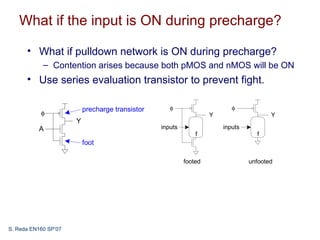
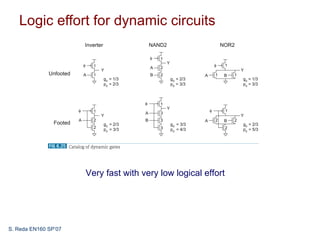
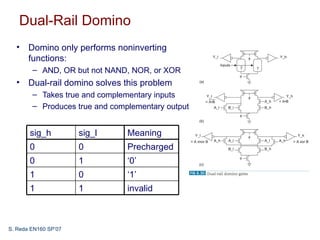
This document discusses dynamic combinational circuit design. Dynamic logic uses a clocked pMOS pullup and operates in two modes: precharge and evaluate. Dynamic circuits require monotonically rising inputs during evaluation. To address this, dynamic gates are followed by inverting static gates to form domino logic. Domino logic evaluates gates sequentially but precharges in parallel, making evaluation critical. Issues like leakage, charge sharing, and noise must also be addressed. Domino logic can provide faster speeds than static CMOS but has challenges to overcome.