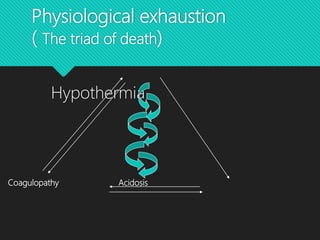
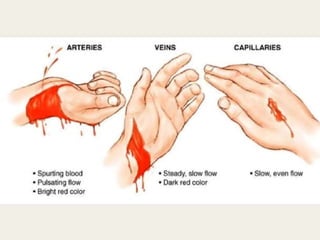
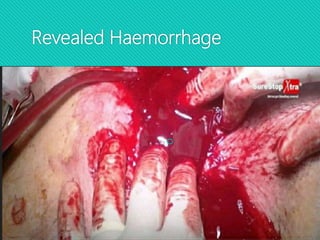
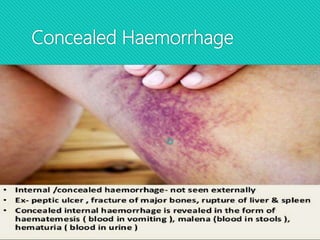
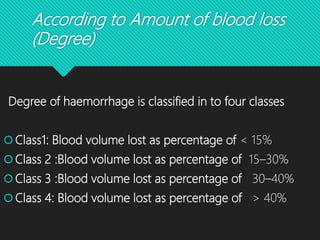
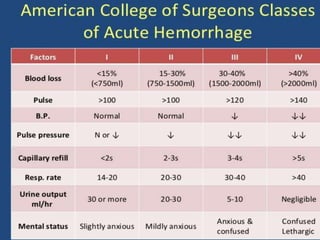
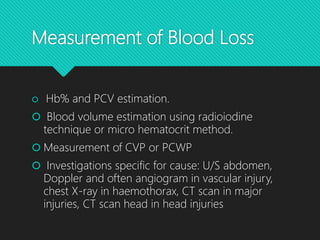
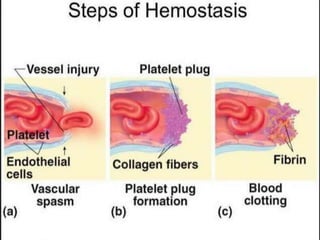
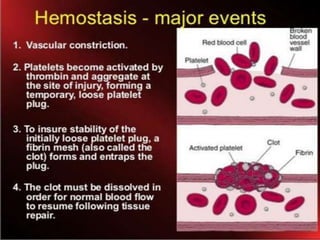
This document discusses haemorrhage or bleeding from blood vessels. It defines haemorrhage and describes the pathophysiology where bleeding leads to hypovolaemic shock and complications like acidosis. It then classifies haemorrhage based on anatomical source, timing, visibility, duration and amount of blood loss. Clinical features and investigations for haemorrhage are provided. Management of haemorrhage focuses on arresting bleeding through pressure, packing and procedures before restoring blood volume.