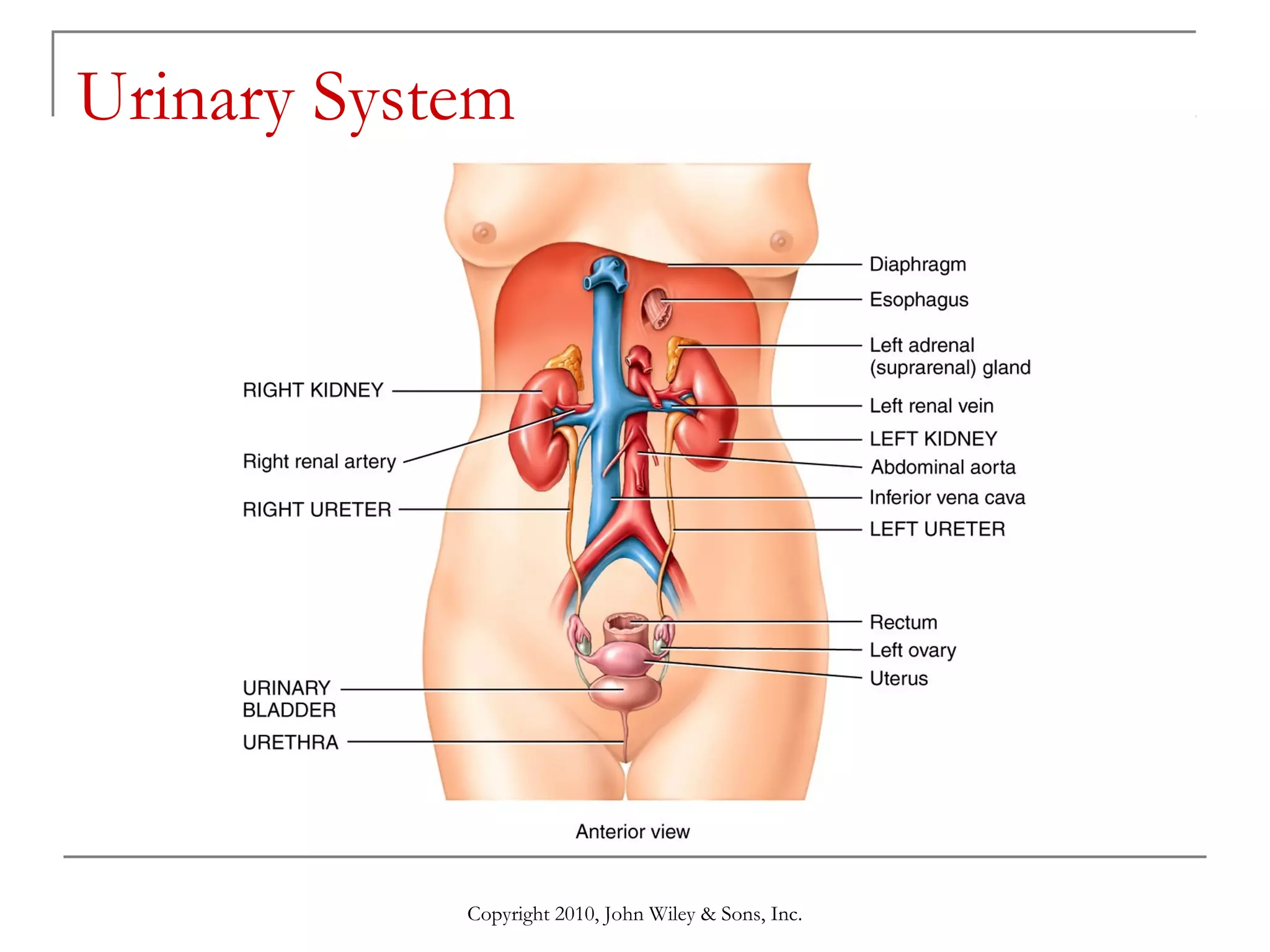
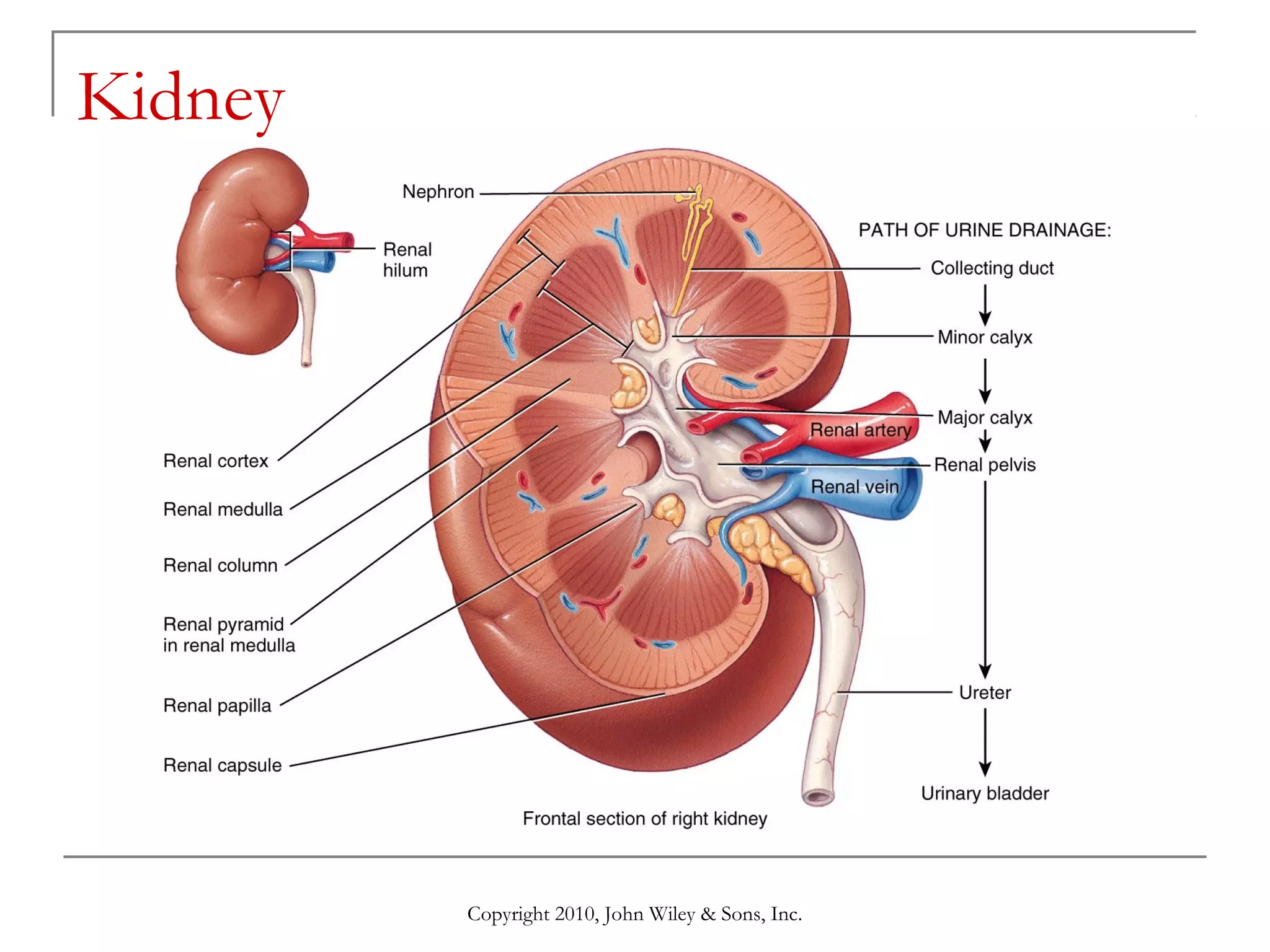
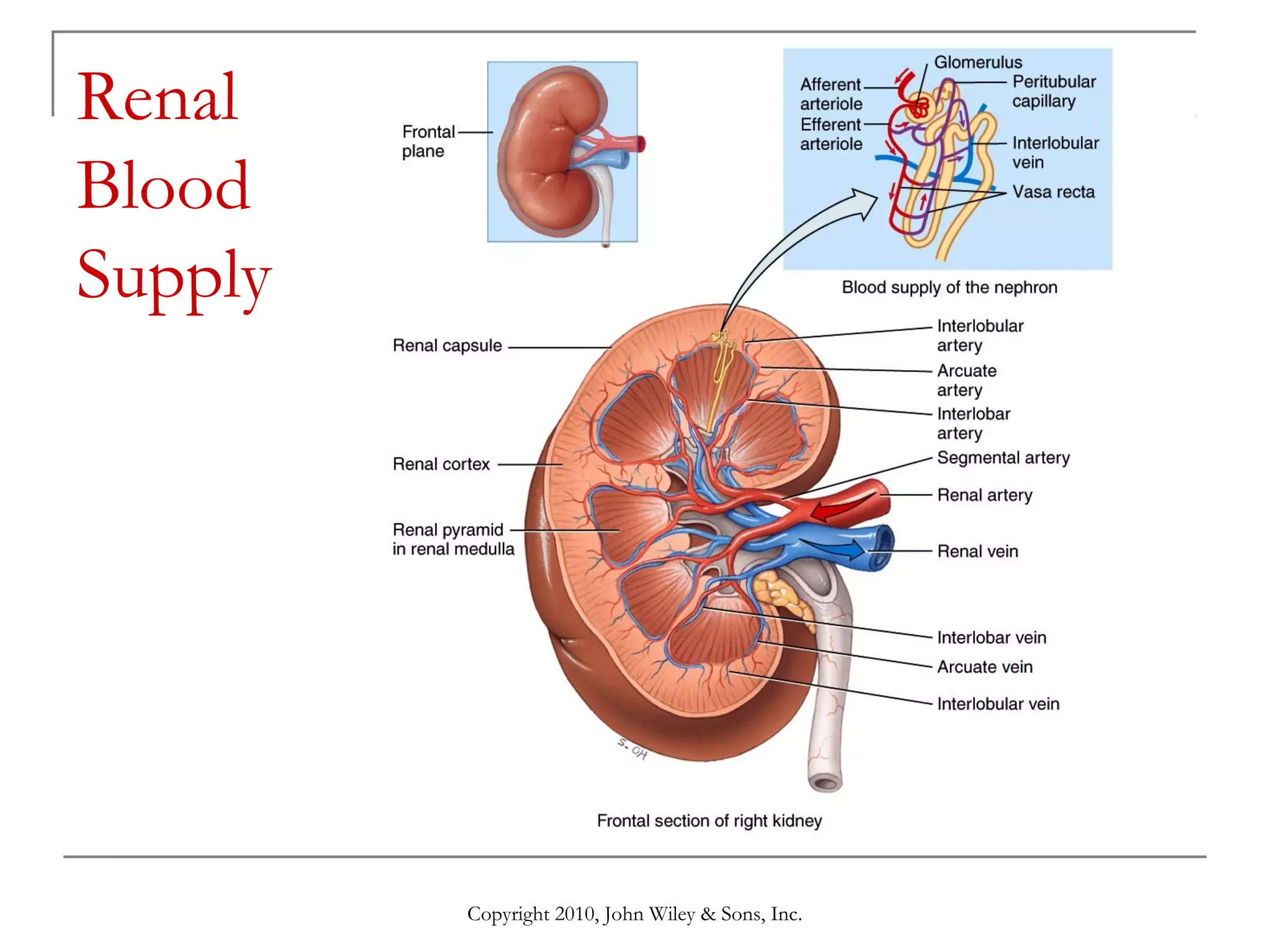
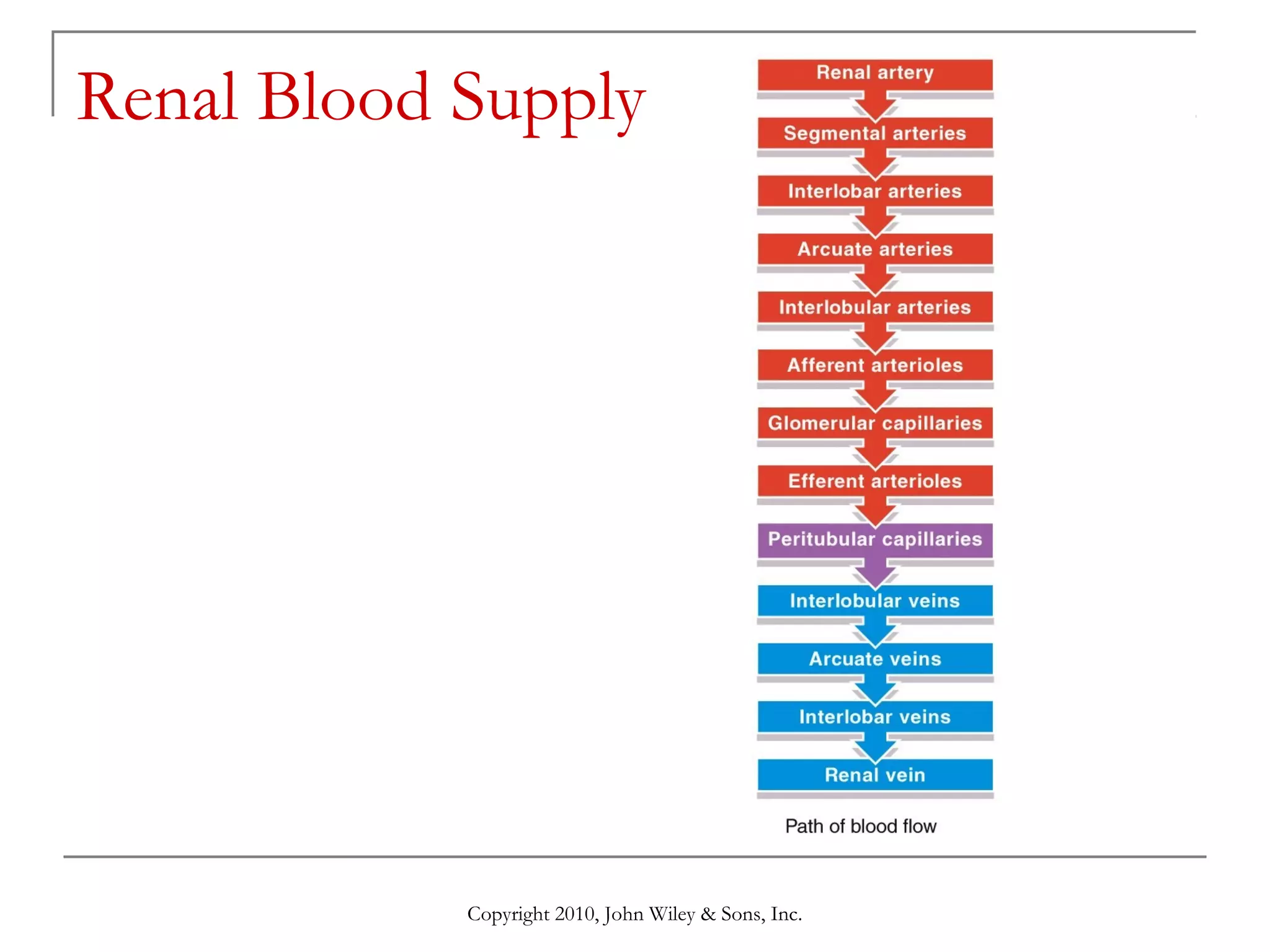
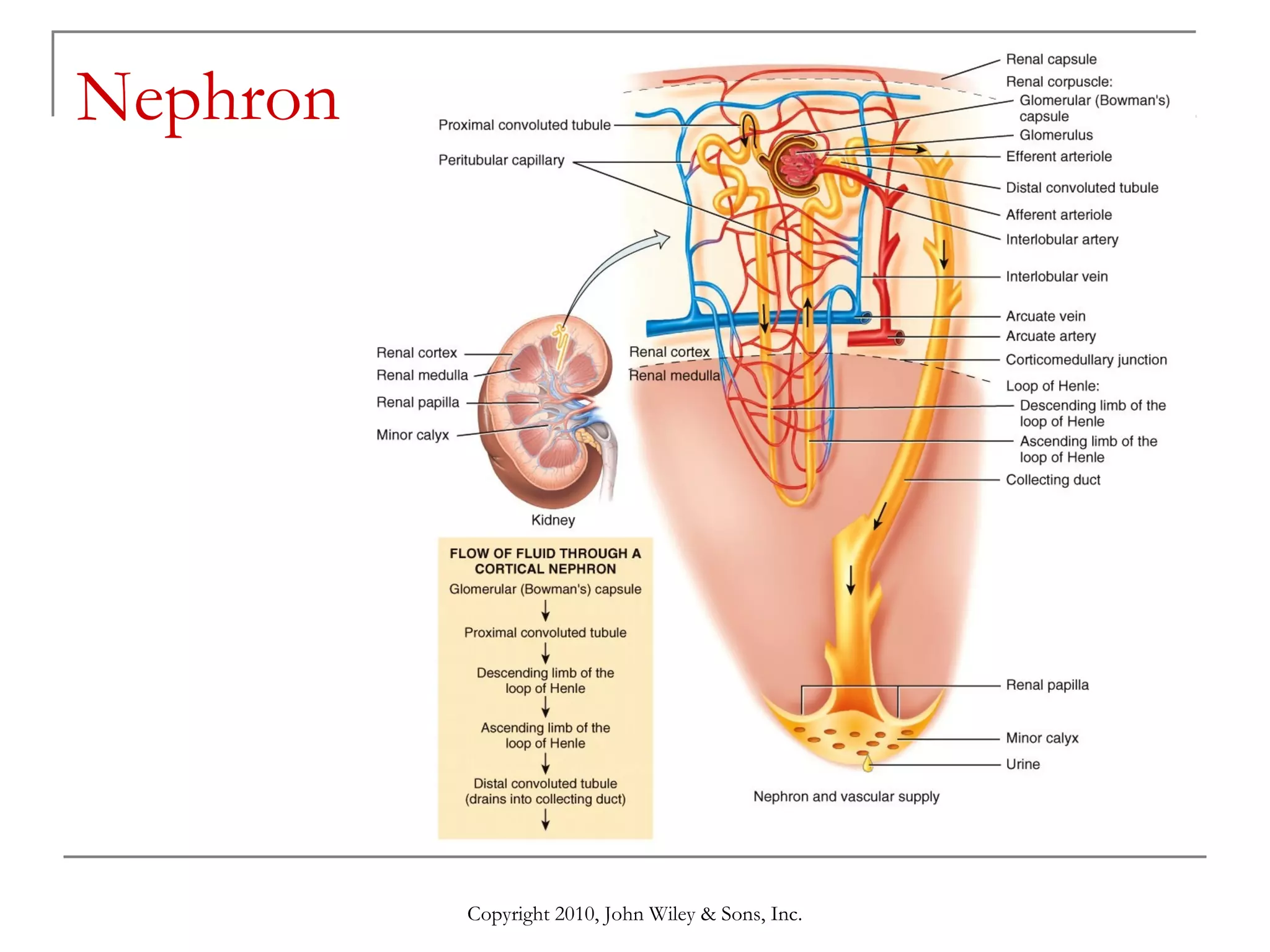
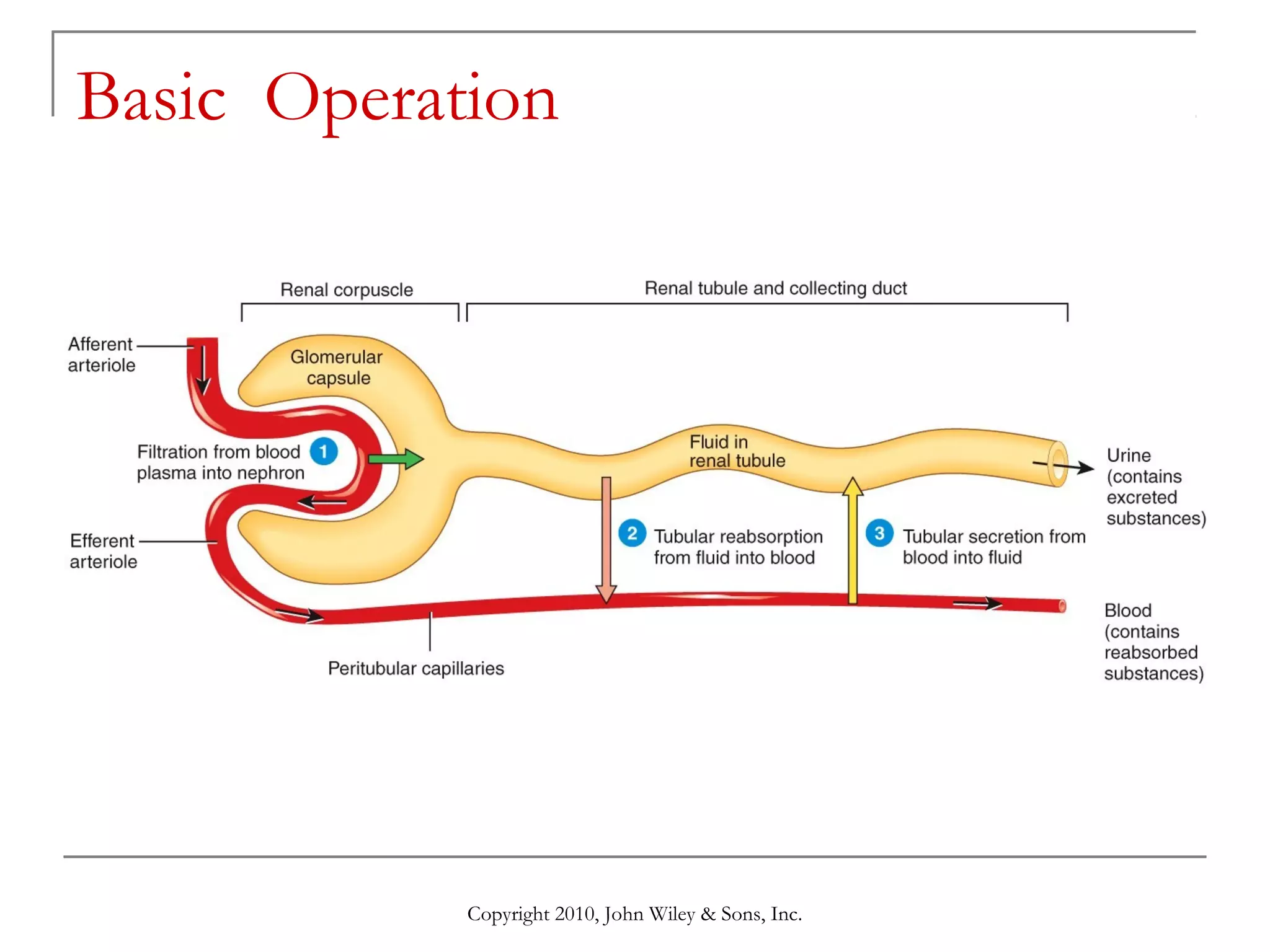
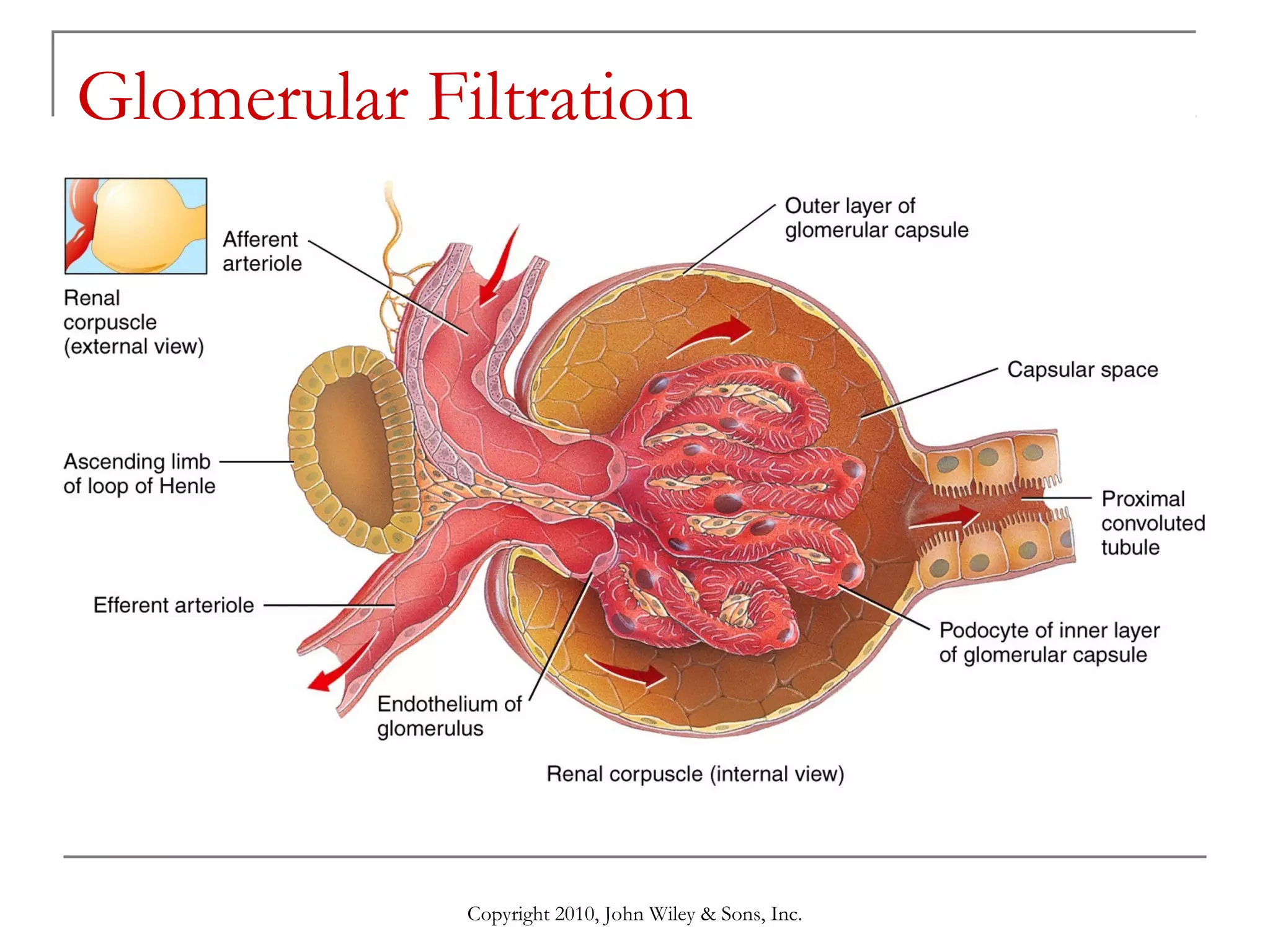
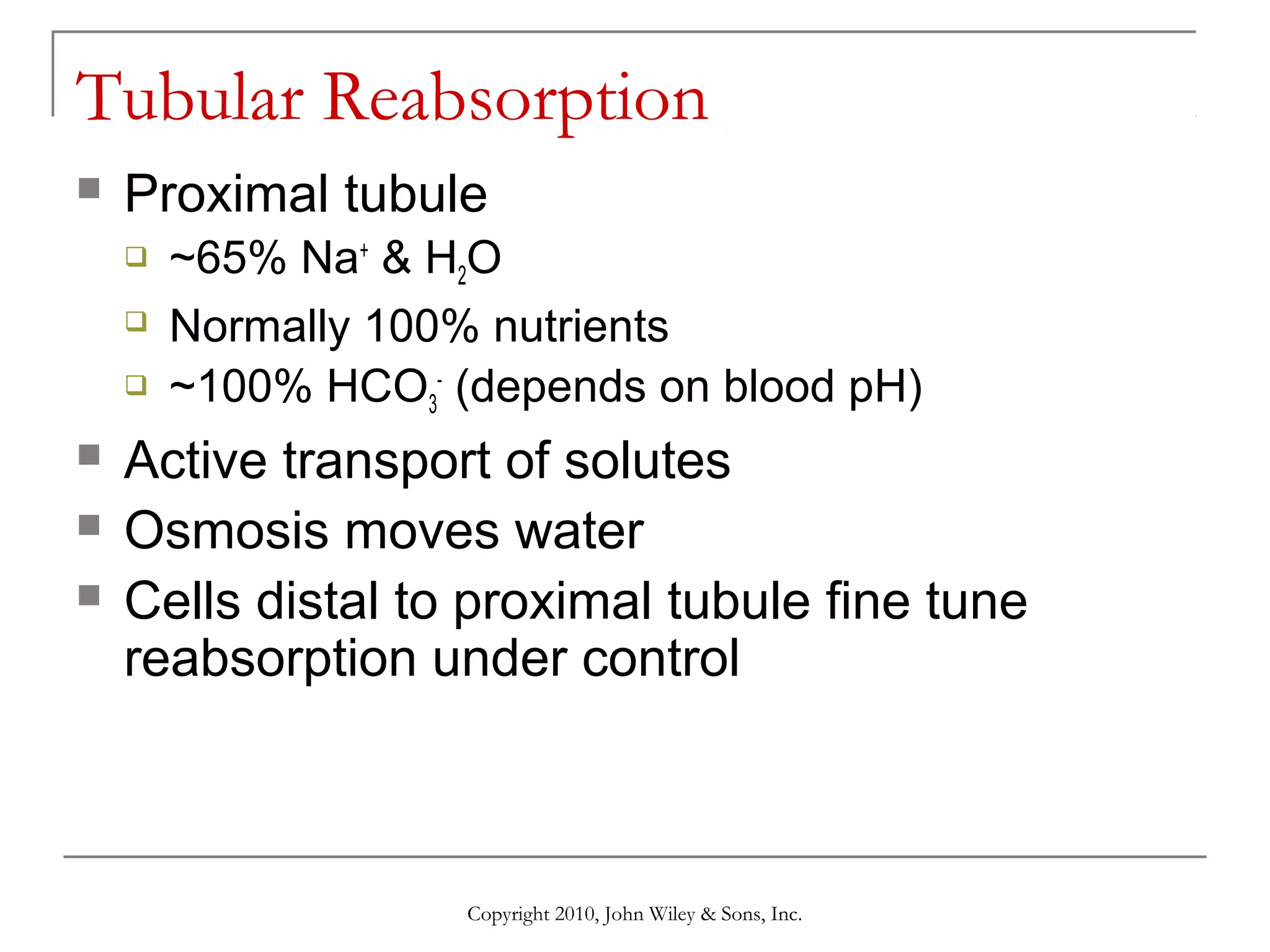
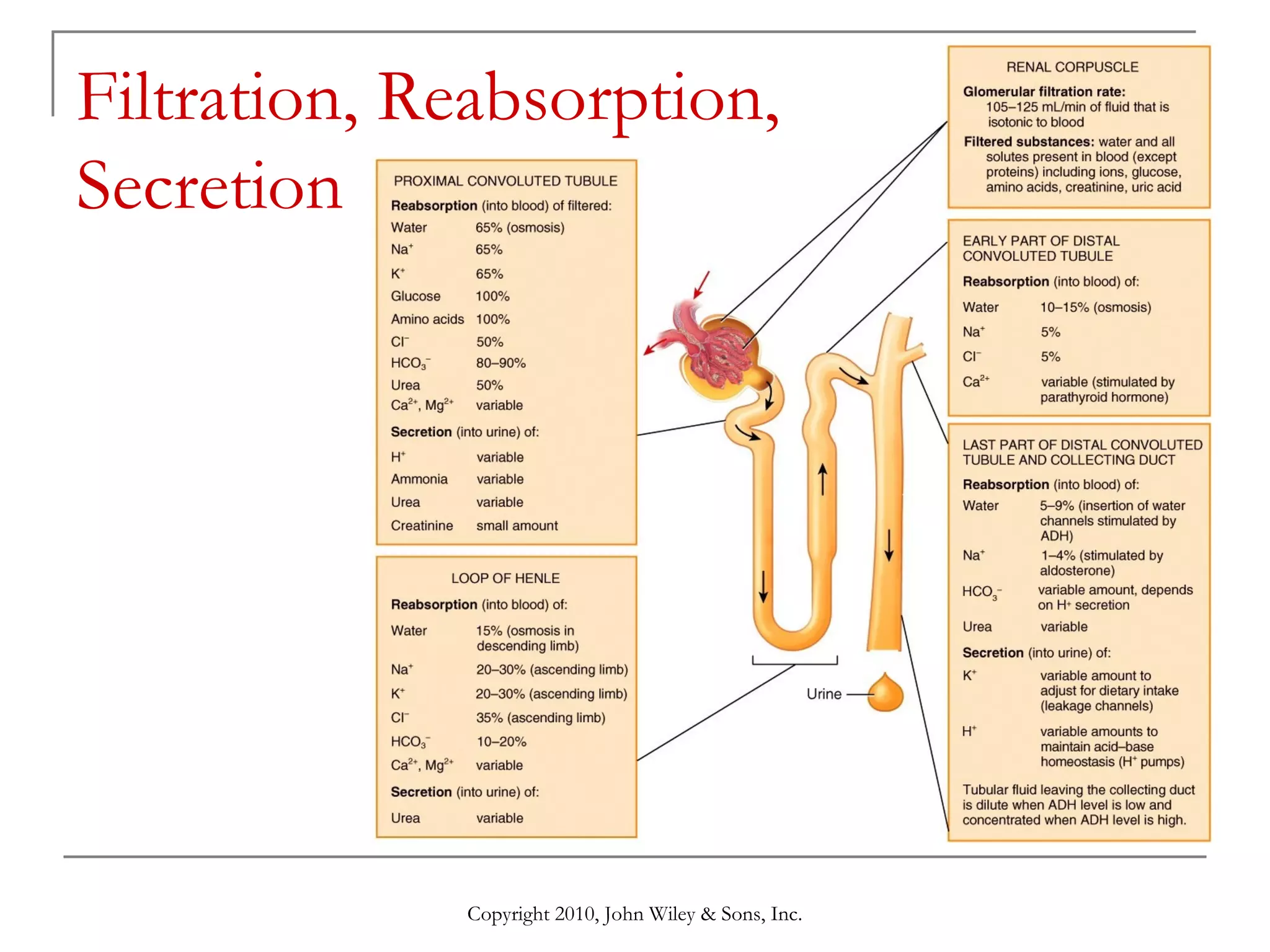
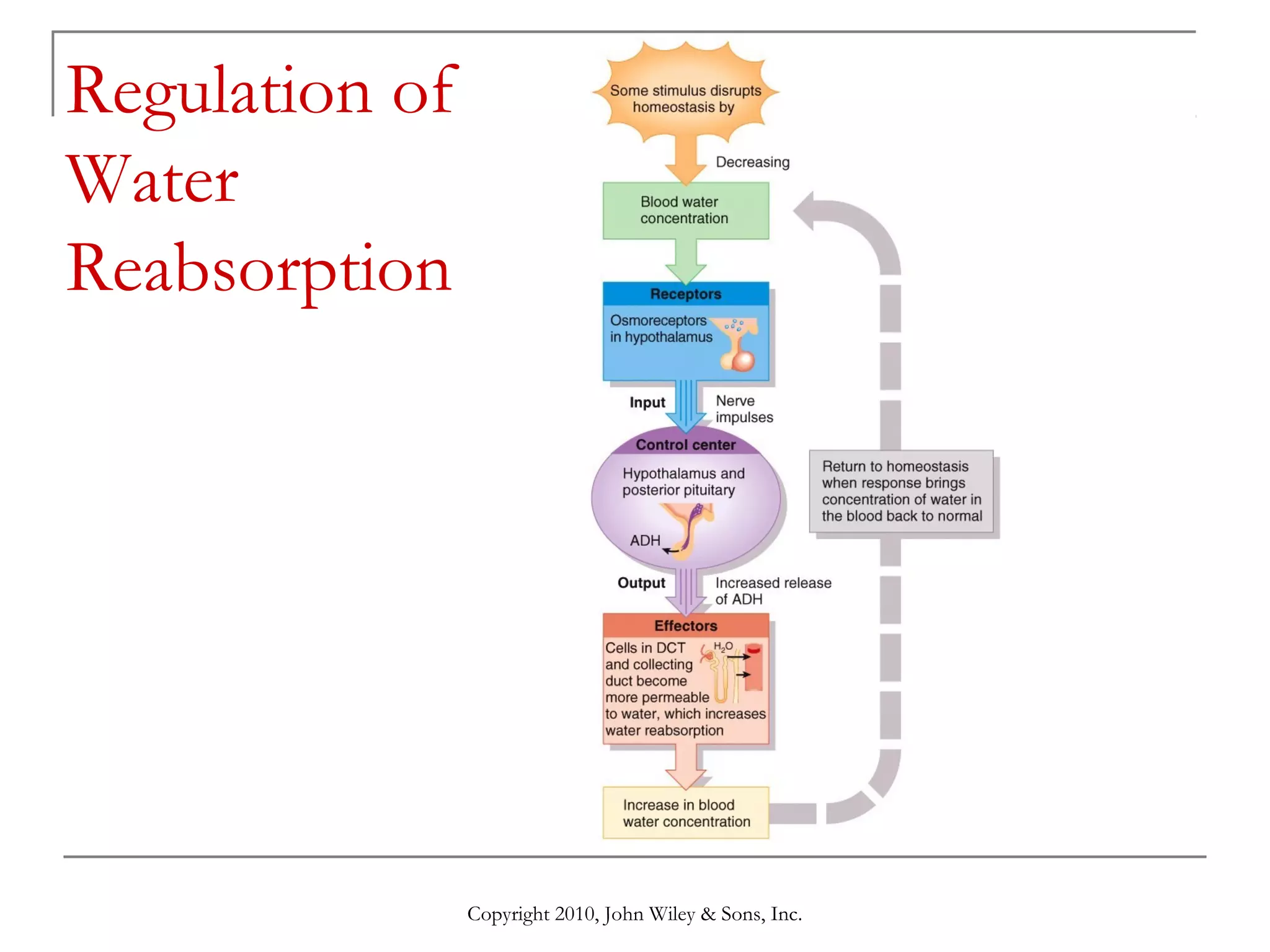
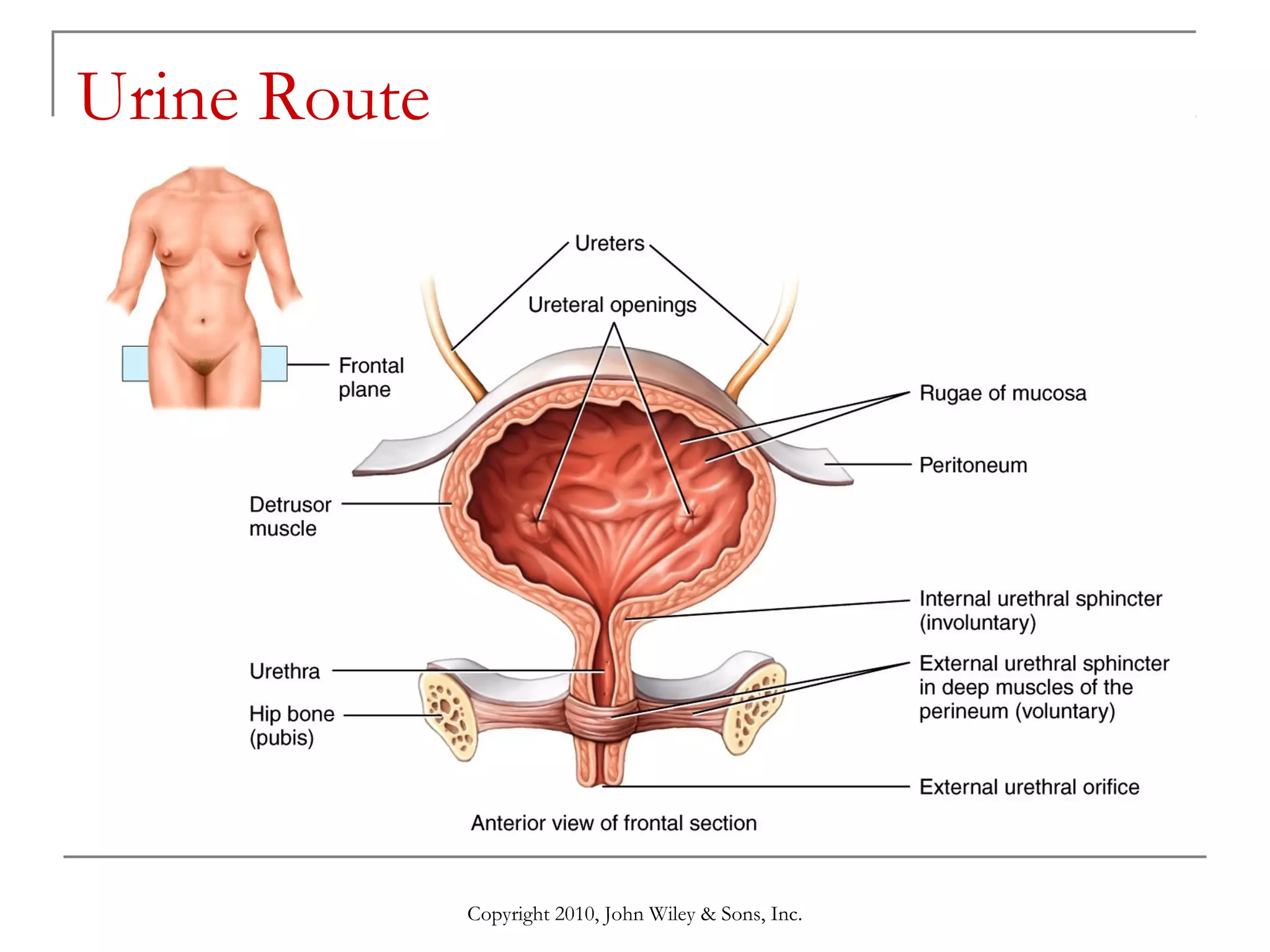
This document summarizes key aspects of the urinary system including the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. It describes the structures and functions of the nephron, including glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and secretion. Hormonal regulation of the urinary system by substances like angiotensin II, aldosterone and ADH is also covered. The document concludes with sections on the composition of urine and age-related changes to the urinary system.