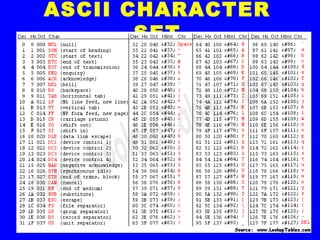
Digital systems represent quantities using symbols called digits that can take various forms such as binary, octal, and hexadecimal. The binary number system uses two symbols, 0 and 1, and is important for digital circuits. Decimal numbers can be converted to binary by repeatedly dividing the number by two and writing the remainders as binary digits. Real numbers are represented internally using a mantissa and exponent in binary form. Character encoding schemes like ASCII and ISCII assign numeric codes to letters and symbols to allow text to be represented digitally, with Unicode now providing a standard coding that supports many languages.
![WEL COME
PRAVEEN M JIGAJINNI
PGT (Computer Science)
MCA, MSc[IT], MTech[IT],MPhil (Comp.Sci), PGDCA, ADCA,
Dc. Sc. & Engg.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3datarepresentation-150410072855-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Representation-1-320.jpg)