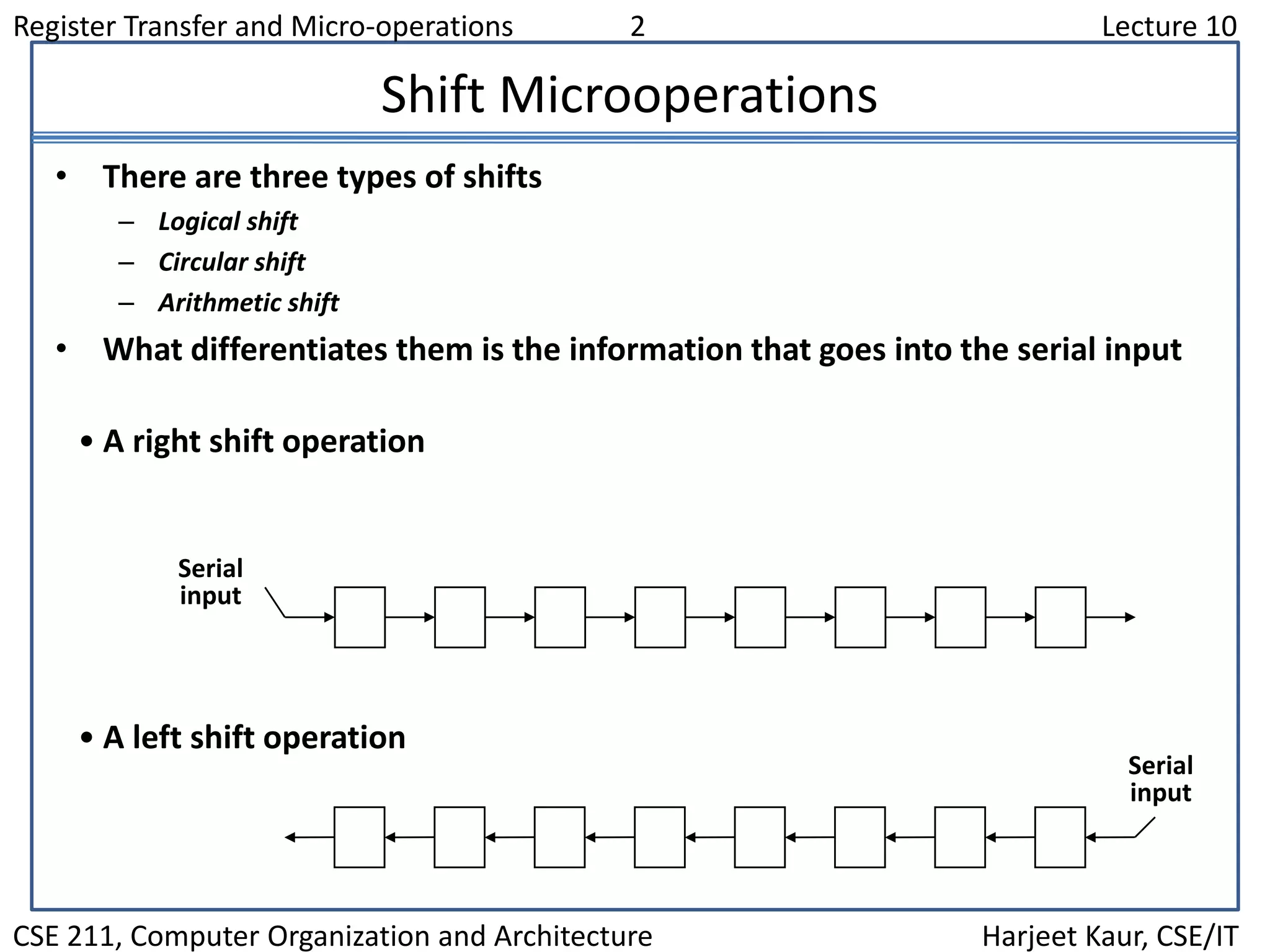
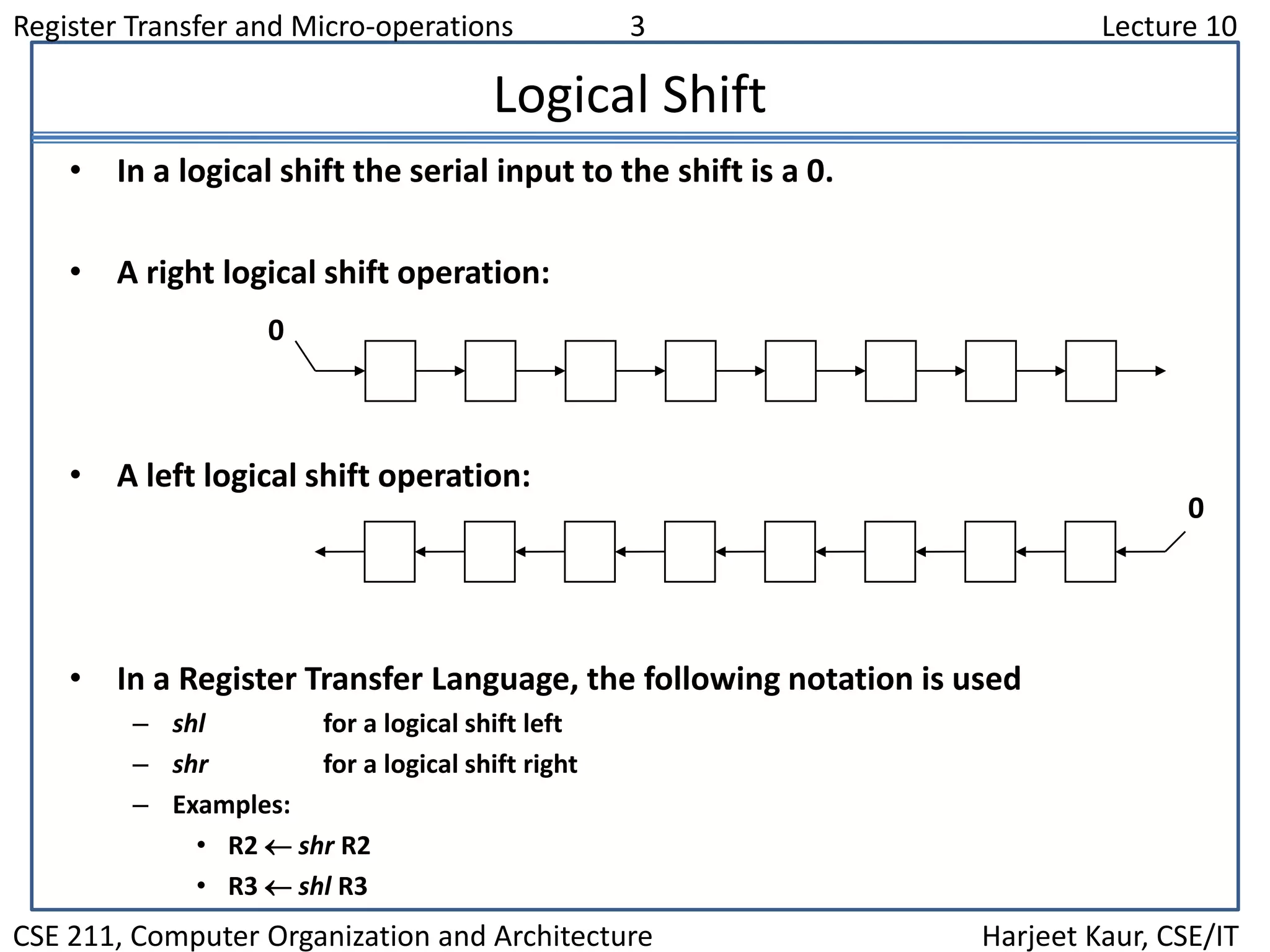
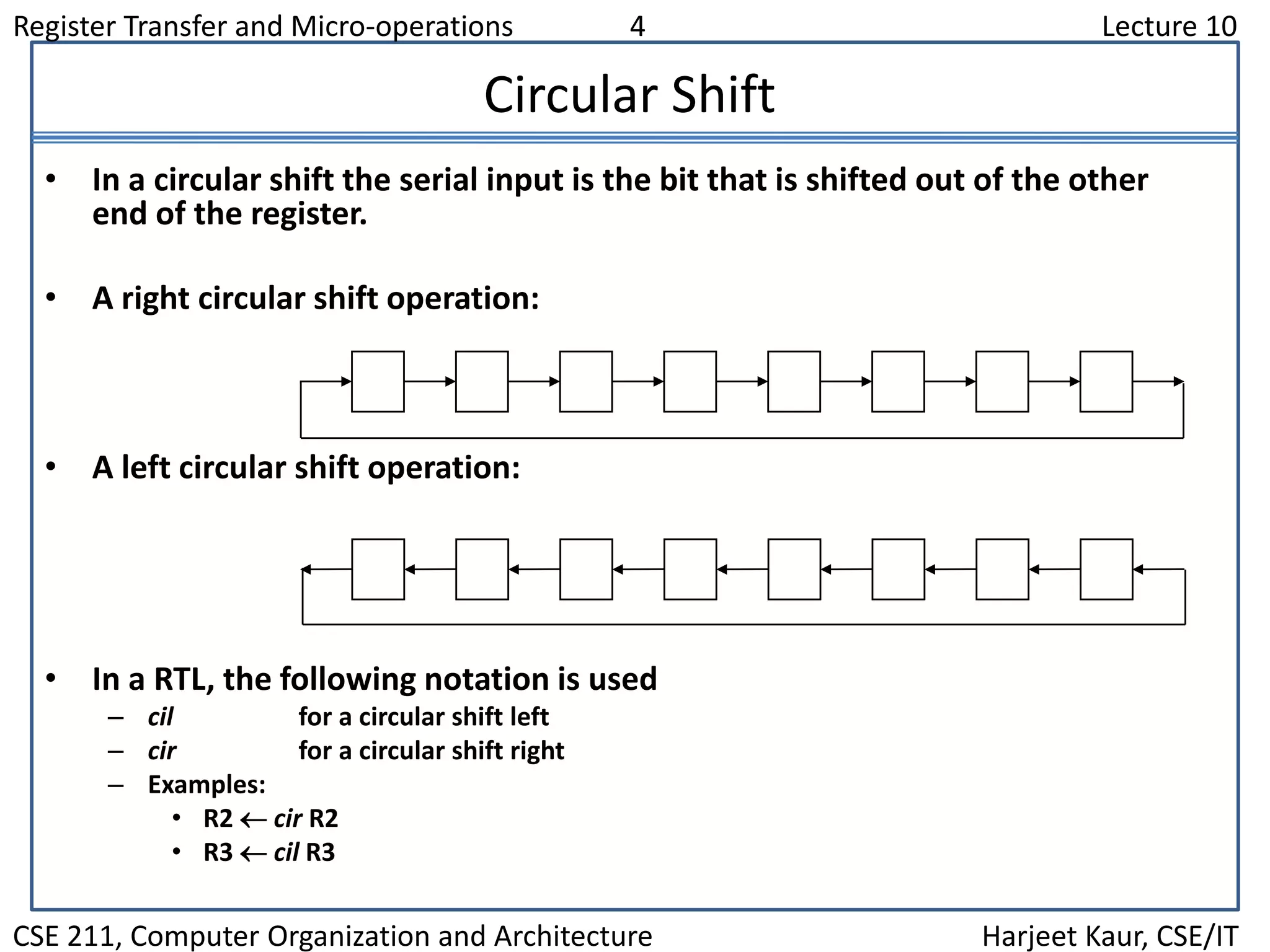
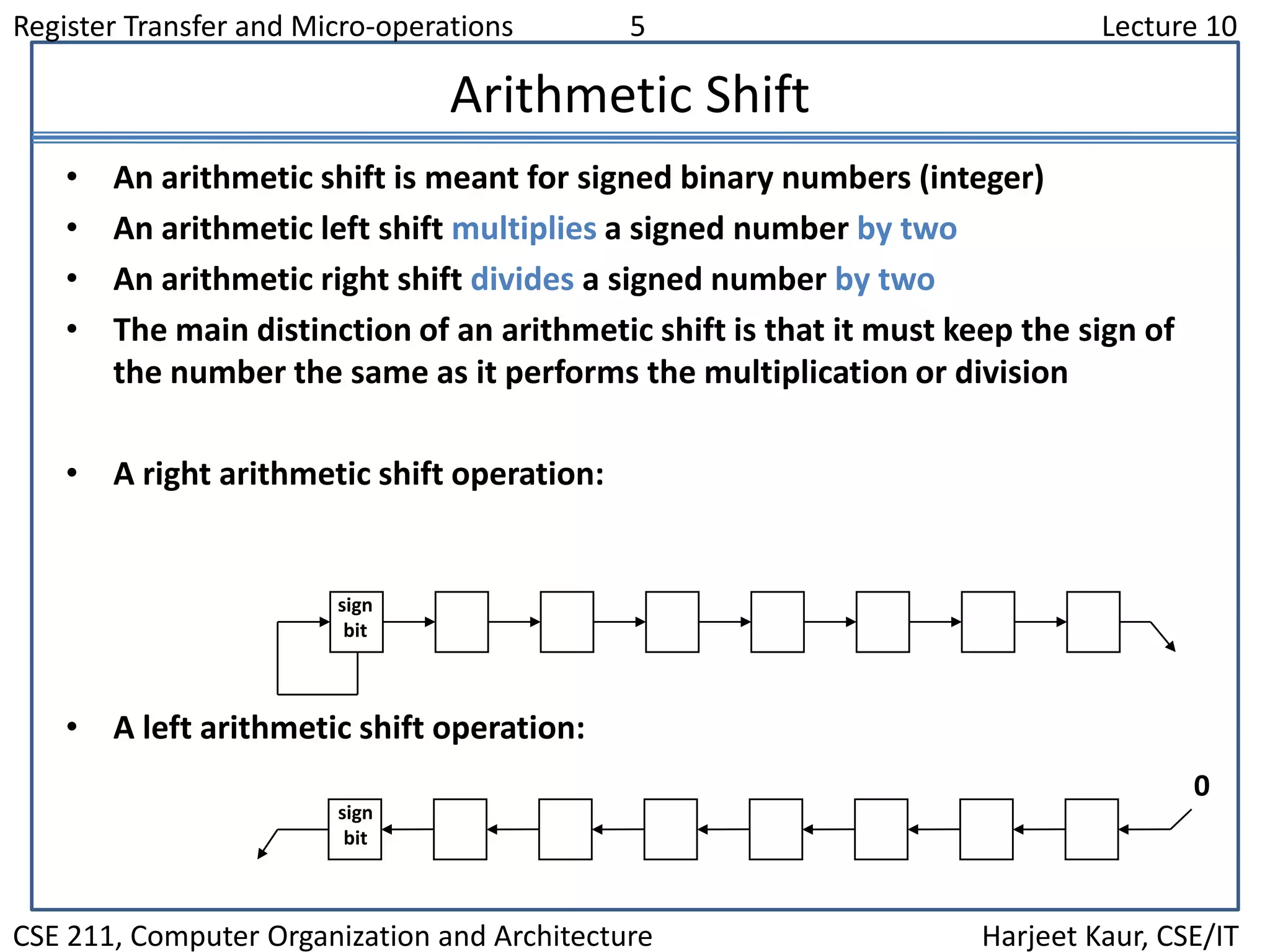
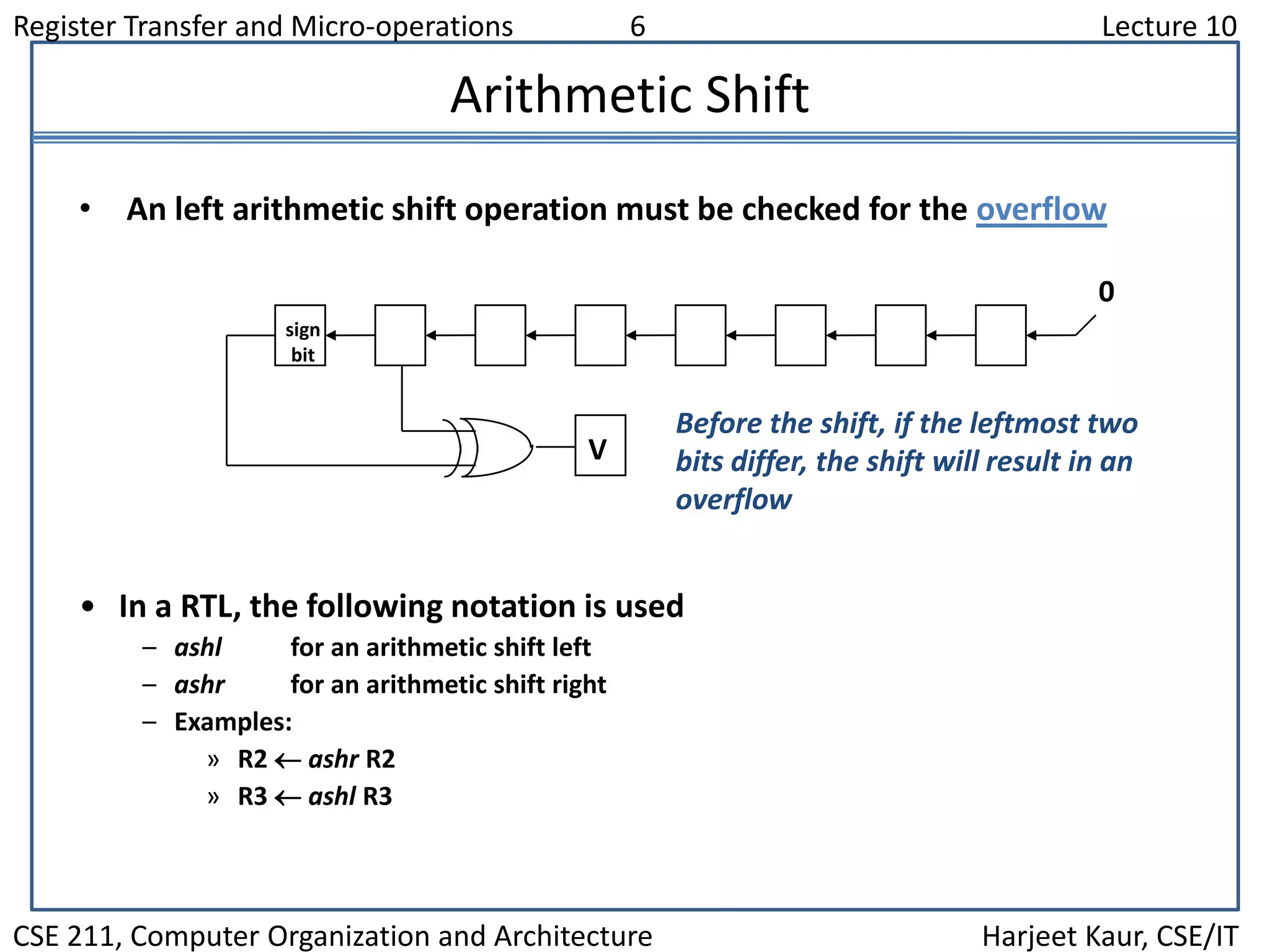
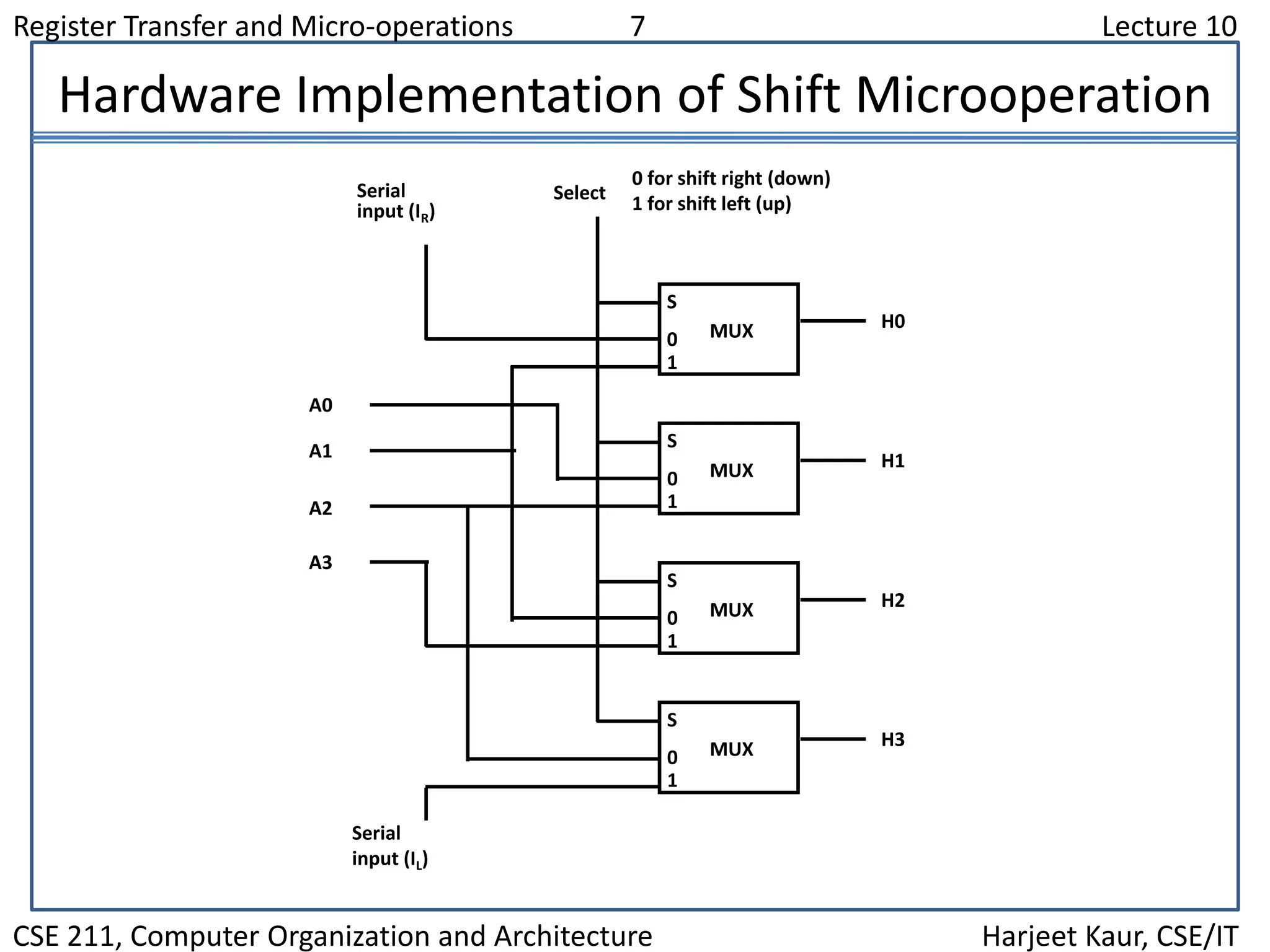
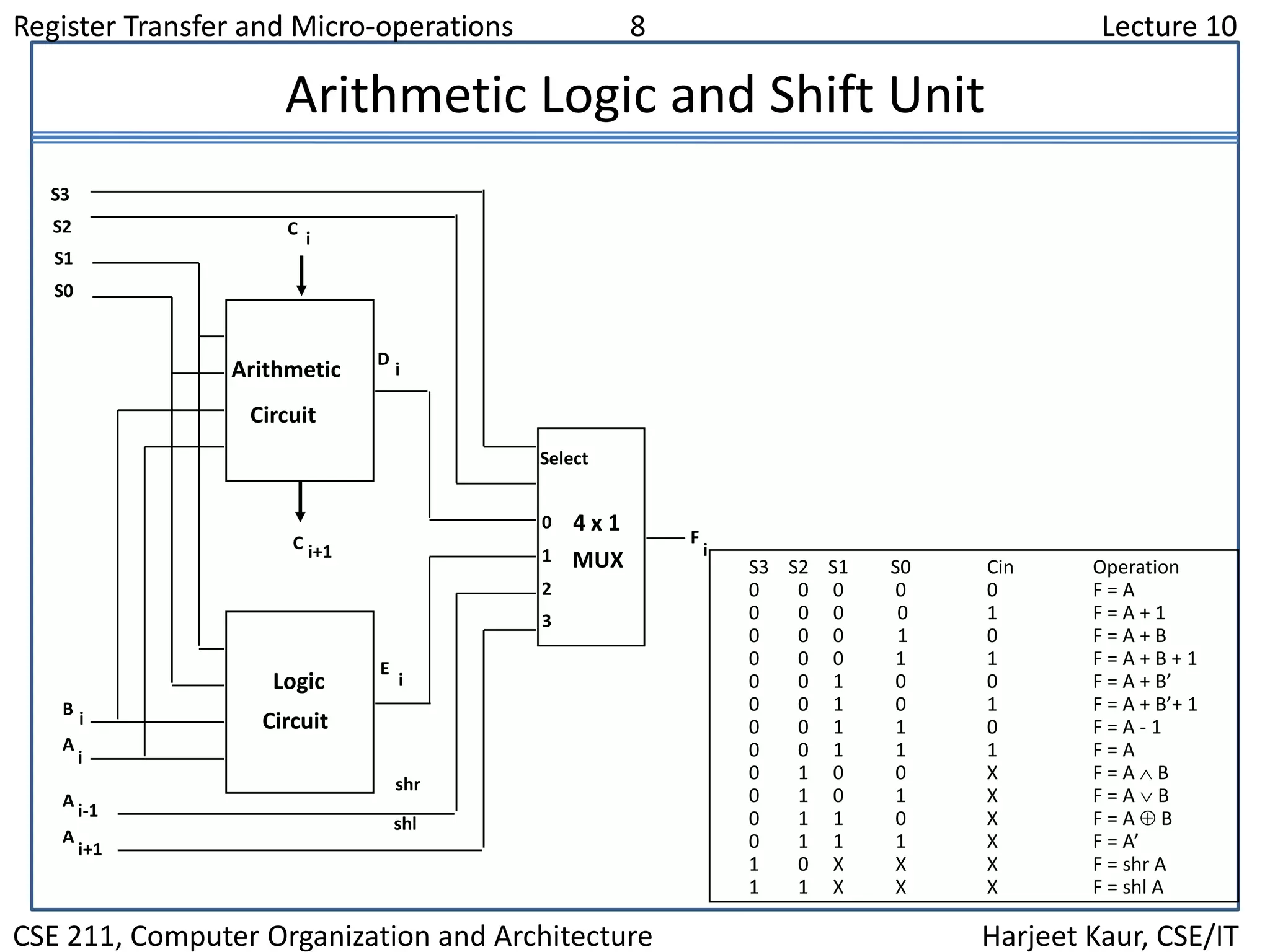
This document discusses different types of shift microoperations in a computer's CPU. It describes logical shifts, circular shifts, and arithmetic shifts. Logical shifts input a 0 into the serial register. Circular shifts input the bit shifted out of the other end. Arithmetic shifts preserve a number's sign during multiplication or division. The hardware implements shifts using multiplexers to select serial input and shift direction. An arithmetic logic shift unit performs different operations including shifts using control signals to select the operation.