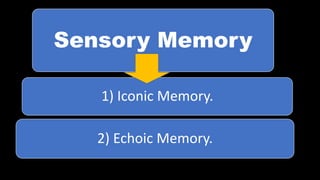
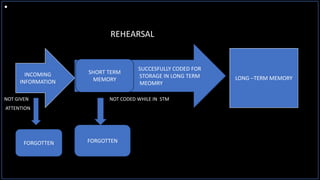
The document discusses the various aspects of memory, including its definition, types, and processes of encoding, storage, and retrieval. It categorizes memory into sensory, short term, and long term, detailing their characteristics and functions. Factors affecting memory such as age, intelligence, and stress are also mentioned.