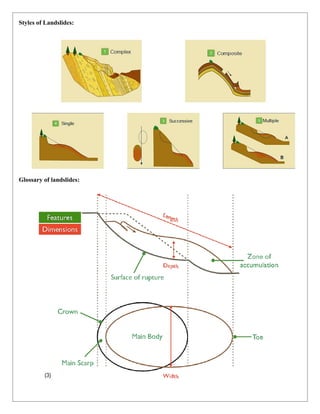
The document discusses landslides as the movement of earth, rock, and debris down slopes, detailing their causes, types, effects, and mitigation strategies. It outlines various geological, morphological, physical, and anthropogenic causes and classifies landslides based on movement rate, materials involved, and nature of movement. The document also emphasizes the importance of preventive measures, community awareness, and emergency preparedness to minimize the impact of landslides.