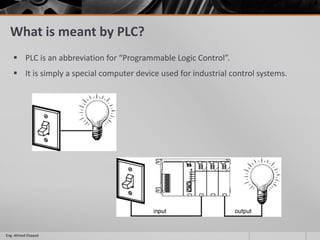
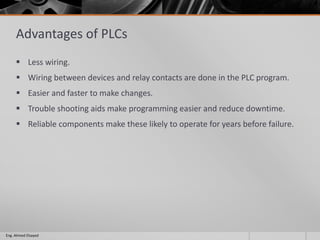
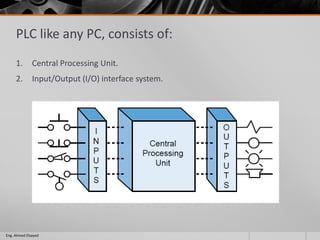
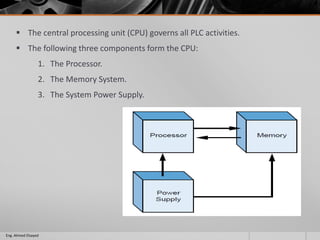
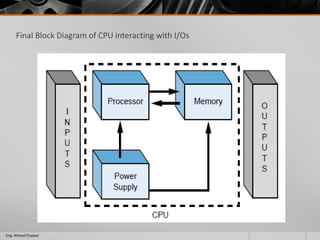
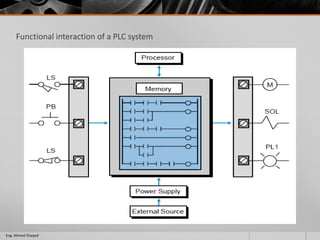
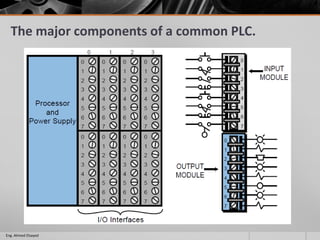
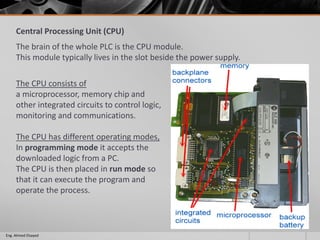
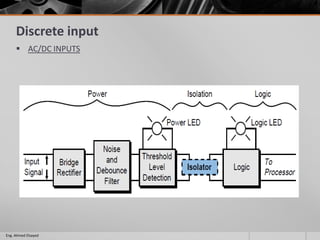
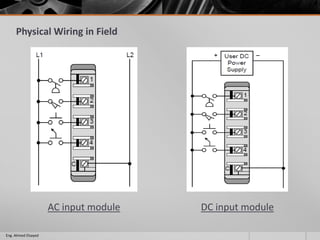
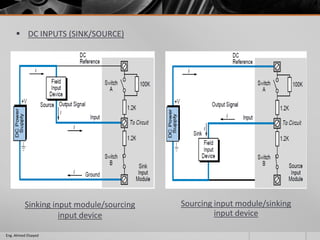
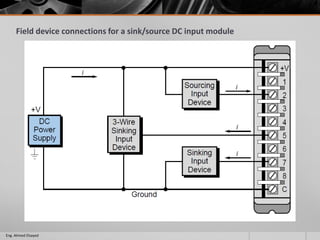
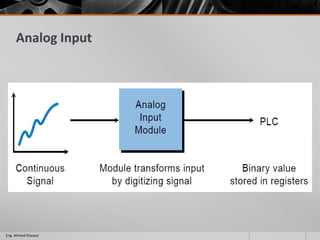
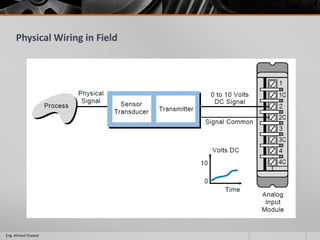
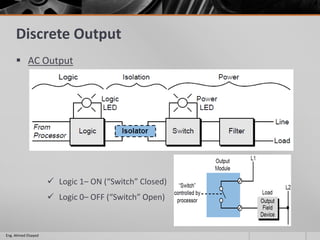
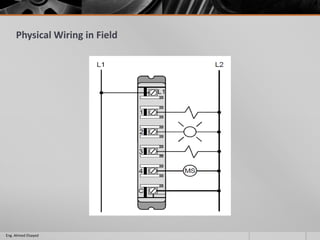
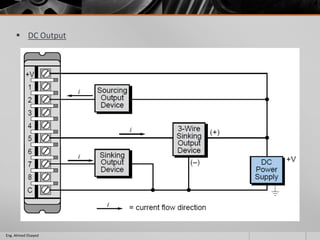
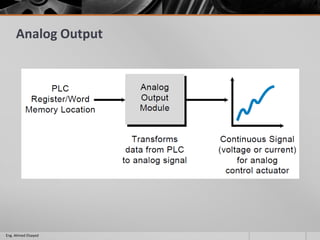
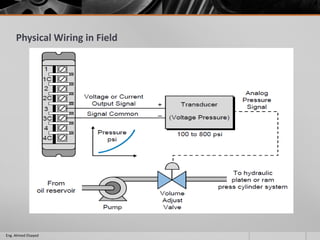
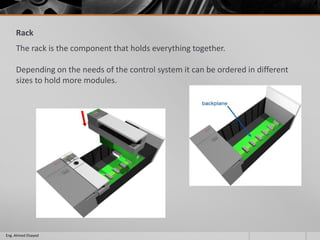
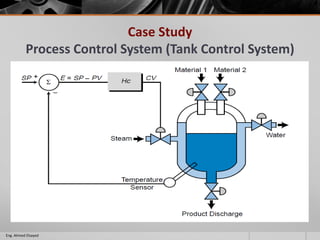
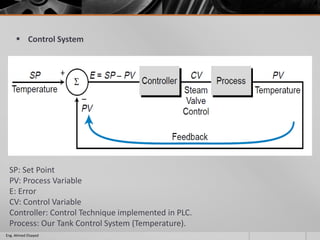
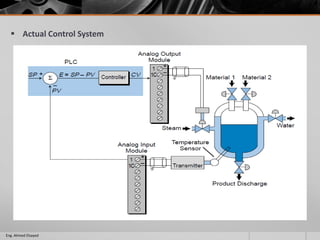
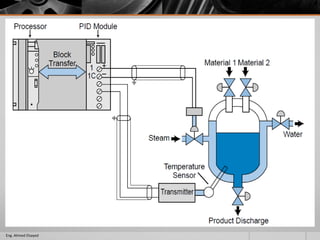
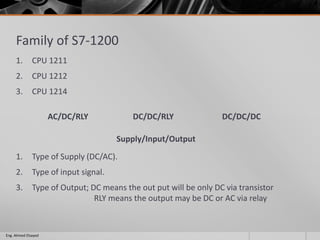
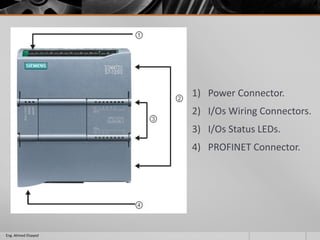
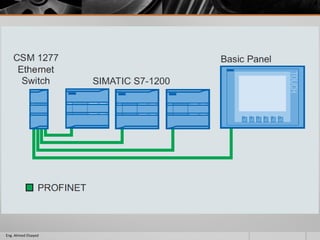
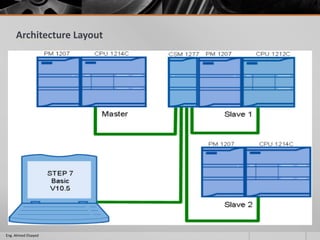
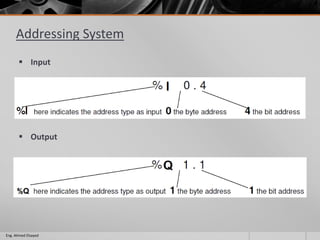
This document outlines a training course on programmable logic controllers (PLCs) using the Siemens S7-1200 PLC and TIA Portal software. The course consists of 9 modules that cover topics such as PLC hardware components, programming basics, function blocks, timers and counters, math operations, diagnostics, closed-loop control, networking, and human-machine interfaces. The introduction module describes the major PLC components, relay ladder logic, and provides an overview of the S7-1200 PLC and TIA Portal software. The course objectives are to teach students how to program and configure the S7-1200 PLC to automate various industrial processes and systems.