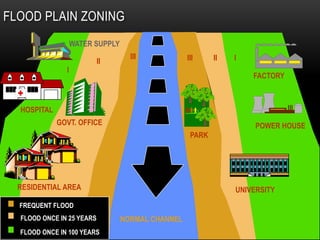
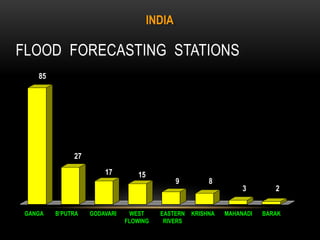
The document presents a comprehensive analysis of floods, focusing on their causes, hazardous impacts, and disaster management strategies in India. It discusses the increase in flood disasters due to urban expansion, ineffective regulations, and climate factors, while outlining management approaches and structural and non-structural measures to mitigate flood risks. The document also emphasizes the importance of coordinated disaster management at various government levels and the need for capacity building and research to improve future flood response.