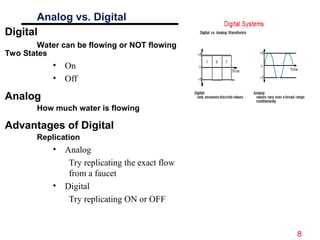
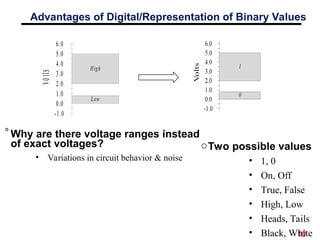
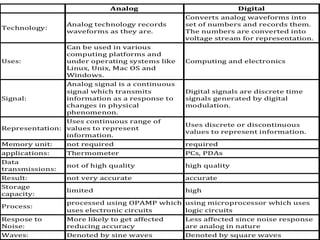
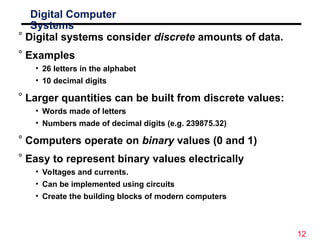
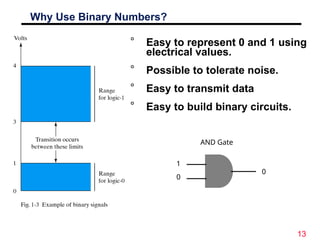
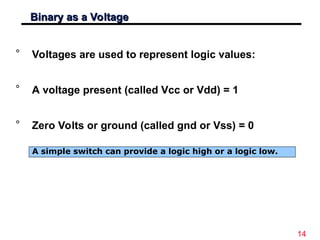
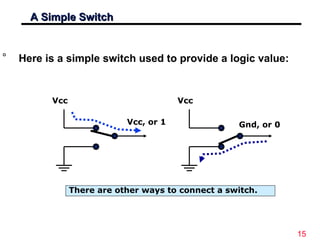
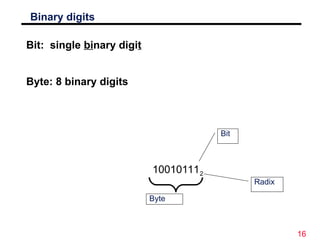
The document discusses digital logic design, emphasizing the interconnection of components in digital systems and their reliance on binary representation. It outlines various number systems, advantages of digital over analog, and the importance of error correction and programmability in digital systems. The text also introduces key concepts such as voltage representation of binary values and their application in modern computing.