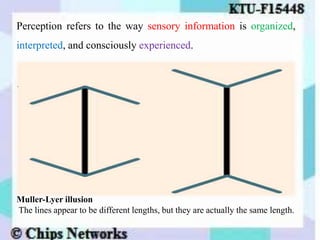
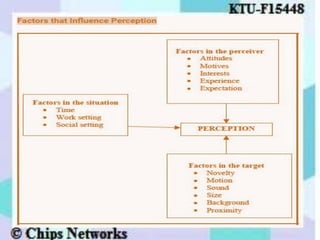
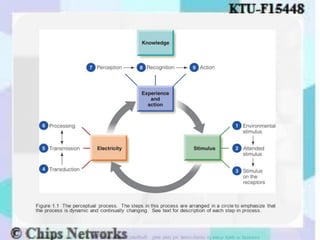
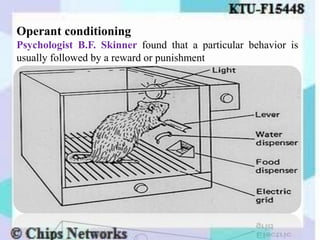
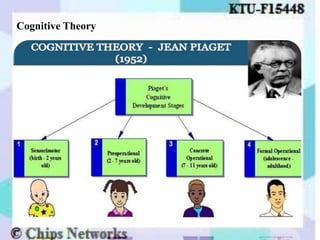
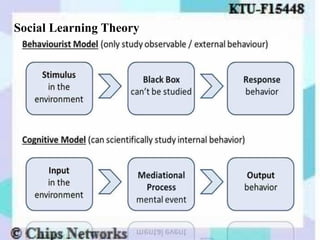
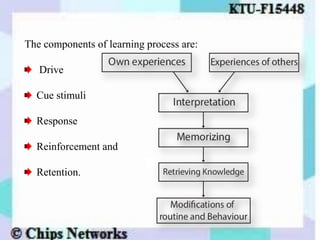
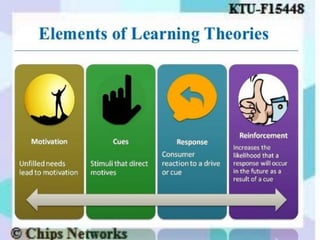
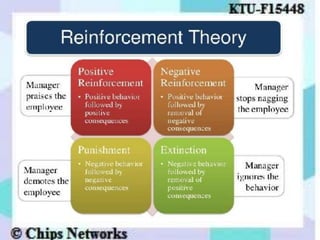
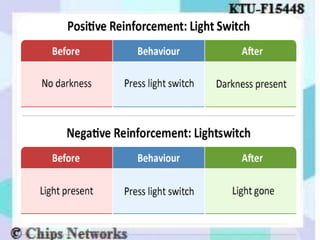
The document discusses perception as the organization and interpretation of sensory information, highlighting bottom-up and top-down processing influences. It explores the impact of perception on employment interviews, performance evaluations, and employee loyalty, emphasizing that perceptions shape hiring decisions and appraisals. Additionally, the document details learning theories, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, cognitive theory, and social learning theory, while explaining the components and reinforcement strategies that facilitate learning.