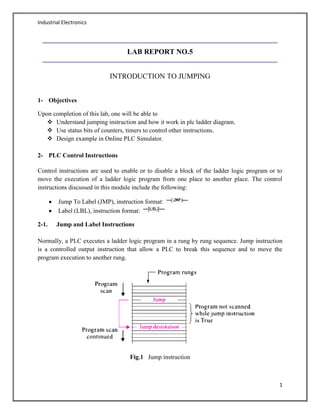
This document discusses jump instructions in PLC ladder logic. Jump instructions allow a PLC program to break its normal sequential execution and move to another part of the program. The key points covered are:
- Jump instructions work with label instructions to redirect program flow. The jump instruction moves execution to the rung with a matching label number.
- Jumps can move execution forward or backward within a program. Multiple jumps can target the same label. Jumps can also be nested within other jumps.
- Advantages of jumps include allowing a PLC to run multiple programs, jumping sections during faults to reduce downtime, and improving scan time performance.
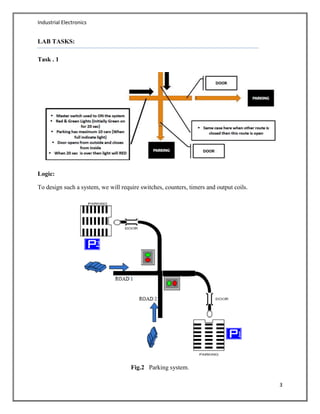
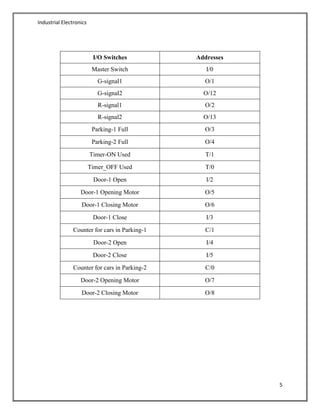
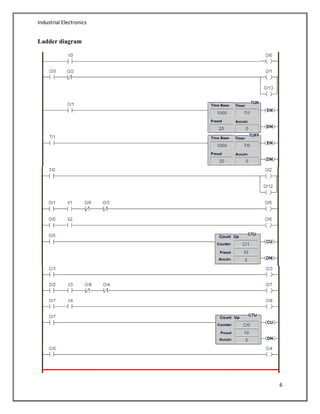
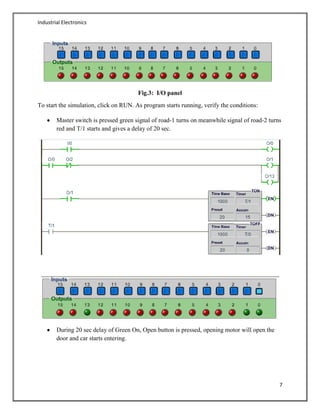
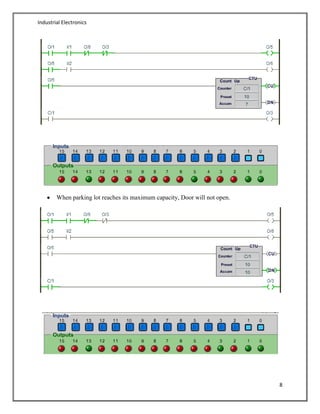
- An example is provided demonstrating a parking lot control system