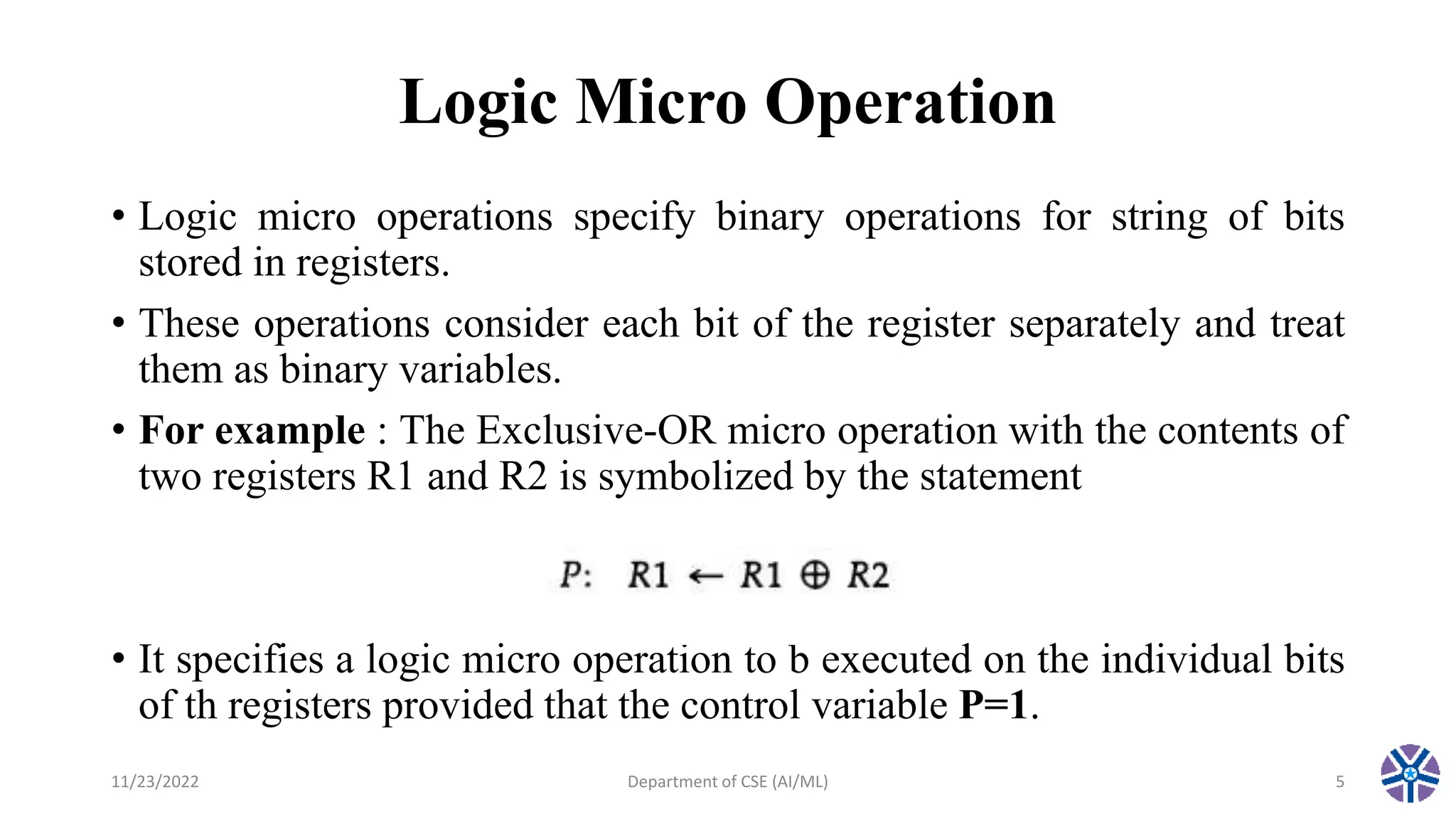
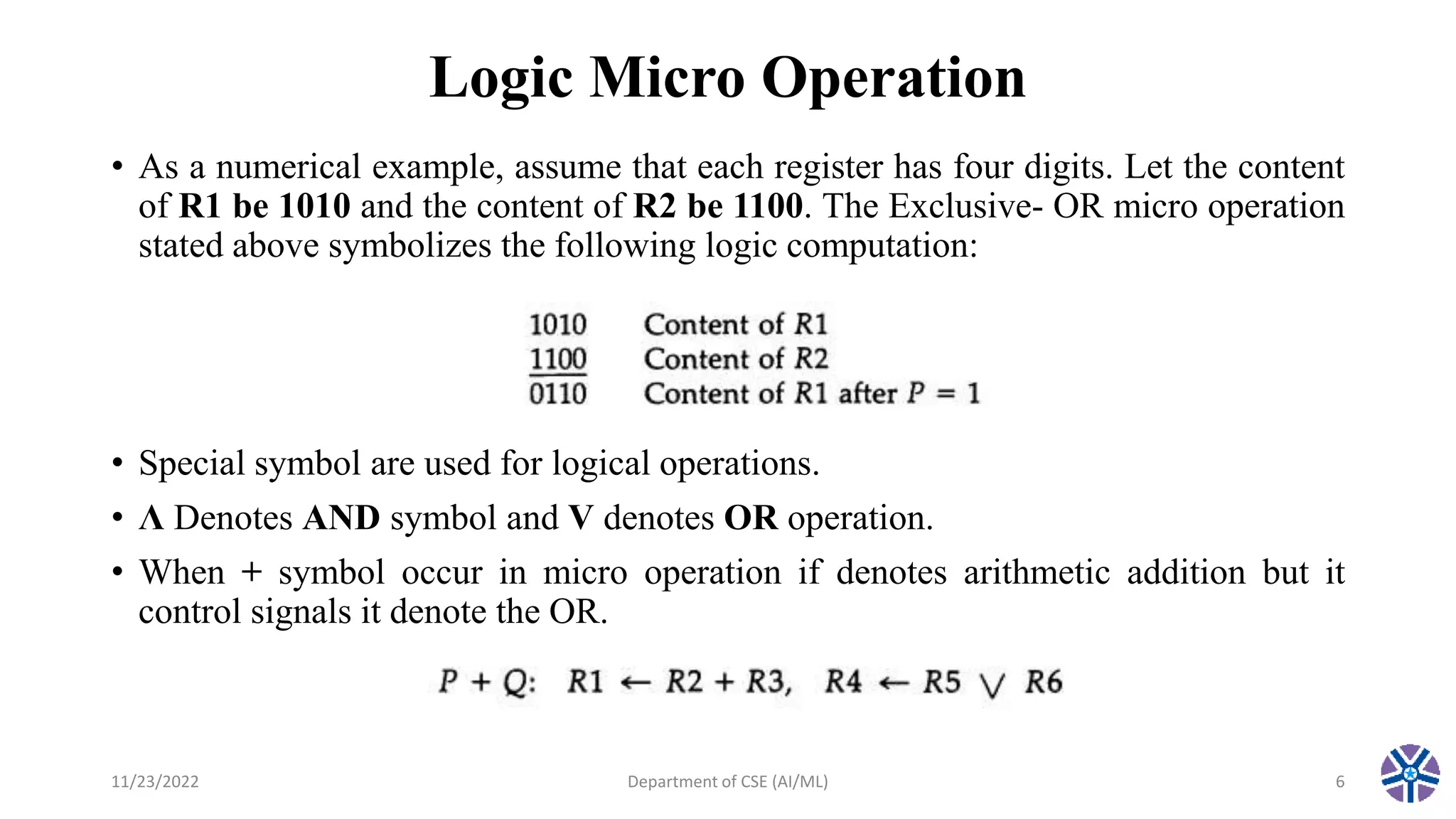
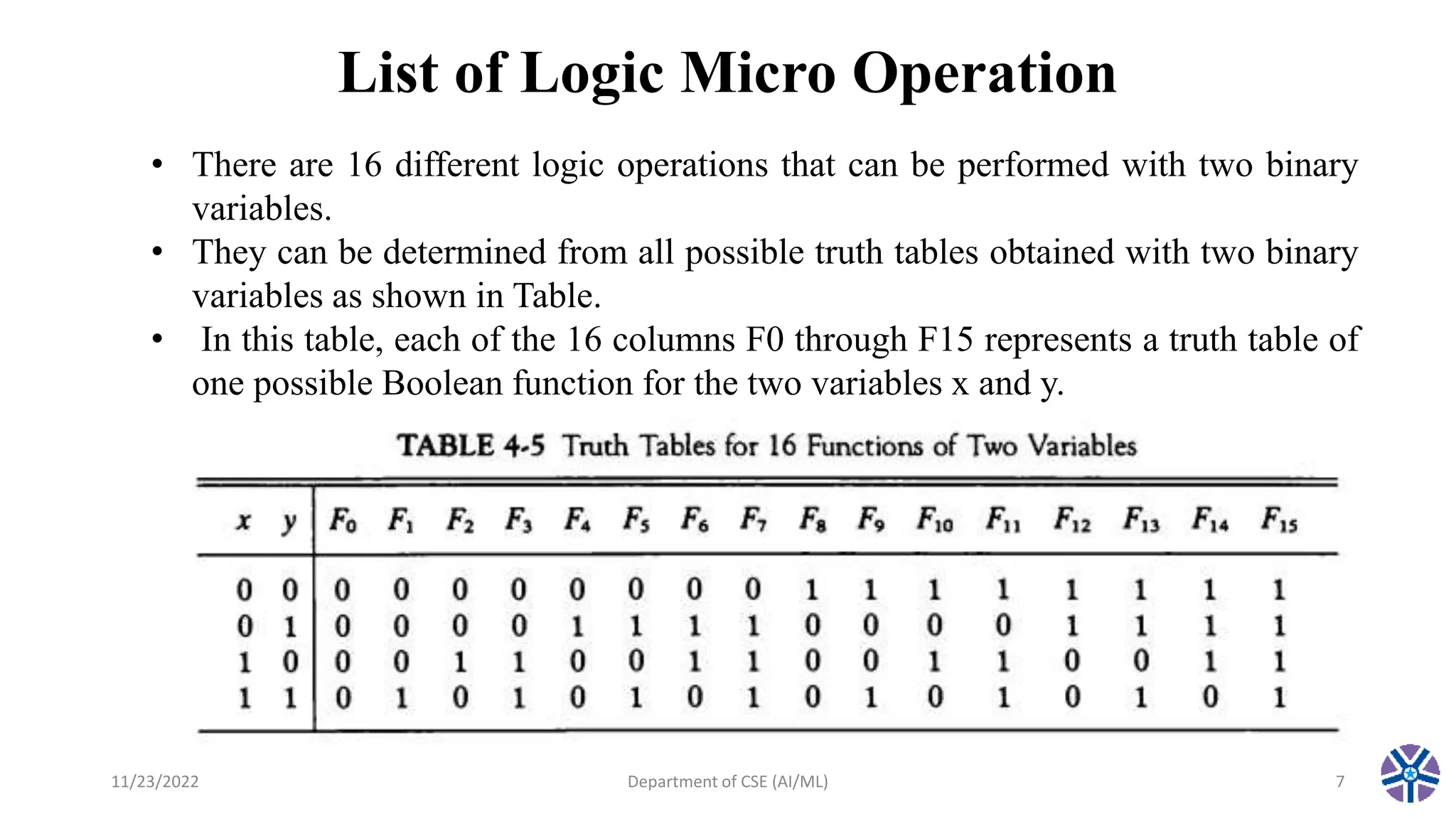
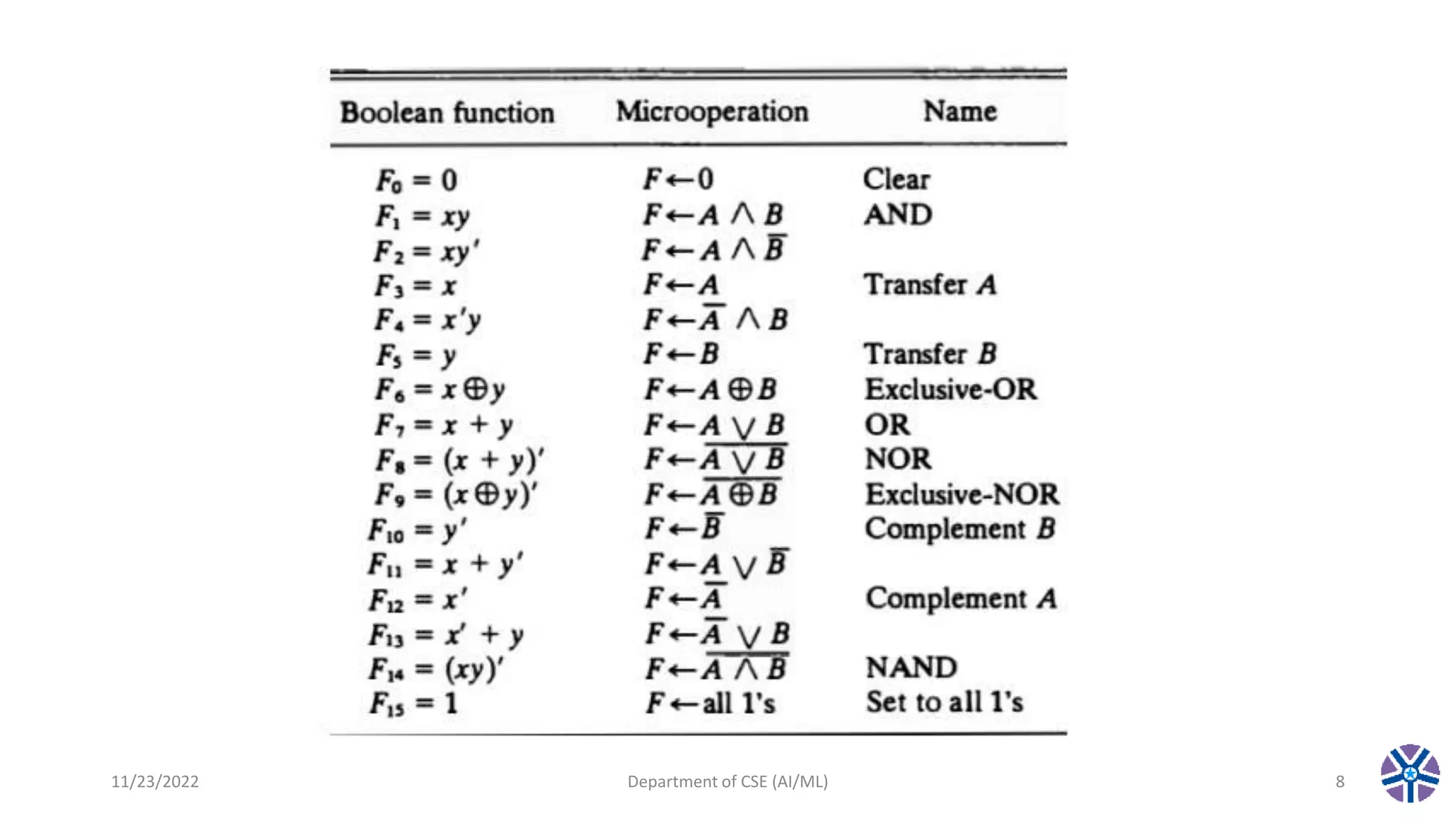
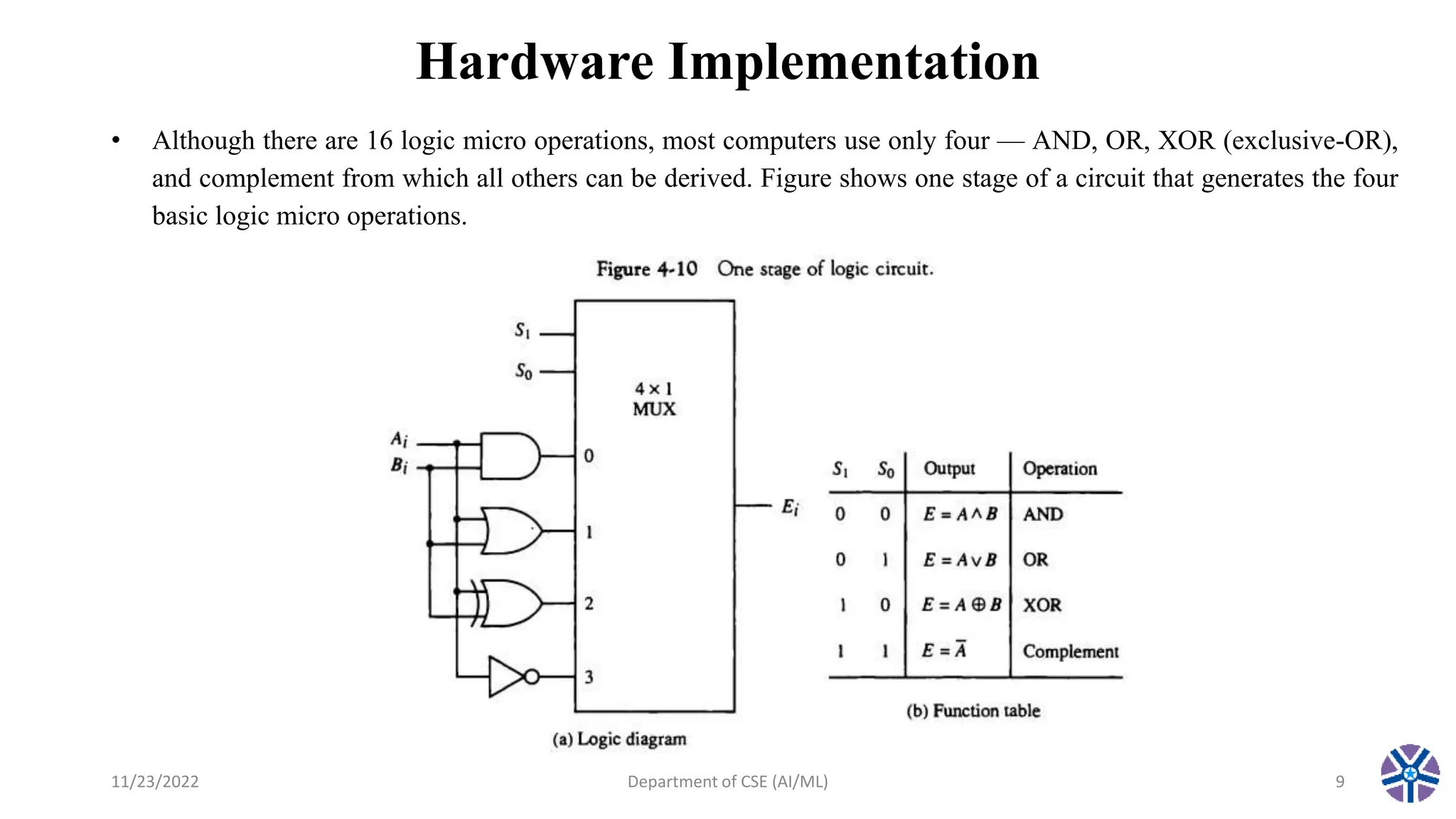
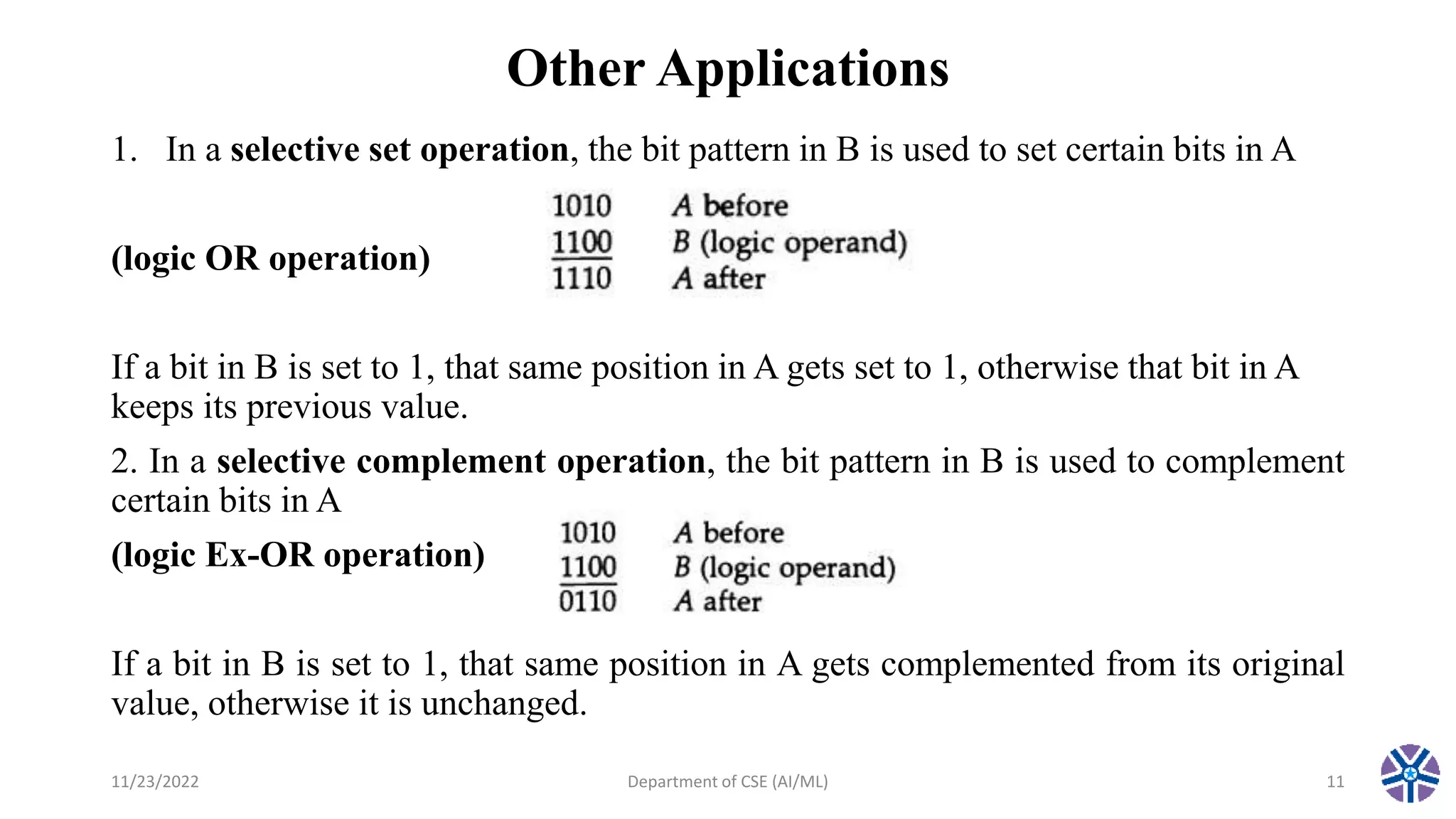
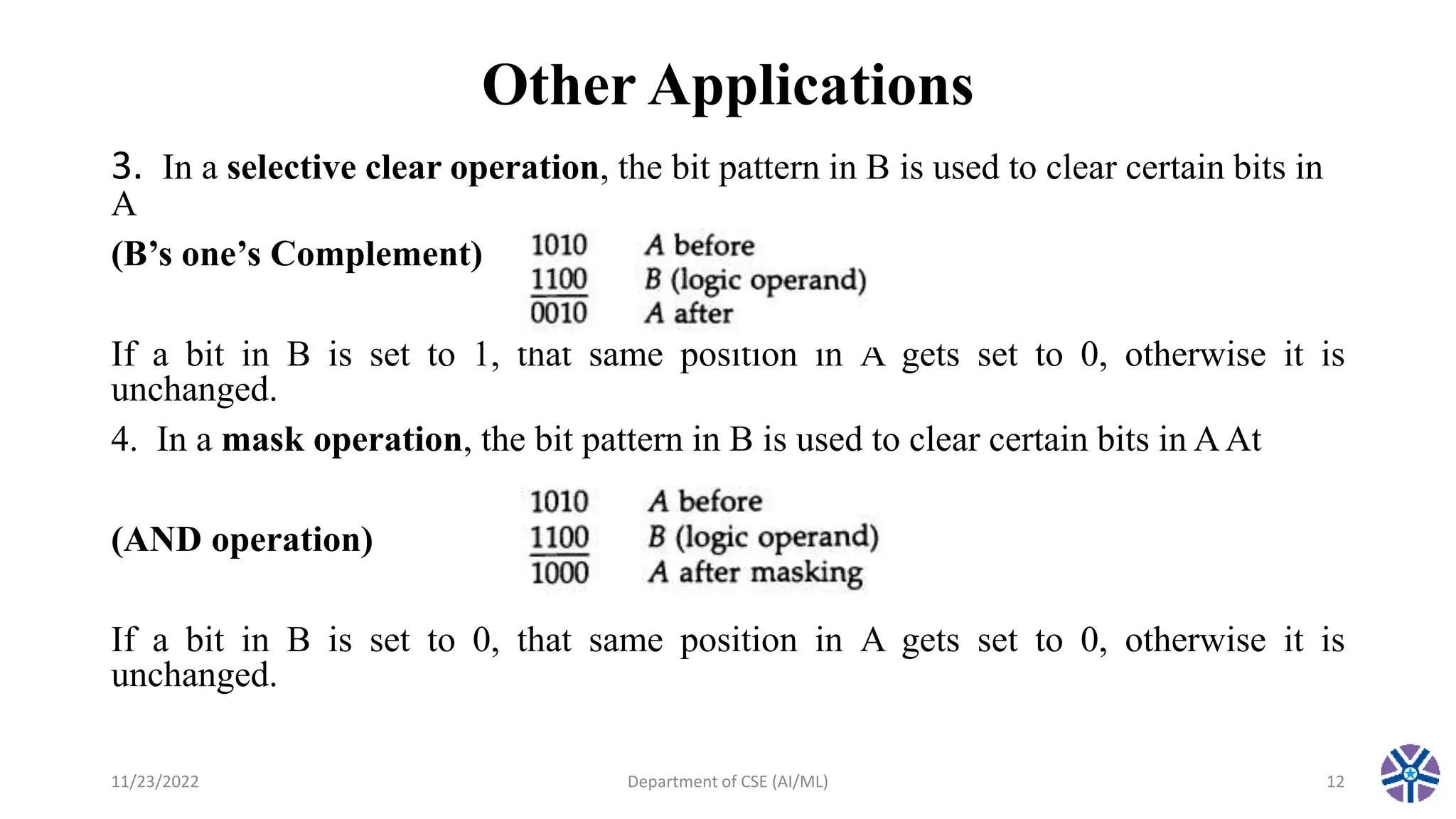
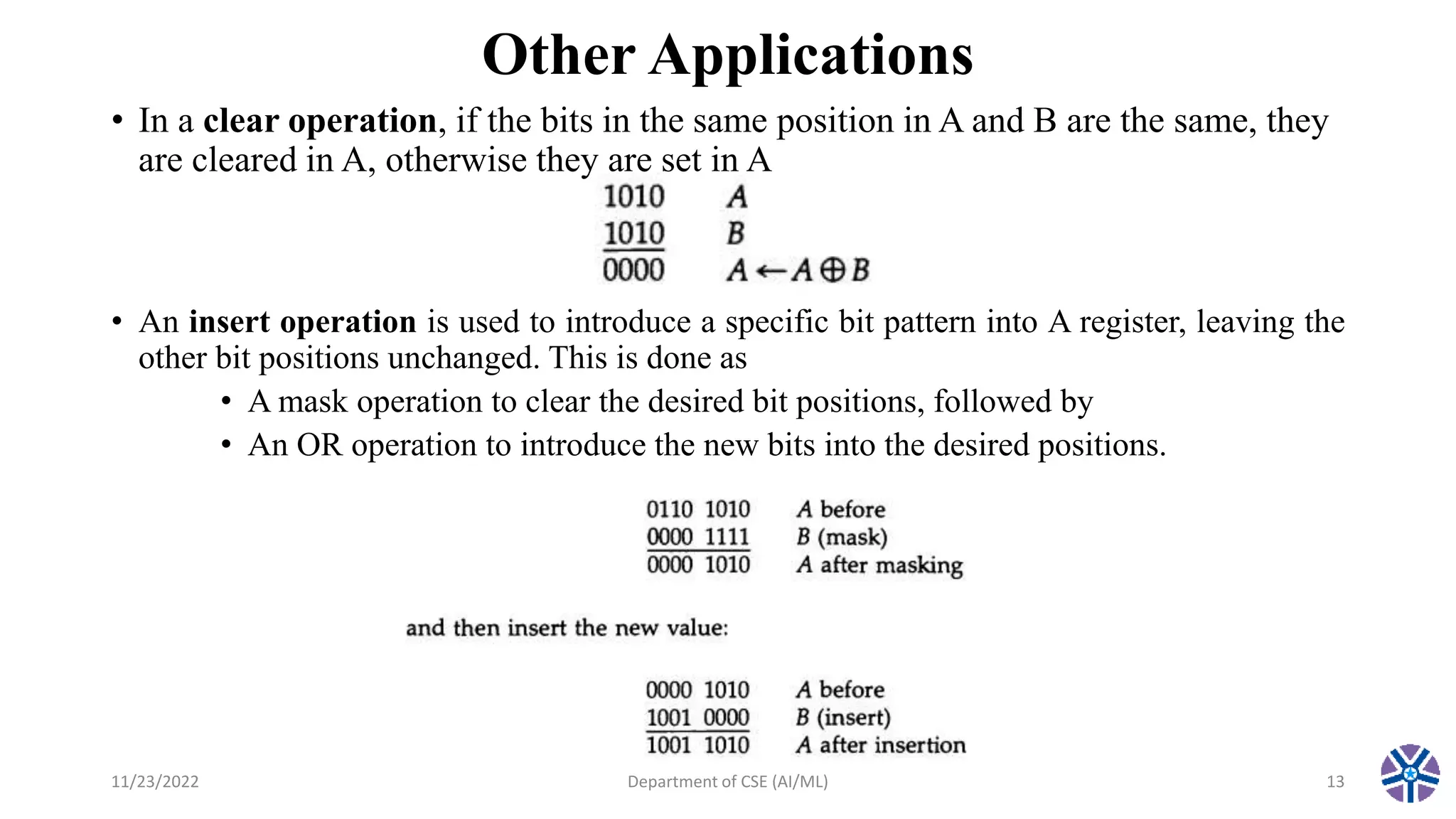
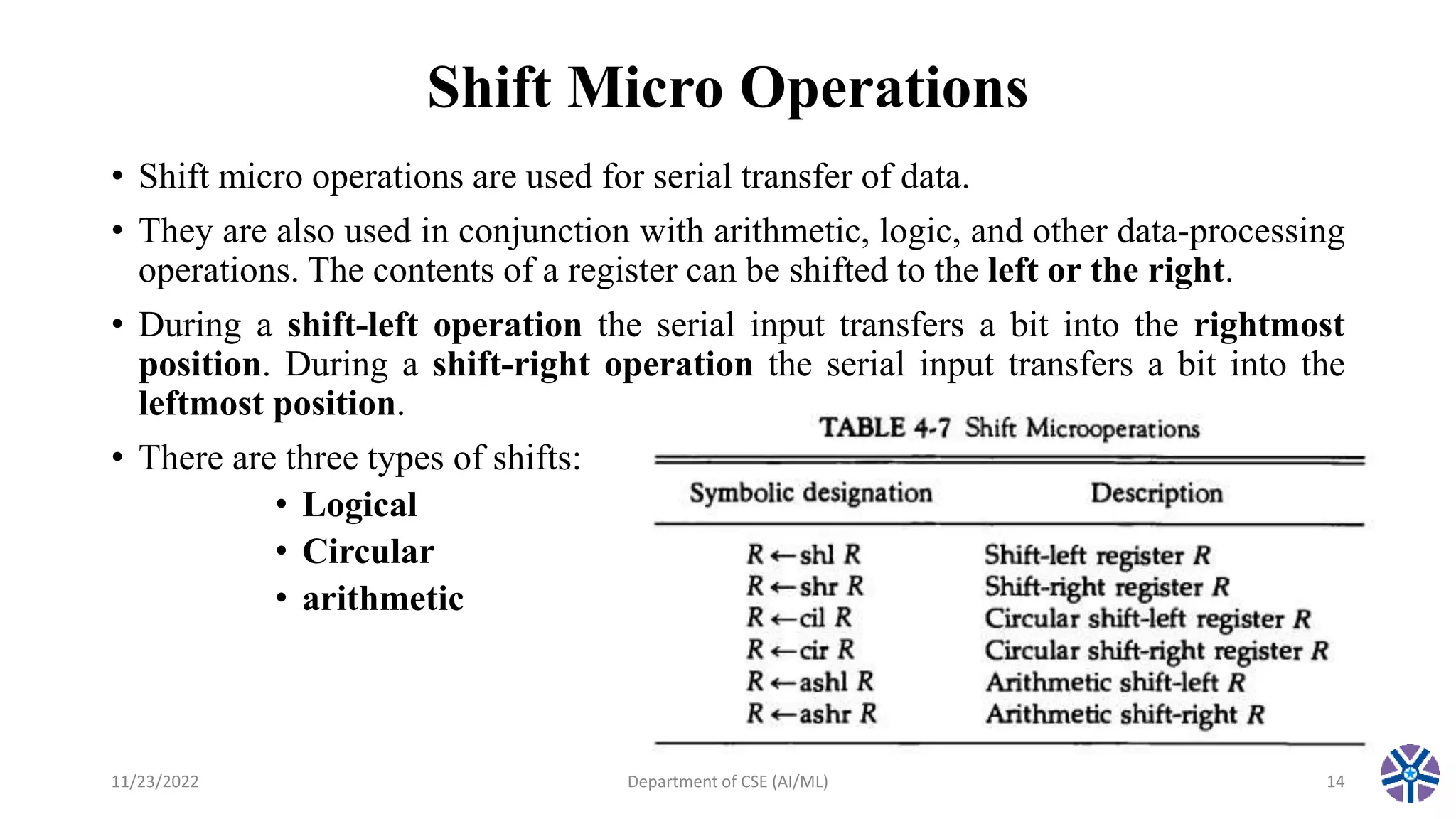
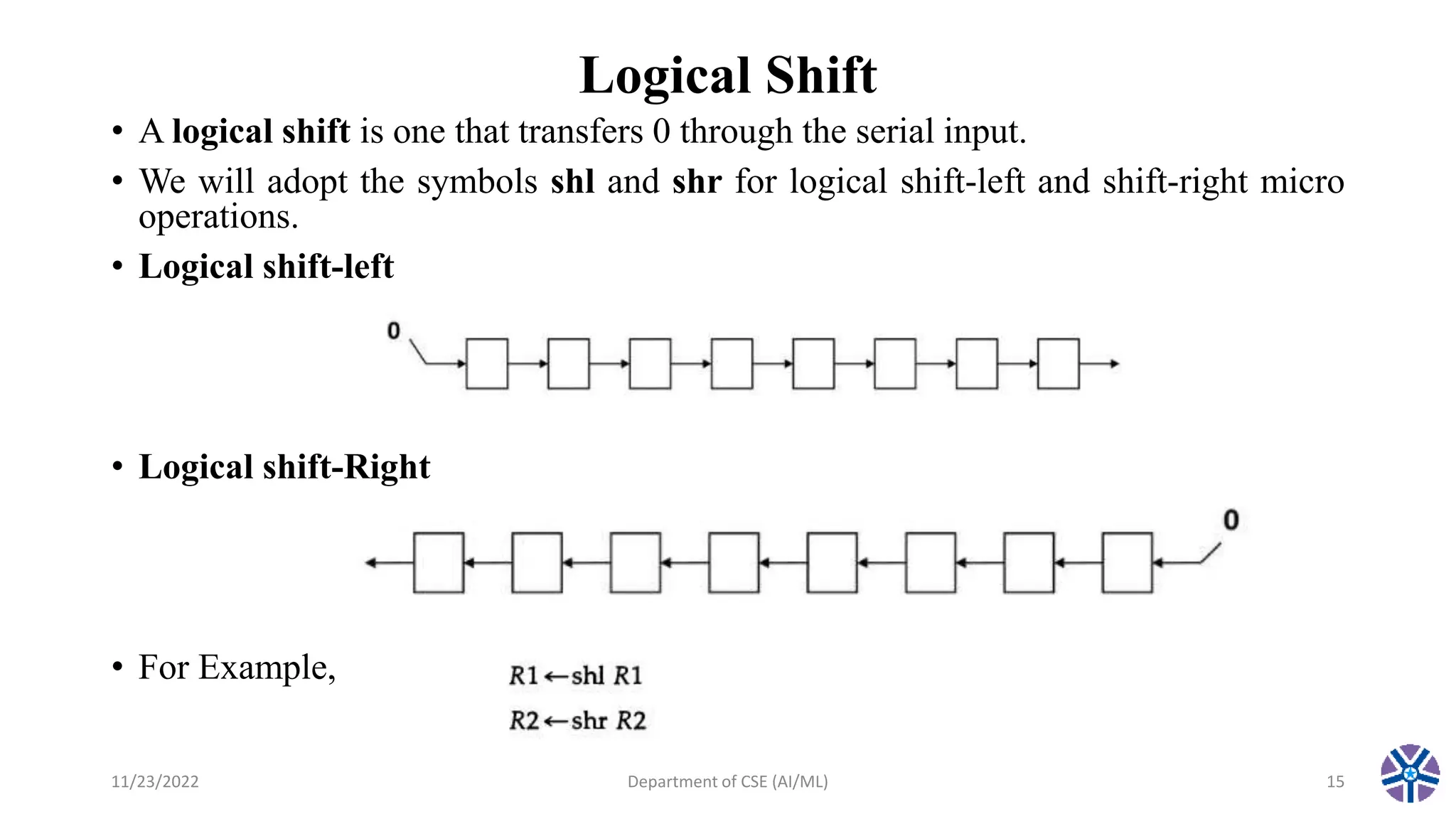
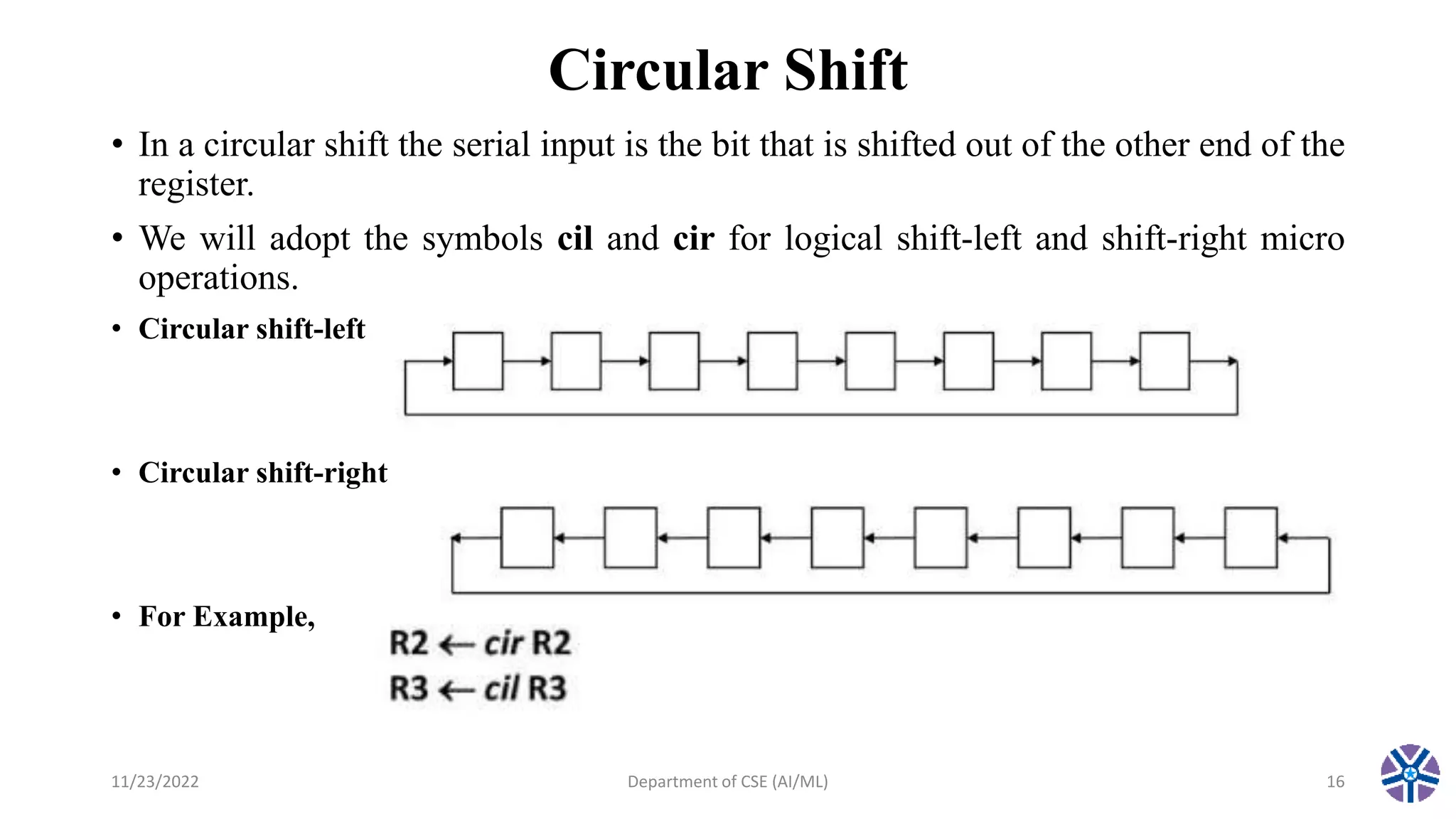
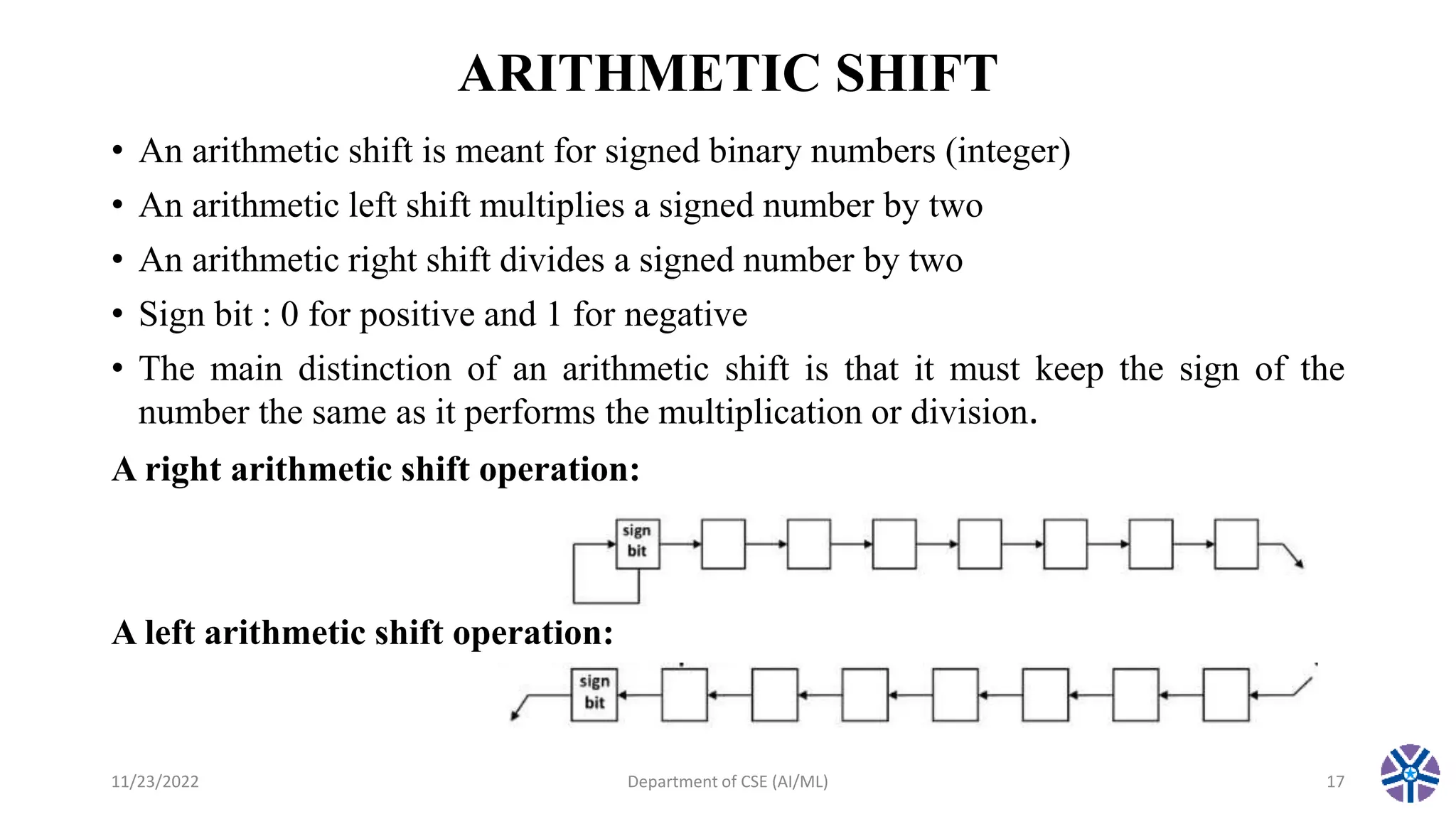
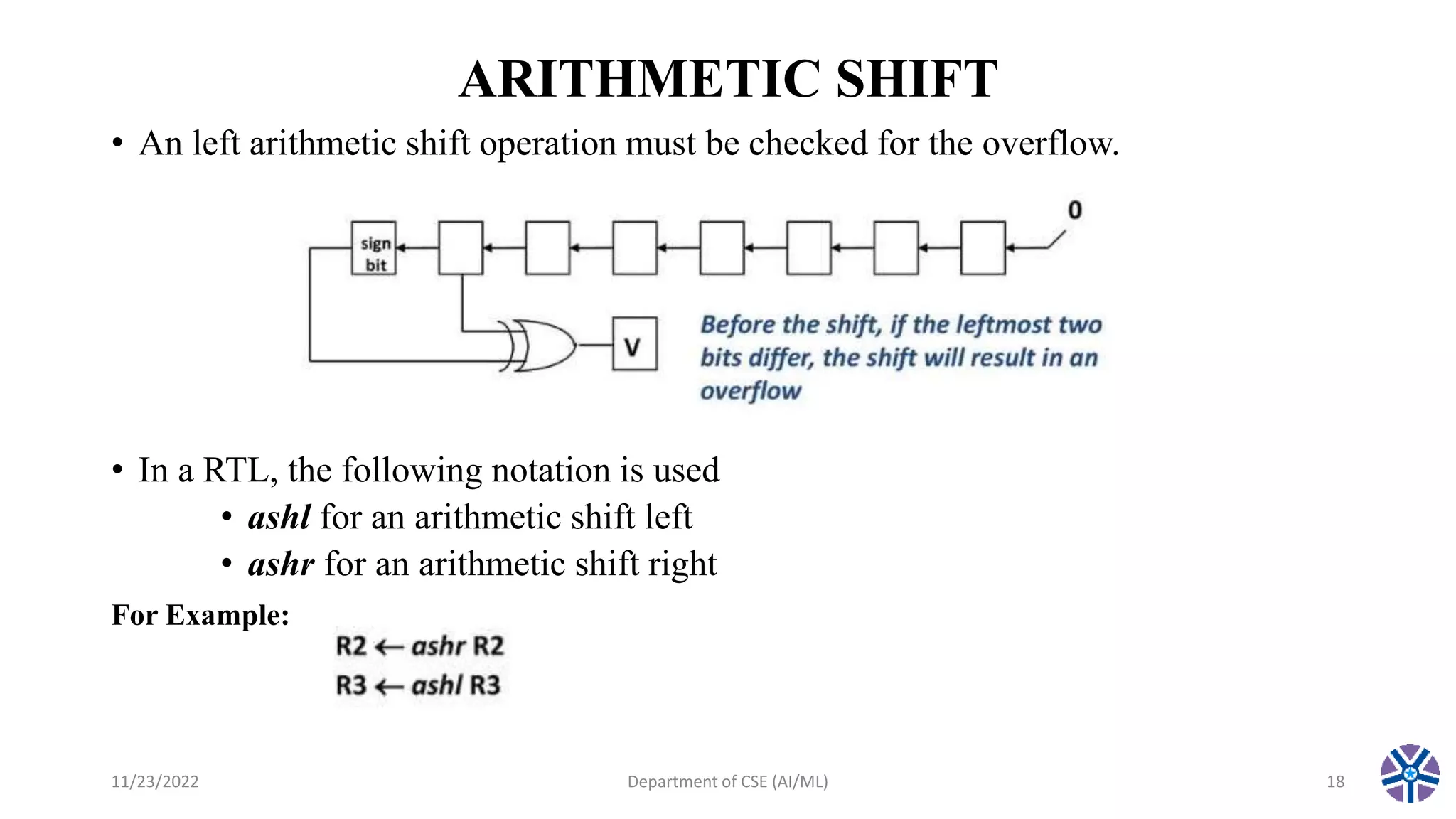
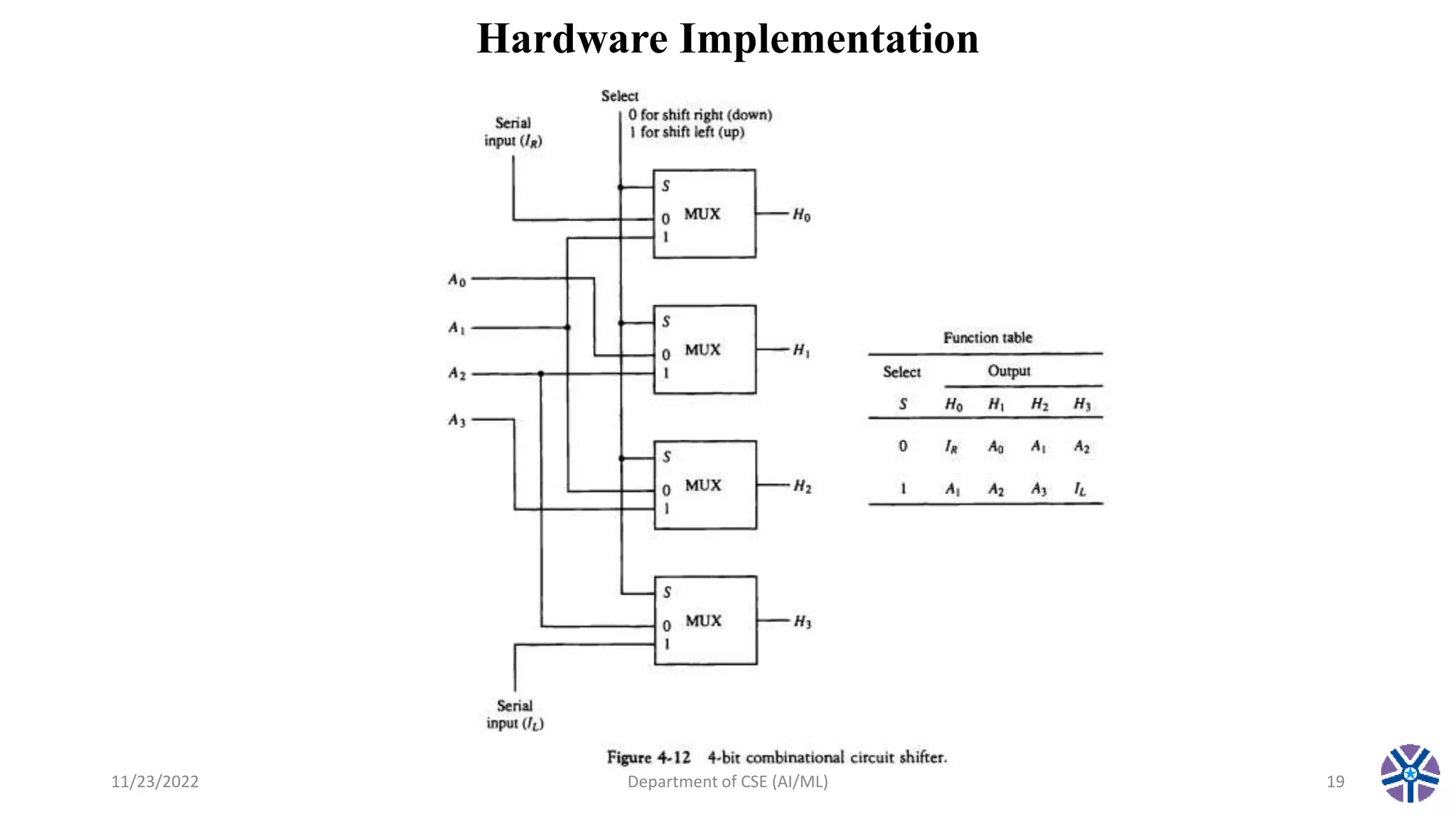
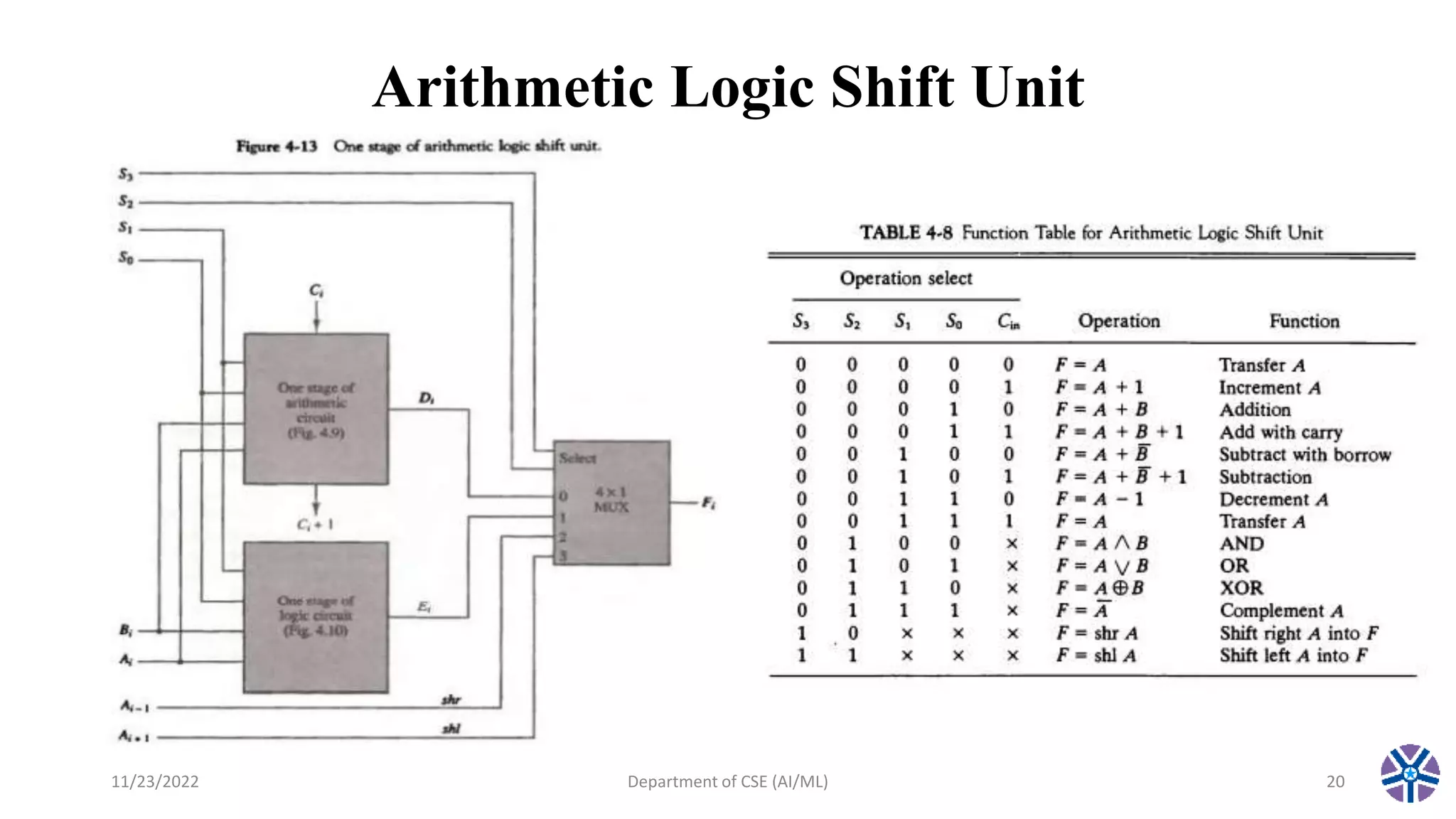
This document summarizes a session on register transfer language and microoperations in computer organization and architecture. It defines register transfer language and describes different types of microoperations including logic, arithmetic, shift, and arithmetic logic shift unit operations. Logic microoperations perform binary logic on register bits. Shift microoperations serially transfer data between registers. The document provides examples and applications of these microoperations.