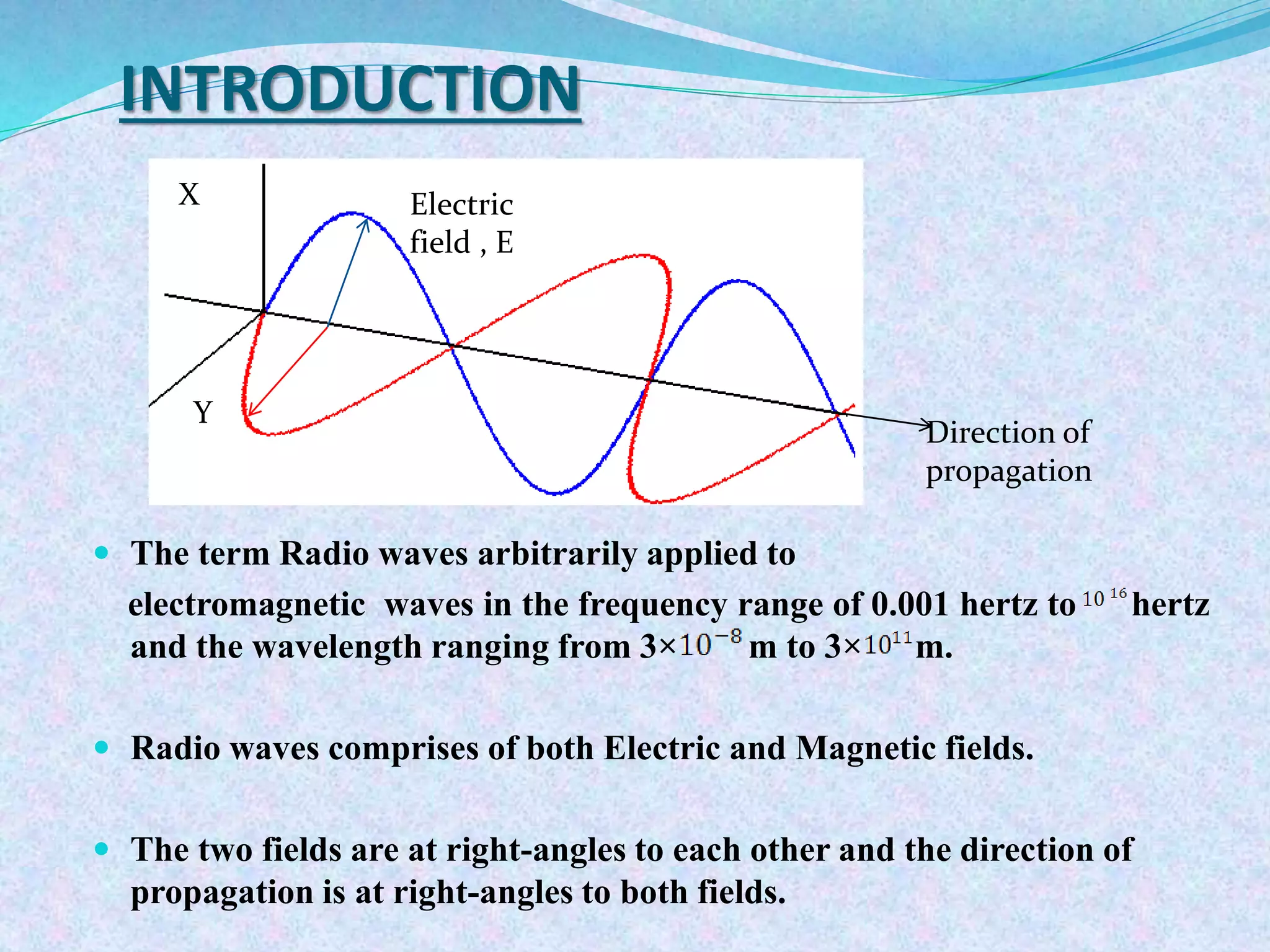
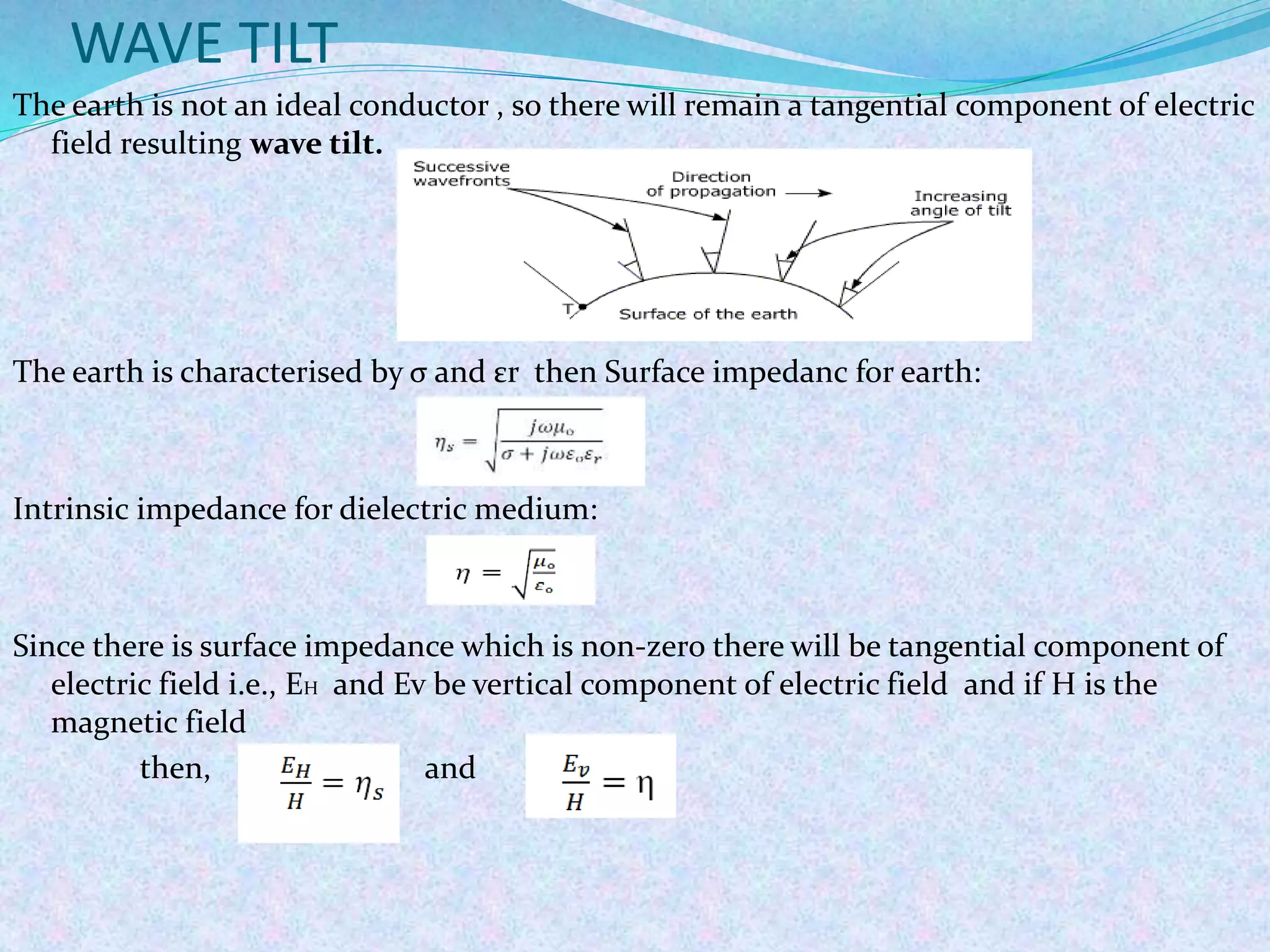
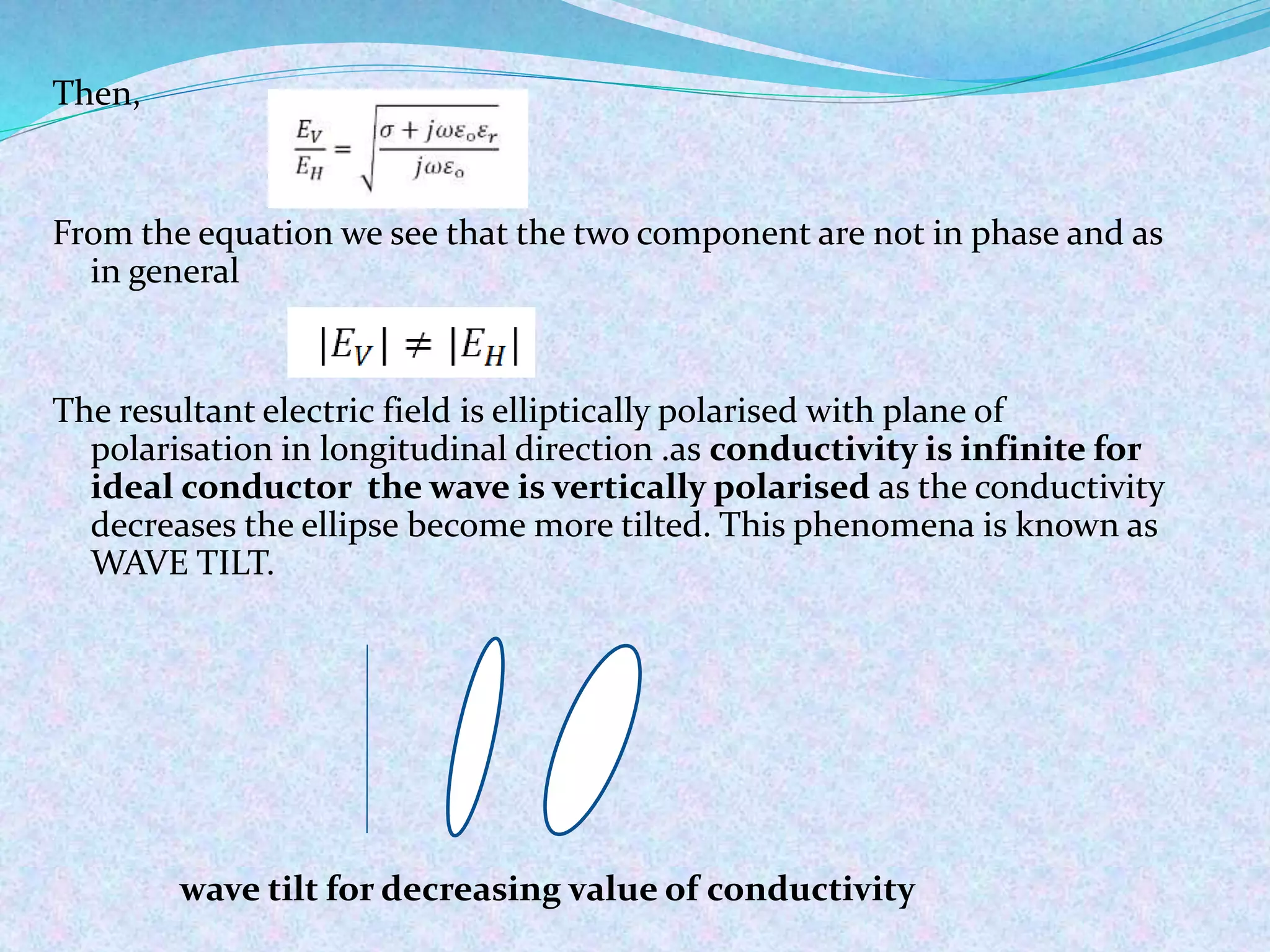
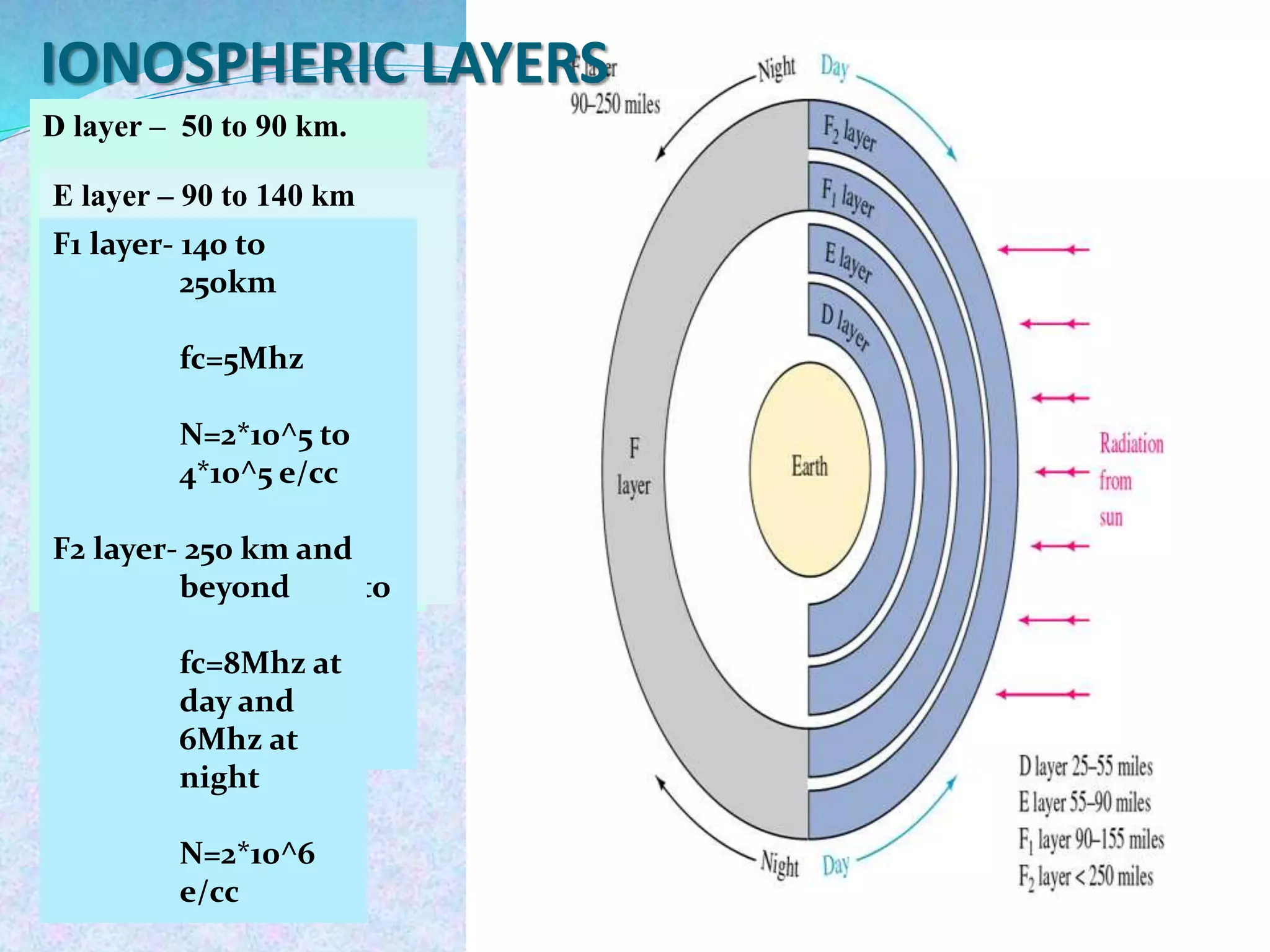
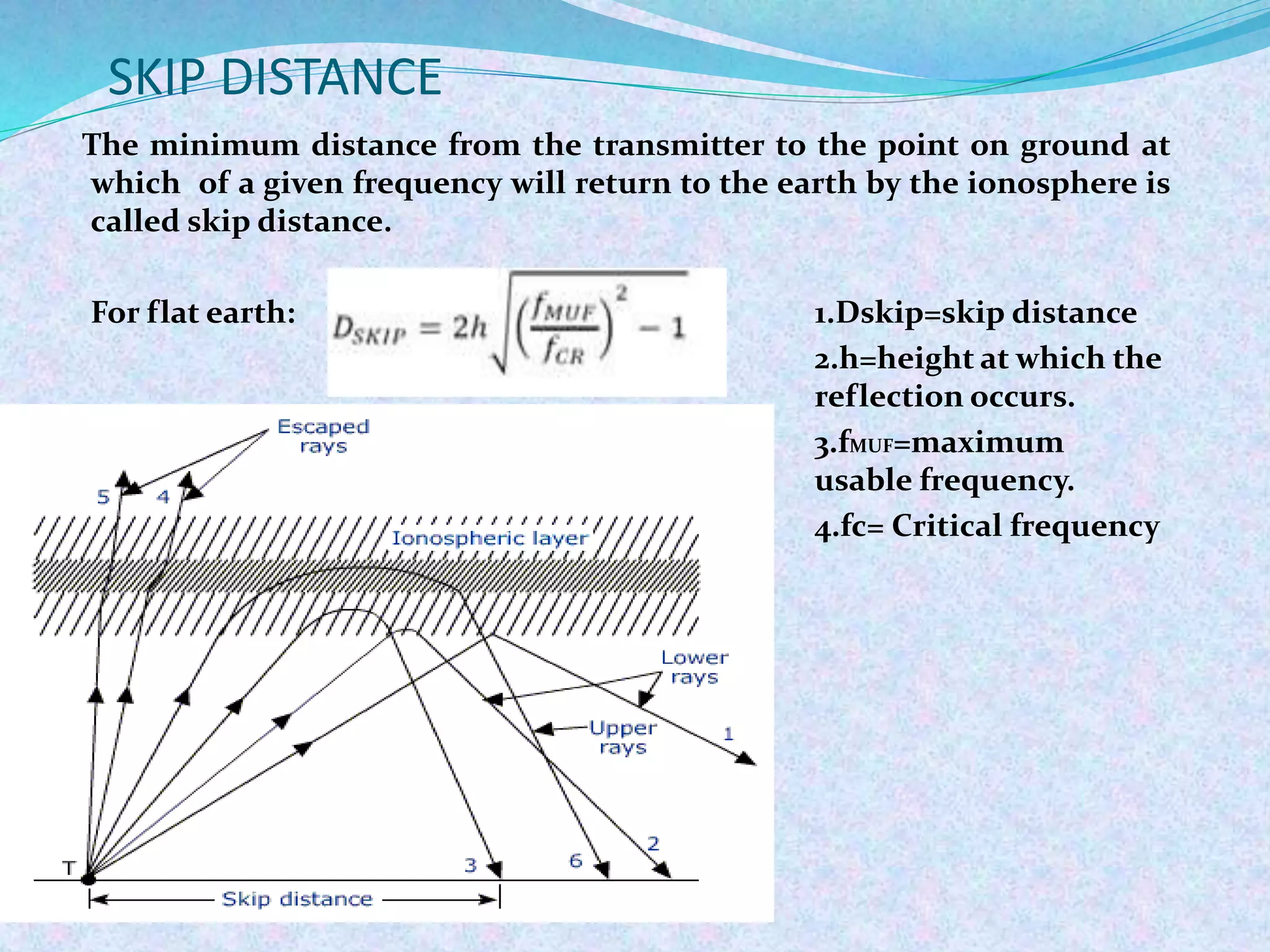
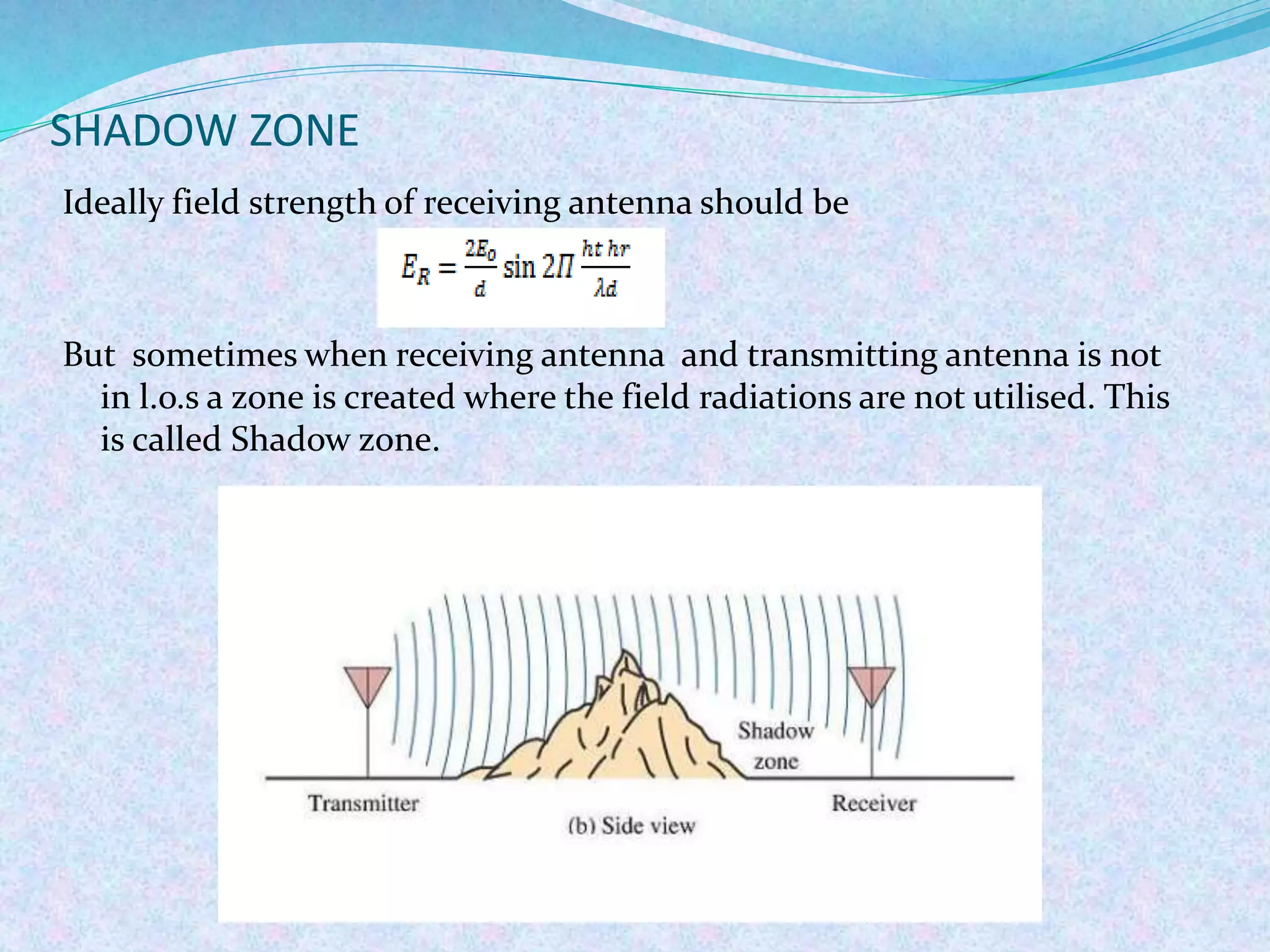
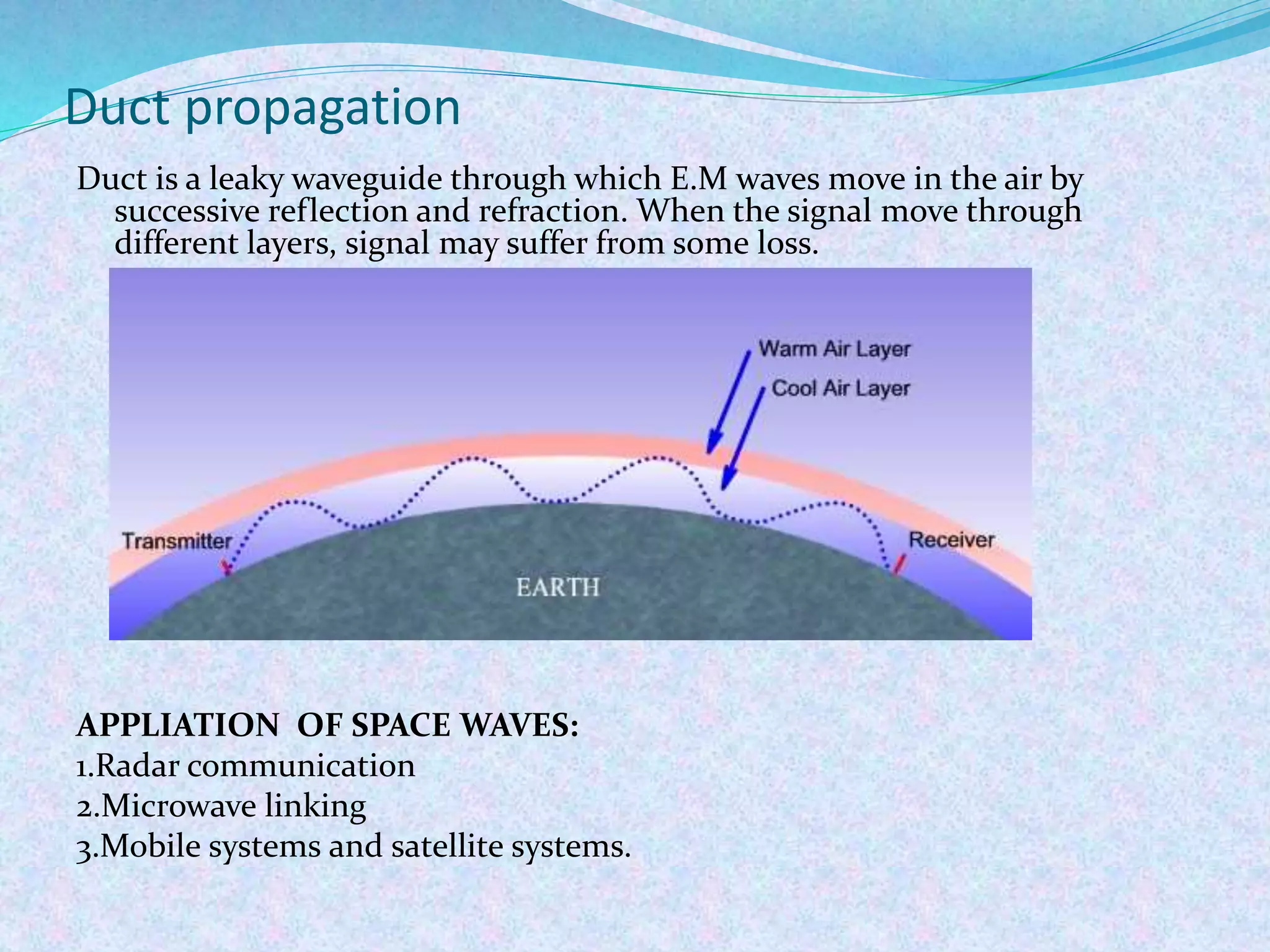
The document discusses radio wave propagation, including its classification based on frequency and different modes such as ground, sky, and space wave propagation. Each mode is defined along with its characteristics, applications, and the effects of environmental factors on propagation. The conclusion emphasizes the significance of radio waves in various communication systems, including mobile phones and broadcasting.