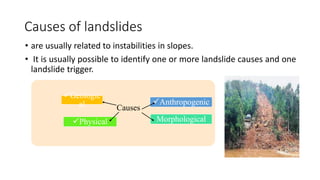
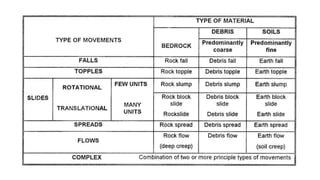
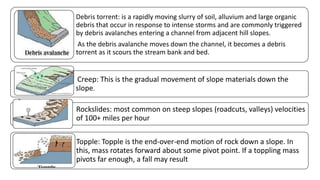
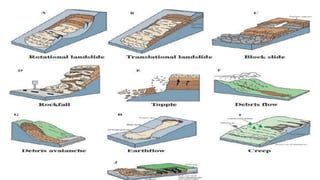
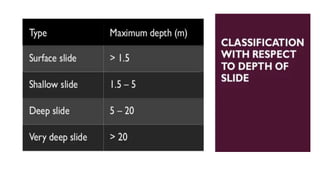
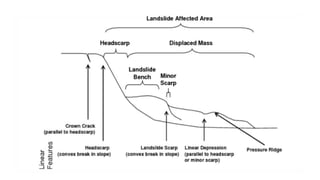
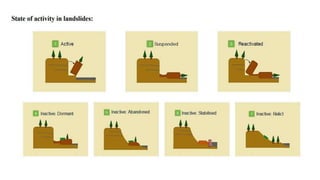
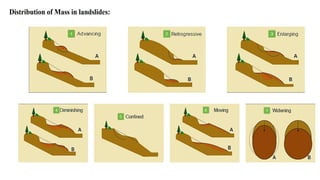
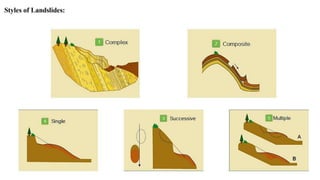
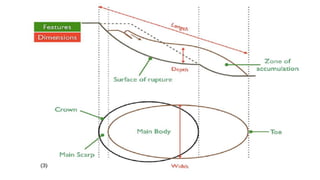
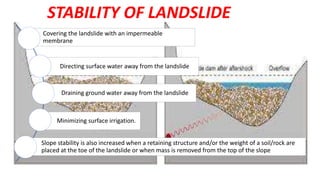
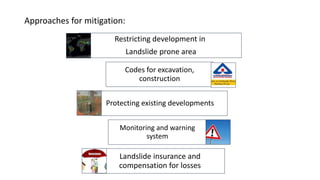
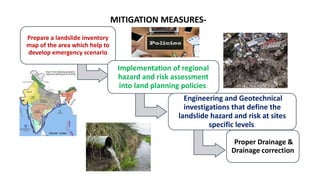
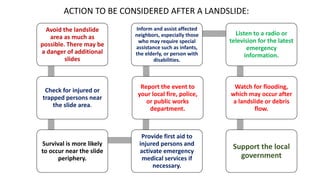
Landslides occur when masses of rock, earth, or debris move down a slope. They are caused by geological, physical, morphological, and anthropogenic factors that contribute to slope instability. Common types of landslides include debris flows, earth flows, debris avalanches, falls, and slumps. Landslides can be triggered by heavy rainfall, earthquakes, erosion, deforestation, and more. They often damage property and infrastructure and can threaten human life. Mitigation approaches include restricting development in high-risk areas, engineering structures to stabilize slopes, monitoring systems, and managing drainage.