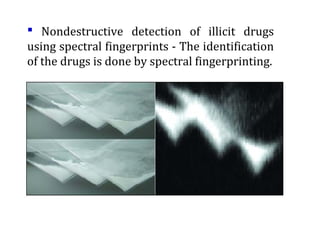
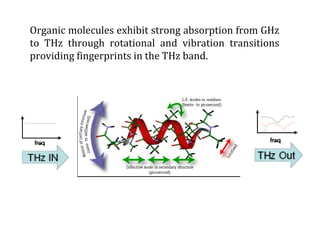
This document discusses terahertz frequency, which lies between infrared and microwave frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. It provides a brief history of terahertz science and outlines some key properties, including its ability to penetrate many materials and resolve fine spatial details. The document then describes several applications of terahertz technology, such as security scanning, medical imaging, manufacturing quality control, and astronomy. However, it notes that terahertz equipment remains large and difficult to implement in real-world settings.