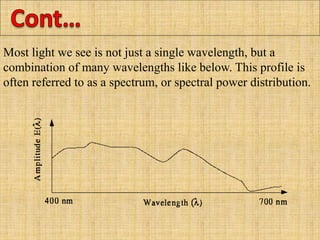
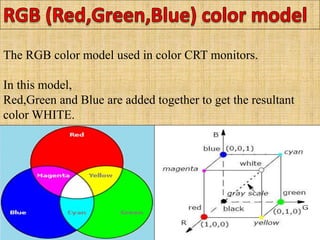
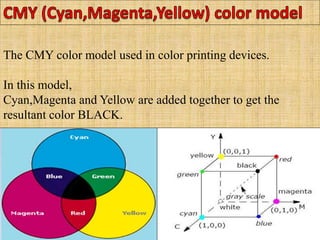
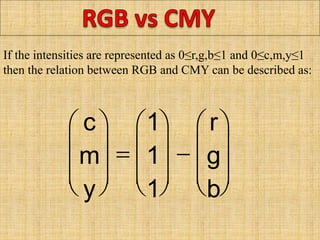
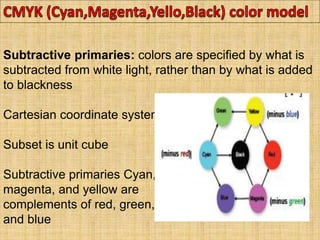
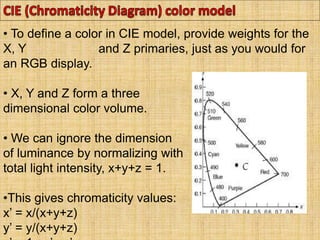
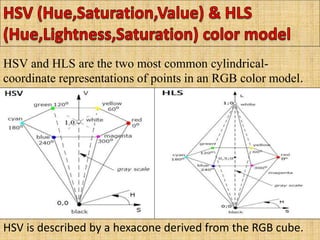
A color model is a specification for representing colors as combinations of primary colors. There are several common color models including RGB, CMY, YIQ, CIE, HSV, and HLS. The RGB model uses red, green, and blue primaries and is used in computer and television displays. The CMY model uses cyan, magenta, and yellow primaries and is used in color printing. The CIE model is based on human color perception and covers the full range of perceivable colors.