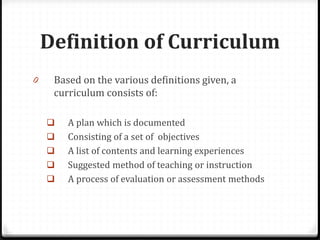
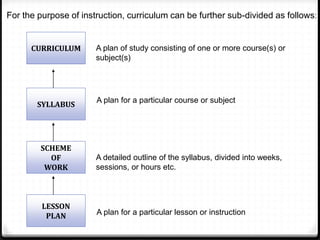
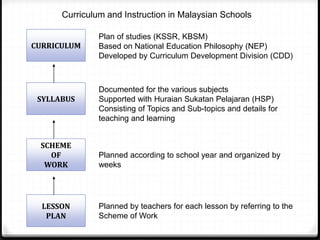
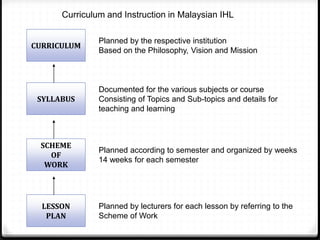
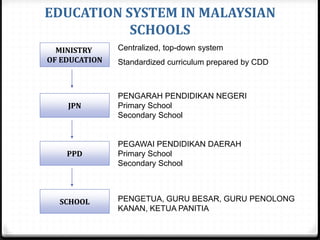
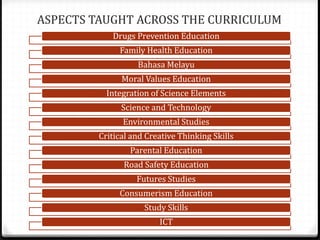
This document provides information about the EDU555 Curriculum and Instruction course for week 1. The course will cover curriculum and instruction principles, procedures, and practices. It will also focus on instructional approaches, methods, techniques and materials. The course outcomes include being able to design curriculum, syllabus, lesson plans and evaluate instructional materials. The course content will cover topics like curriculum models, evaluation, school curriculum, syllabus design, instructional objectives, and microteaching. Assessment includes tests, presentations, course design projects, lesson plans and class participation. Policies on grading, dress code and attendance are also outlined.