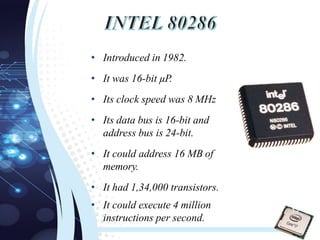
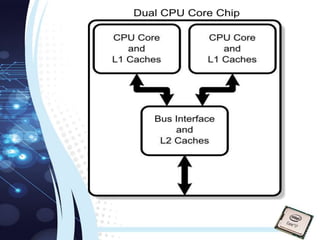
This document traces the evolution of microprocessors from 4-bit to 64-bit models over several decades. It discusses early microprocessors developed by Intel and other companies, including the 4004 (4-bit, 1971), the 8008 and 8080 (8-bit, 1972 and 1974), the 8086 and 8088 (16-bit, 1978 and 1979), the 80386 (32-bit, 1985), and the introduction of 64-bit processors in the 2000s. Each new generation brought increased processing power, through higher bit sizes, clock speeds, transistor counts and features like caches and multicore designs.