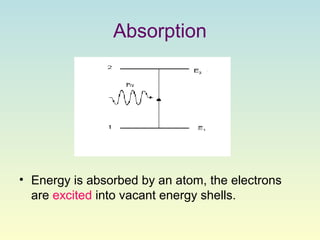
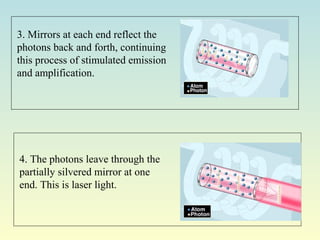
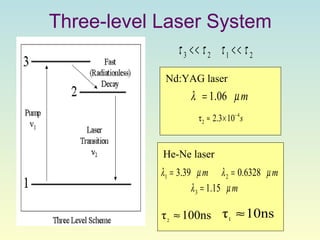
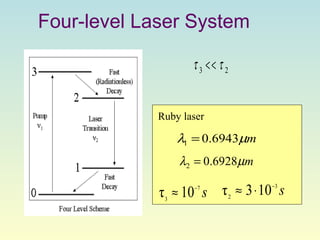
Lasers produce a coherent beam of light through stimulated emission of radiation. They work by pumping a gain medium like ruby or gas to create a population inversion, where more atoms are in an excited state than a lower state. This inversion allows for stimulated emission, where photons emitted are all in phase, parallel, and the same wavelength, producing a directional, concentrated beam. Lasers have many applications including optical storage devices, surgery, manufacturing, and more due to their unique monochromatic and coherent properties.