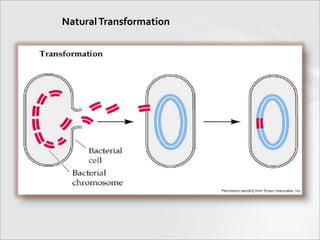
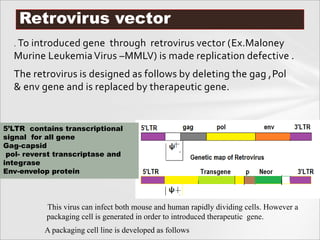
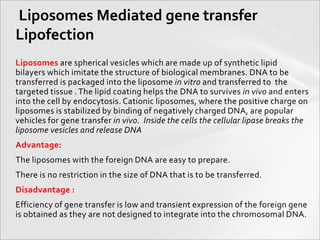
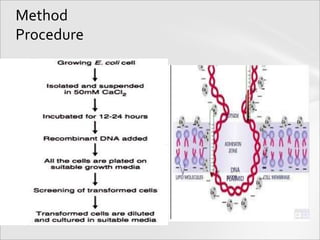
The document outlines various methods for gene transfer and transformation in host cells, including natural transformation, electroporation, and particle bombardment. It details the mechanisms and advantages of each method, such as the use of calcium phosphate for bacterial transformation and liposomes for gene delivery. Additionally, it describes the application of viral vectors in gene therapy, highlighting the complexities involved in ensuring efficient gene integration and expression.