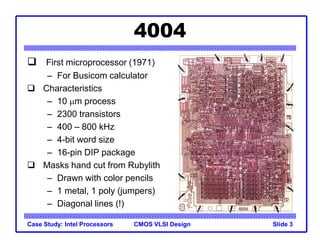
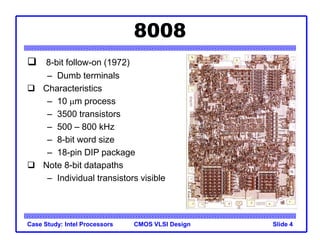
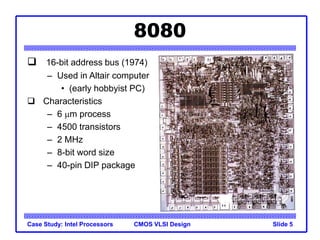
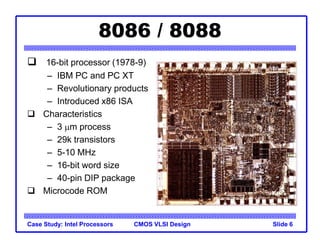
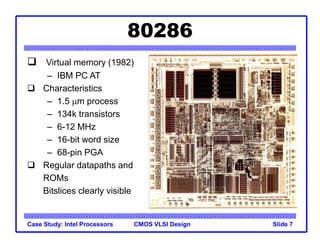
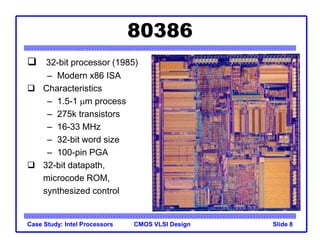
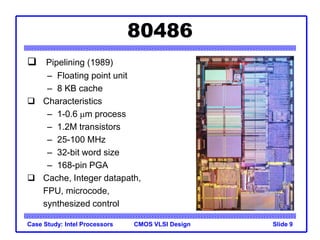
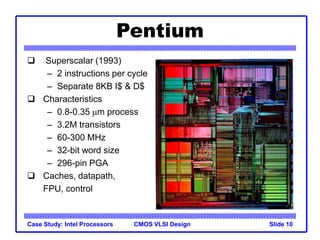
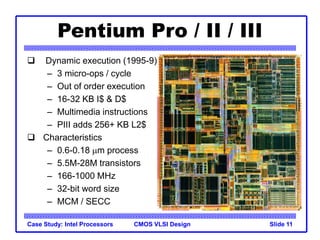
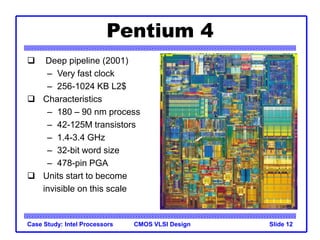
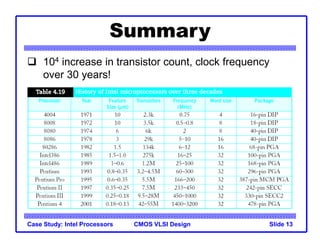
The document outlines the evolution of Intel microprocessors from the 4004 in 1971 to the Pentium 4 in 2001, highlighting key characteristics and technological advancements of each processor generation. It details the increasing number of transistors, improvements in processing speed, and changes in architecture over the 30-year period. Ultimately, it demonstrates a 104-fold increase in transistor count and significant increases in clock frequency.