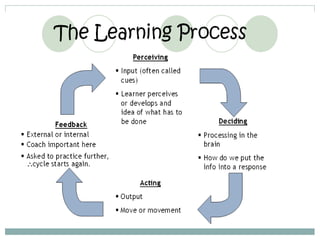
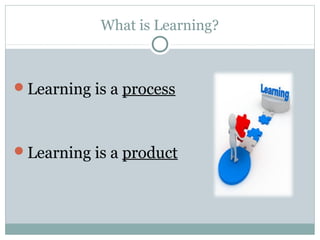
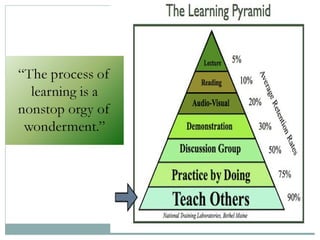
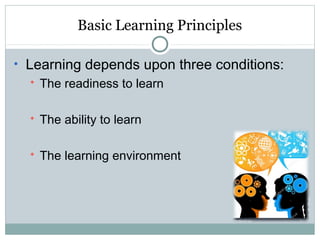
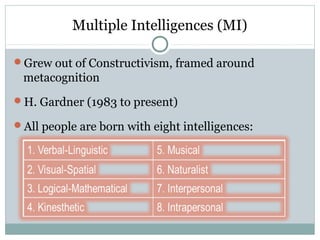
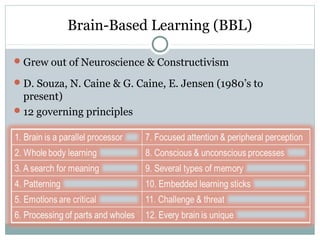
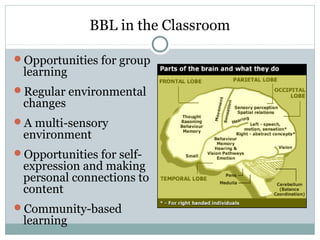
This document defines learning and discusses several theories of learning. It begins by defining learning as a change in behavior through experience or practice that results in the acquisition of knowledge or skills. Several learning theories are then outlined, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, and multiple intelligences theory. Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors while cognitivism examines mental processes. Social learning theory and social constructivism emphasize social and contextual factors. Multiple intelligences theory proposes eight types of intelligence. Principles, classroom applications, and references are provided for each theory.