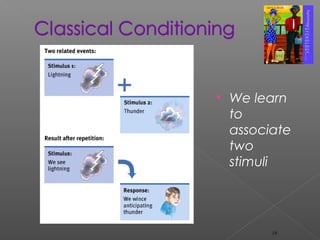
1. Learning involves acquiring new knowledge, behaviors, or skills through experience. It can occur through classical conditioning, where organisms learn to associate stimuli, operant conditioning, where behavior is modified by its consequences, or cognitive learning which requires perception and understanding.
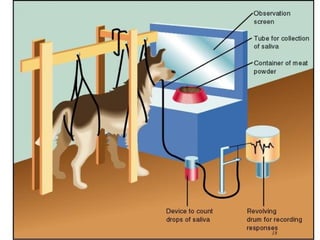
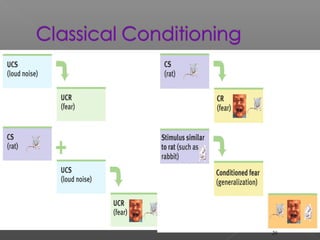
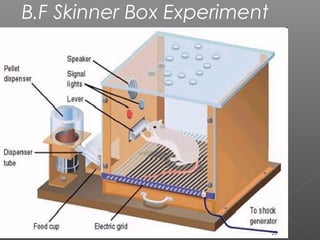
2. Major theories of learning include associative learning proposed by Aristotle and others, where events linked in time become associated; Pavlov's classical conditioning experiments; Thorndike's laws of effect and exercise; Skinner's operant conditioning research; and cognitive learning involving insight and problem solving.
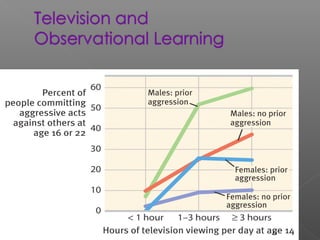
3. Learning is influenced by reinforcement which increases behavior and punishment which decreases it. Theories and experiments by thinkers like Pavlov, Skinner, Bandura, and Kohler