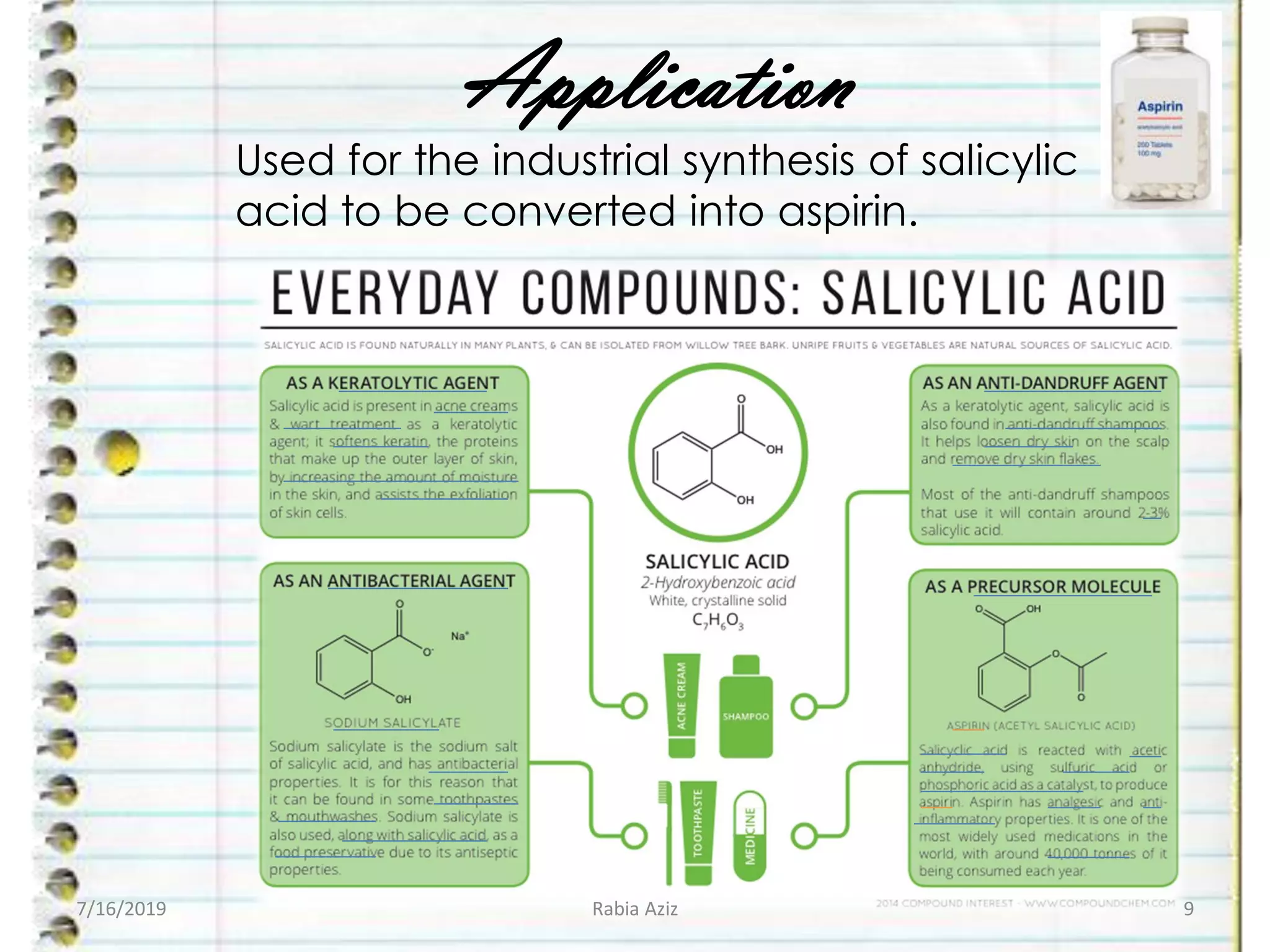
The document discusses the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction, which is a carboxylation chemical reaction that modifies phenol to produce salicylic acid, an important precursor for aspirin. It details the reaction mechanism, including the role of a base (NaOH) to increase the nucleophilicity of phenol and facilitate the reaction, with various steps such as deprotonation and electrophilic attack. Additionally, it emphasizes the industrial significance of salicylic acid and its pharmacological properties.