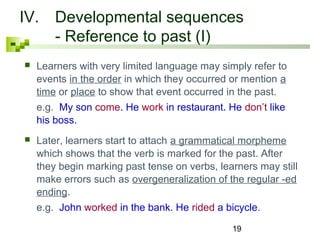
Learner language, also known as interlanguage, refers to a language system that develops between a learner's native language and the target language being learned. This developing system has characteristics of both the native language and target language, as well as general patterns that emerge across learners. Studying learner language and the errors they make provides insight into how learners acquire a new language over time and the developmental sequences they progress through, such as first acquiring simple grammatical structures before more complex ones. While the first language influences the interlanguage, many developmental patterns are similar across learners of different native languages.
















![IV. Developmental sequences
18
- Relative clauses
The pattern of acquisition for relative clauses (the
“accessibility hierarchy” for relative clause in English):
• Subject (‘The girl who was sick went home’)
• Direct object (‘The story that/which I read was long’)
• Indirect object (‘The man who[m] I gave the present to was
absent’)
• Object of preposition (‘I found the book that John was talking
about’)
• Possessive (‘I know the woman whose father is visiting’)
• Object of comparison (‘The person that Susan is taller than is
Mary’)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4learnerlanguage-141211103303-conversion-gate02/85/Learner-Language-18-320.jpg)