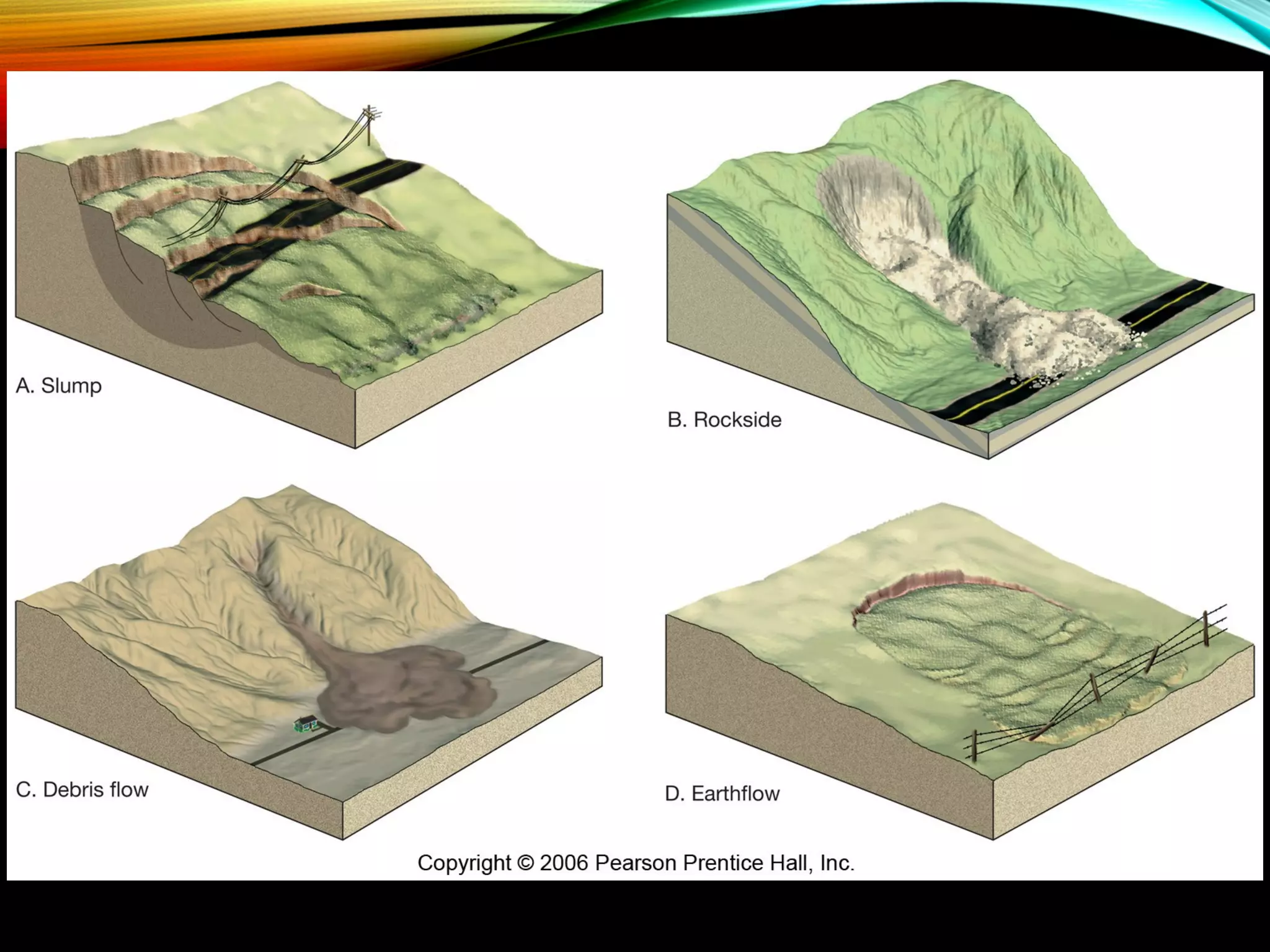
This document discusses geological hazards caused by landslides. It defines landslides as the downward sliding of land mass along steep slopes due to gravity. Heavy rains, earthquakes, floods, terrain cutting and droughts are among the main causes. Different types of landslides are described such as rock falls, lahars, earthflows, slope failures, slumps and debris slides. Areas with steep slopes, volcanoes, coasts and river valleys are prone to landslides. Landslides can damage infrastructure and block traffic. Classification, prevention measures and examples of landslide disasters are also summarized.