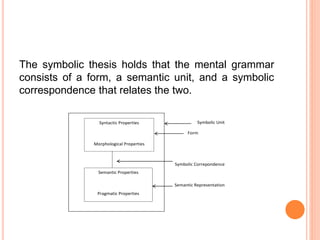
Cognitive linguistics emerged from developments in linguistics in the 1960s-1970s. It views language as grounded in human cognition and experience rather than as an autonomous system. Some key principles of cognitive linguistics include: meaning arises from conceptualization rather than being truth-conditional; semantics is encyclopedic rather than compositional; and linguistic knowledge comes from language usage. Cognitive linguistics investigates various topics like categorization, grammar theories, discourse analysis, and language acquisition using these principles.