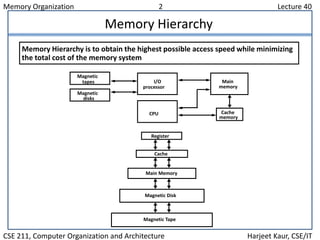
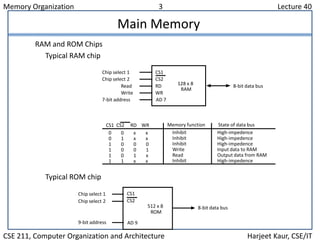
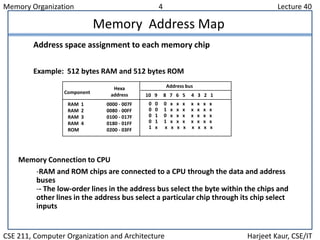
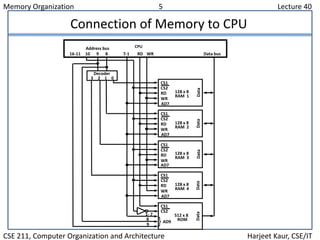
The document discusses computer memory organization. It describes the memory hierarchy from fastest to slowest as registers, cache memory, main memory, and auxiliary memory such as magnetic disks and tapes. The main memory section explains RAM and ROM chips, how they are connected to the CPU via address and data buses, and how the address lines select individual bytes or chips. It provides an example memory map assigning address ranges to different RAM and ROM chips and shows how a decoder chip selects the appropriate chip.