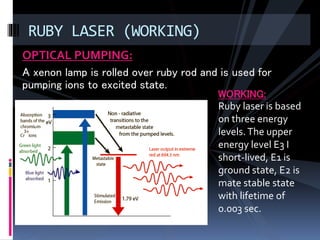
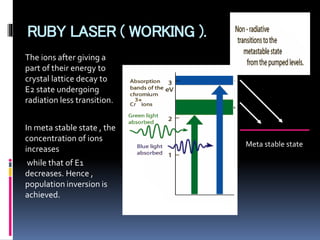
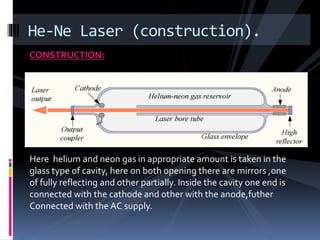
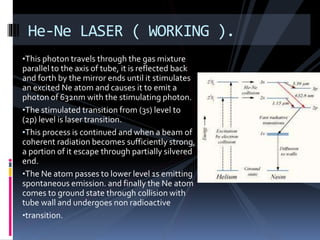
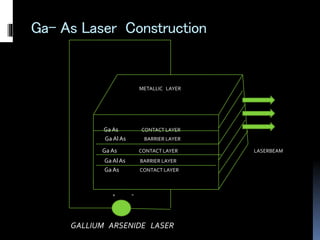
This document provides an overview of different types of lasers and their applications. It discusses solid state lasers like ruby lasers, gaseous lasers like He-Ne lasers, and semiconductor lasers like Ga-As lasers. For each laser, it describes the active medium, construction, pumping mechanism, working principle, and some applications. Ruby lasers were historically used for applications like holography and tattoo removal. He-Ne lasers emit red light at 632nm and are used in applications like bar code scanners and holography. Semiconductor lasers like Ga-As lasers are compact, efficient sources used in devices like DVD players, fiber optic networks, and laser printers.