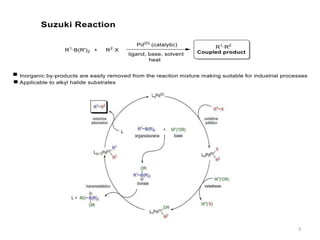
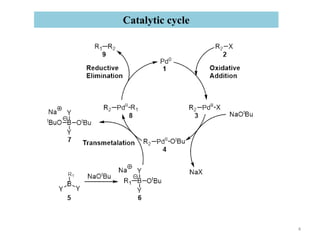
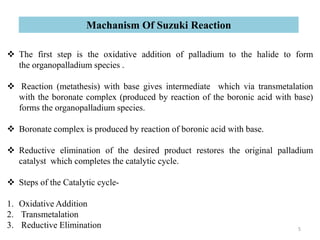
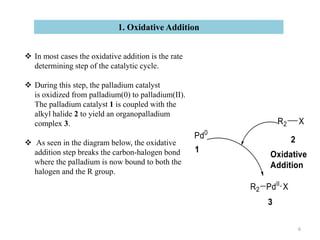
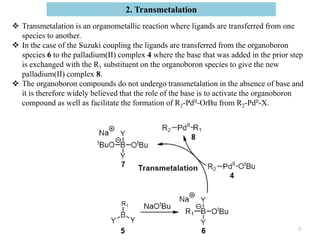
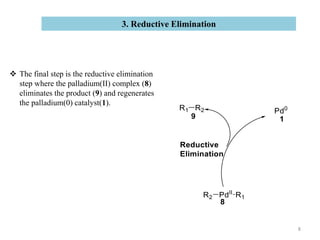
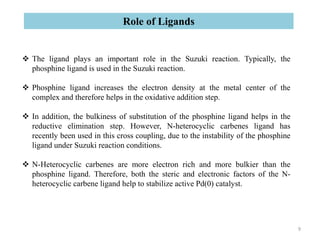
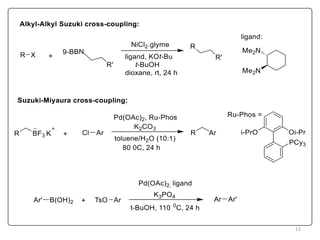
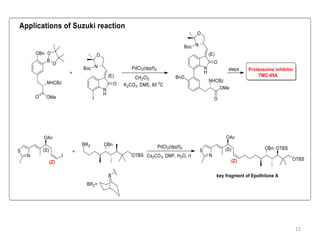
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction where an organoboron compound reacts with an organohalide compound to form a carbon-carbon bond. It is catalyzed by palladium and involves three main steps - oxidative addition, transmetalation, and reductive elimination. The Suzuki reaction is widely used in chemical synthesis due to its mild reaction conditions, tolerance of functional groups, and ability to form C-C bonds under aqueous conditions.